It's strange, but the three goals set for athletes, bodybuilders and diabetics, absolutely coincide:
- increased insulin sensitivity of muscle cells and a decrease in the fat cells of the body;
- regular control of insulin release;
- painstaking and practical daily exercise.
But the difference between these people is obvious. Athletes can be disturbed by the regime of training and nutrition, but for diabetics, people with metabolic syndrome or obesity, it is vitally important to determine the systems of exercise and eating behavior, since such a "healthy lifestyle" becomes for them a life-long medicine No. 1.
The first wave of information that swept the Internet was associated with the spread of the weight-reducing diet of Michel Montignac. The French nutritionist used his revolutionary research of the Canadian professor J. Jenkins, one of the first researchers of the behavior of food carbohydrates in the human body, to compose his system of healthy nutrition.
The second wave, however, not so powerful, rose in 2009.Scientists of the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Sydney carried out research on "postprandial insulinemia in response to a 240-kcal dietary load".In total, 38 products were involved in the experiment. It is this list, in one form or another, that "walks" through the expanses of the Internet under the name of the Table( list, list) of insulin indices.
Metabolism of carbohydrates
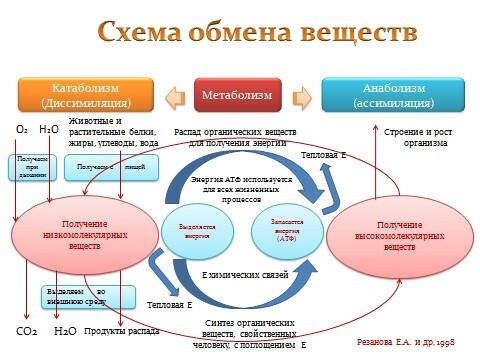
The body receives most of the energy for vital activity from the metabolism of carbohydrates. Very simplistic, the assimilation of dietary carbohydrates can be represented by the following scheme:
- during the assimilation of food simple carbohydrates quickly and independently break up into glucose and fructose, and immediately enter the blood;
- complex carbohydrates require fermentation for cleavage;
- process of food fermentation and increase of blood glucose level, in turn, triggers the mechanism of insulin hormone production by the pancreas - insulin wave( insulin response).
Next, insulin needs to connect to glucose and "follow" through the bloodstream into muscle or adipose tissue. In the absence of insulin, the cellular membranes of these tissues are absolutely impermeable to glucose.
The necessary amount of glucose is immediately used by the body to maintain life.
Part of the glucose after polymerization is converted into glycogen, deposited in the liver and muscles.
- hepatic glycogen maintains a normal level of glucose in the blood between meals;
- muscular is stored in stores for "help" in extreme situations, but is mainly used for prolonged or peak physical exertion;
- is a rest linked by insulin, glucose is deposited in fat cells.
Disturbance of the sensitivity of fat cells to insulin, caused by a violation of carbohydrate metabolism, leads to post-receptor impairment of glucose metabolism-visceral obesity, which eventually leads to type 2 diabetes mellitus.
If the pancreas does not respond adequately to the increase in blood sugar( produces an inadequate amount of the hormone), a very large amount of undigested glucose is constantly present in the bloodstream, and insulin-dependent diabetes develops.
An excess of insulin causes the use of liver glycogen stores, turning it back into glucose. The liver, devoid of glycogen, gives the command SOS, thereby causing a false sense of hunger. There is a vicious circle that leads to obesity, metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus 2.
It turned out to be important to know which products will satisfy the body's need for glucose. For example, 10 grams of carbohydrates is contained:
- in a dessert spoonful of honey( 13 g);
- in half the average apple( 100 g);
- in a portion( 100 g) of stewed beans;
- in 20 grams of white bread.
Easily assimilated carbohydrates of honey will quickly get from the gastrointestinal tract into the bloodstream, and the polysaccharides of apple, beans or bread will take some time to break up the .In addition, from the same number of initial carbohydrates will produce a different amount of glucose. It is for this comparison of products that the concept of the glycemic index is introduced.
Glycemic Index

The glycemic index( GI) characterizes the degree of assimilation of complex carbohydrates from foods and the subsequent level of blood saturation with glucose. The value of GI depends on the ability of complex carbohydrates to digest under the influence of digestive enzymes and from a number of "external" factors associated with cultivation, production technologies, storage conditions and cooking of food products.
The GI value was determined experimentally - after taking a certain product, for 2 hours, every 15 minutes, a blood test for sugar was performed. Naturally, for such a comparison of the behavior of dietary carbohydrates and the compilation of a table, the usual glucose was taken as the reference point-the assimilation of 100 g = 100% or 1 g of glucose equals 1 conventional unit of GI.
Glycemic load
Simultaneously with GI, the concept of Glycemic Load( GH) was introduced, because the metabolism of carbohydrate metabolism is affected not only by the structure of carbohydrates, but also by their direct quantity.
The GN can characterize the load on the pancreas that is tested when the necessary amount of insulin is produced in response to a specific food product. For example, the load of 50 grams of carbohydrate potatoes is 3 times higher than from the same 50 grams of carbohydrates vermicelli. Some thought this a low indicator of the load.
For the calculation of such loads, the formula is adopted - GN = GI product * amount of carbohydrates in 100 g / 100.
Grade of total daily glycemic load: & lt;80 - is considered low, from 80 to 120 - average, 120 & gt;high. People who need a low carbohydrate diet are recommended by the GN = 80-100.
Insulin index
The development of research technologies and modern instruments have made it possible to conduct a number of studies and accurately assess not only the amount of glucose that has entered the blood, but also the time for which insulin helps to get rid ofher.
