In late stages of complications of diabetes mellitus, foot stops pathologically: there are purulent-necrotic formations, trophic ulcers, lesions of bones and joints. The cause is specific changes that occur in the tissues of the joints and bones surrounding the soft tissues: muscles, tendons, peripheral nerves, vessels.
Symptoms
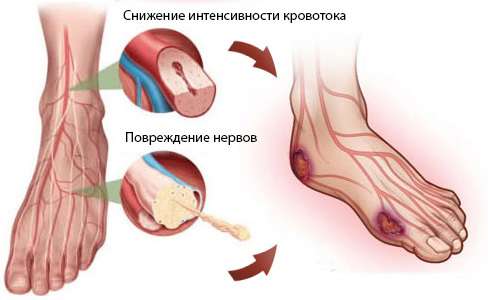
Symptoms of a diabetic foot are manifested when:
- affects the nervous tissue - there is polyneuropathy, which is noticeable in the destructive processes on the foot;
- is affected by blood vessels - diabetic angiopathy progresses, it leads to a neuroischemic form of the diabetic foot.
Symptoms of diabetic foot with diabetes in later stages are manifested by ulcers on the skin and gangrene in case of infection.
At first, the diabetic foot syndrome does not bring pain and suffering due to the absence of painful impulses, as the nerve endings on the foot are more likely to have died.
Further the patient will complain about the presence of:
- edema and redness on the feet;
- cold in the fingers, soles and in the entire ankle joint;
- "needles" or "goose bumps" in the muscles of the legs;
- rapid fatigue from a long walk;
- cramps in the calves of the legs;
- bone deformities, preventing the selection of suitable shoes.
How does the foot ulcer form?
Neuropathic defect occurs in the areas of the soft tissues of the foot: the soles, the spaces between the fingers due to the greatest pressure of the soles of the soles and the hard floor.
Gradually the foot deforms, the stratum corneum develops( hyperkeratosis starts) and the skin thickens. The layer of hyperkeratosis presses on the overlying tissues from below, the bones from above. There is an autoclosis and an inflammation, and a foot ulcer is formed at a diabetes at the expense of destruction of own cells by hydrolytic enzymes.
Absence of treatment at first can lead to the appearance of superficial ulcers, then - deep, trophic. Deficits fatty tissue under the skin, tendons, joint and bone structure. Osteomyelitis and gangrene are the cause of death or disability, since an amputation of the feet is necessary.
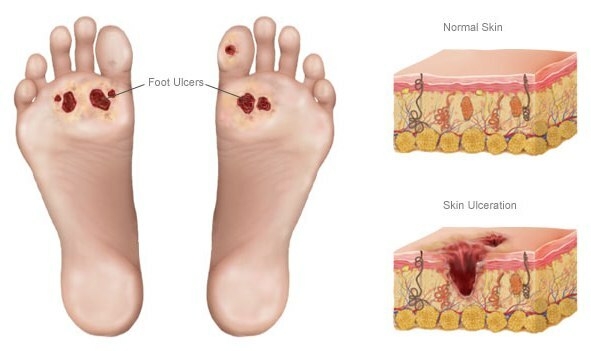
With a reduced pain sensitivity or a constant presence on the soles of calluses and abrasions, a patient with diabetes mellitus requires a thorough care of the feet. Care should be taken to monitor the skin condition over soft foot tissues, avoid:
- sunburn soles;
- walking in tight shoes;
- walking barefoot on sand, grass and ground;
- chemical burns when removing the cornified skin on the sole, and do not apply keratolytic ointment or cream with salicylic acid.
Pathogens( staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus, fungi, spirochetes and other anaerobic organisms) penetrate into small cracks and wounds. Defective skin in the form of trophic ulcers become for them an ideal microflora, which leads to gangrene at first superficial, then inside: adipose tissue under the skin, muscle fibers, ligaments and bones.
Now in the smallest vessels there is a thrombosis, the pathology spreads in healthy tissues. This infection of trophic ulcers and underlying tissues can be accompanied by gas evolution.
Atherosclerosis is the cause of foot ulcers
Diabetes often causes atherosclerosis, therefore arterial vessels( medium and small) undergo diffuse changes with disturbance of blood flow in the main segments and the channel of microvessels.
Syndrome of diabetic foot ischemic form in atherosclerosis is manifested by the presence:
- of intense pain, especially at night;
- relief of pain when lifting a pillow for the head, while sitting;
- cold ankle skin, having an unnatural pale or cyanotic-pinkish-red color;
- of acral necrosis, passing into trophic ulcers on the phalanges of the fingers or the edges of the heels;
- secondary infection, leading to diabetic gangrene.
Sharko Edema and Joint Education
Kidney pathologies or cardiovascular failure promote the accumulation of ankle formation in the ankle - the formation of neuropathic edema. Finally, the cause of neuropathic pastoznosti while doctors do not know.
Presumably, fluid accumulates in the foot due to:
- frequent nerve system disorders of the vegetative system;
- of a large number of arteries and veins shunts;
- changes in hydrodynamics( pressure) in small sosudiki.
Due to prolonged destructive osteoporosis, hyperostosis, osteolysis, a diabetic foot syndrome occurs against the background of osteoarthropathy. The bones are so deformed that the swollen foot becomes a "bag of pips" or "Sharco's joint".Such patients are required to order orthopedic shoes and urgent treatment of diabetic foot.
Diagnosis
Before treating a diabetic foot, the joint of Charcot needs to undergo a diagnosis. Laboratory methods:
- blood tests: general and after bacteriological inoculation;
- glycemic profile( determine the daily level of sugar in the blood);
- contents of ulcers;
- blood flow by Doppler ultrasound.
Next, they are examined on both ankle:
- neurological condition;
- angiography of vessels;
- radiography.
Treatment Methods
There are several treatments for diabetic foot.
Operations
Surgical treatment of the diabetic foot( Sharco's joint) is carried out to restore blood flow:
- by distal venous shunting in situ;
- thrombarterectomy;
- by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty.
If gas is released and gangrene develops in diabetes mellitus it is necessary:
- excision of dead tissue by surgery;
- intravenous administration of antibiotic drugs;
- to monitor blood glucose levels.
In the presence of severe atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels, the treatment of the diabetic foot with a reconstructive method is not always used. In order not to conduct a surgical operation the physician must:
- DO NOT miss the initial onset of trophic ulcers;
- DO NOT allow gangrene to progress.
For this, the doctor prescribes:
- treatment of wounds and trophic ulcers, using preparations against bacteria;
- general antibacterial therapy;
- measures to improve trophic foot;
- preparations to restore normal innervation and improve metabolism.
Medications
The first signs of dry skin on the soles of diabetes are the basis for the doctor to prescribe medications to eliminate the development of the syndrome of the diabetic foot( the joint of Charcot), because the skin misses the pathogenic microflora. For drug treatment appoint:
- insulin and drugs to reduce blood sugar;
- antibiotics with a wide spectrum of action, for example, from a number of cephalosporins( Clindamycin, Lincomycin);
- pain medication: Analgin, Ibuprofen, Diclofenac;
- medications to improve the transport of blood through blood vessels: Agapurin, Normoven, Pentoxifylline;
- local antibacterial and antiseptic medicines, lincosamides;
- complex medications( Amoxiclav, Ampiox)
- macrolides( Erythromycin).

Scheme and dosage appoint doctors: the endocrinologist and neurologist in accordance with the pathological process of Charcot's foot, the presence of trophic ulcers, as well as the indicators of bacteriosia, the rate of regeneration of the surface of ulcers and wounds. Prophylaxis of diabetic foot is carried out.
In the appointment of a comprehensive treatment of the syndrome of the diabetic foot( Sharco joint) and for the prevention:
- excludes bad habits of the patient( drinking and smoking);
- is controlled by carbohydrate metabolism;
- are prescribed inhibitors of angioprotectants and aldose reductase;
- detoxification methods are used: enterosorption, plasmapheresis, hemosorption;
- is prescribed drugs against seizures and physiotherapy procedures;
- provides maximum rest for the patient by using a wheelchair, one or both crutches, soft and wide shoes;
- removes horny masses, dead tissues and processed edges of wounds.
Treatment with folk methods
Treat folk remedies for diabetic foot syndrome( Sharco joint, trophic ulcers) at home with concomitant medication.
- Decoctions. Cook on the bath 20 dry cherry fruit, pre-pouring them with boiling water( 1 tbsp.).We use it to wash ulcers.
- Applications. Humidified clove oil bandage is applied to the wound and ulcer surface. Inside on an empty stomach, drink 2 drops of oil.
- Compresses. Mix fresh-liquid honey( 100 g) with mummies( 5-10 g).We impregnate the band with a strip of bandage or gauze and fix it on ulcers or wounds with bandages. Replace the strip 2 times a day.
Use of softwood sapwood in your home:
- pour liquid gum to the center of the ulcer or wound and apply a bandage. Repeat 2-3 times a day, pre-treating the ulcer with alcohol. Dry gum is dissolved in alcohol, completely filling it in a jar;
- re-heat grease with butter( 1: 1) and use a cream to lubricate ulcers or wounds.
At home, as a prevention of the syndrome should:
- protect diabetic feet from injury;
- to exclude cuts and abrasions, bruises and bruises;
- Do not apply too hot baths or foot baths to prevent burns;
- eliminate calluses on the feet and fingers, prevent their appearance;
- apply a cream or ointment against fungal nail and skin damage;
- to fight with ingrown nails without traumatizing the skin;
- wear loose shoes;
- adhere to a low-carb diet;
- maintain normal blood sugar levels.