To introduce the concept of an insulin index, the knowledge of the fact that not only carbohydrates give a command to the pancreas to produce insulin served as an impetus. Meat and fish - products that do not contain carbohydrates or are characterized by their low content, during digestion, also contribute to the injection of insulin into the blood.
An insulin index( AI) is a value that characterizes a food product in terms of an insulin response to it. This indicator is especially important for Type 1 diabetics and allows more accurate prediction of the magnitude of insulin injection.
The author of the methodology and the introduction of the term AI is the Australian professor of dietetics Janet Brand-Miller.
It was under her leadership that 38 food products were tested.
In subjects, after taking one of the products, for 2 hours every 15 minutes, blood was taken for analysis of GI and AI.To assess the AI products for 100% of the standard, an insulin release was obtained in response to the capture of glucose from carbohydrates of white bread from a serving of 240 kcal. All other doses of products also corresponded to 240 kilocalories. As a result of the analysis, it was found that the GI and AI values of the increase in glucose and the response release of insulin generally coincide - the coefficient of pair correlation is 0.75. Some non-carbohydrate products, such as beef, fish and eggs, predictably produced an outlier.
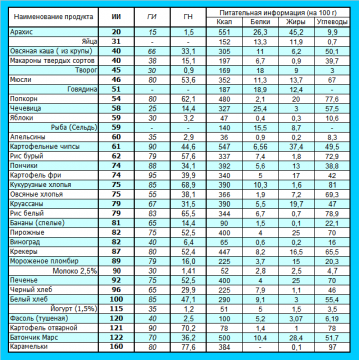
The expectation of detection of AI in meat, eggs and fish was justified, but impressed with its values - 30-59.
Unexpected discovery was the behavior of the dairy product line( except for cottage cheese).Especially struck by the figures shown by yogurt - GI 35 and AI 115!
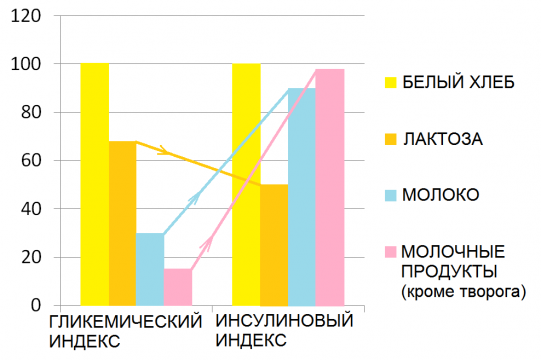
Scientists can not yet explain what caused the discrepancy between GI and AI of dairy products, and why they give higher insulin response rates than just for the intake of lactose dissolved in water. Moreover, and, what is especially paradoxical, there is no correlation between weight gain and the consumption of dairy products.
Practical application of GI and AI
General recommendation for all but insulin-dependent diabetics - comparing the two parameters, you need to focus more on GI, and then adjust your diet to AI and other parameters. But to neglect AI is not necessary - increased production of insulin depletes the insulin gland, gives the command to store fat, and not to use the reserves already available.
Proper nutrition
Diabetics should adhere to the following recommendations:
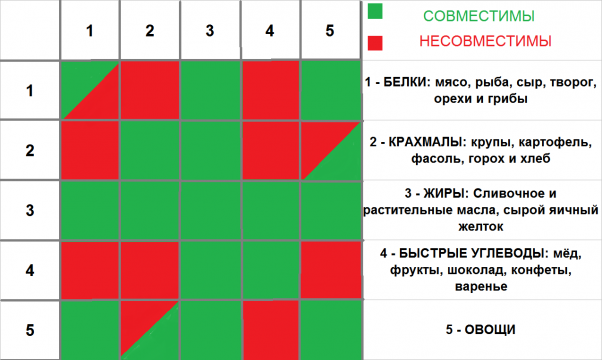
- Do not combine fast carbohydrates with unsaturated fats - cakes should not be eaten with meat, do not drink meat dishes with sweet drinks.
- Limit the outer combination of proteins with carbohydrates - for example, cottage cheese + honey.
- Choose products with a combination of "carbohydrates + unsaturated fats": salmon, avocado, nuts;sesame seeds and sunflower seeds, flax, mustard;soybeans and chocolate.
- Choose products with low and medium GI, and monitor the total daily GN.Apply all known culinary techniques to reduce GI.
- Breakfast should consist mainly of proteins - a classic American breakfast "cereal with milk( yogurt) and orange juice" makes the body "wake up" with a large secretion of insulin.
- For dinner, plan carbohydrate foods. Proteins and fats in the evening are guaranteed to lead to the release of insulin during sleep.
- For hormone-dependent diabetics - do not eat dairy products in the afternoon.
- Do not snack with dairy products.
- Do not buy products with "dietary", "low calorie" and "fat-free" labels. Such information, in fact, indicates that natural fats have been replaced by carbohydrates.
- Study product labels carefully for maltodextrin, malt, xylose, corn syrup and other sugar substitutes.
In conclusion, in addition to following a diet, daily exercise and taking medication, regular tests are recommended for patients suffering from diabetes or in pre-diabetic condition:
- self-monitoring of blood pressure level - daily;
- visit to the ophthalmologist - every 6 months;
- analysis for HbA1c-glycosylated hemoglobin - every 3 months;
- total blood and urine analysis - once a year;
- check of stops - 1 time in 6 months;
- control weighing - 1 time per month;
- self-monitoring of blood glucose level before and after meals - 2 times a week, and insulin-dependent diabetics - daily.



