 SMA or spinal muscular atrophy is a group of several types of hereditary pathologies that result in a partial or complete loss of motor neurons of the spinal cord in the anterior part.
SMA or spinal muscular atrophy is a group of several types of hereditary pathologies that result in a partial or complete loss of motor neurons of the spinal cord in the anterior part.
This problem occurs due to the mutation of the DNA of the SMN1 gene, which produces a protein, because of the mutation, the amount of protein in the patients is below the norm, and this is a guaranteed loss of motor neurons.
This disease is characterized by a disruption in the work of the striated muscles of the legs, head and neck. Patients badly manage to move arbitrarily:
- crawl;
- walk;
- hold your head;
- to swallow.
Hands at the same time work fine, there is sensitivity and good mental development.
Contents
- Historical facts
- About SMA available and cognitive
- Classification and symptoms by type differences
- Verdig-Hoffmann amyotrophy
- Disease of Dubovitsa
- Kugelberg-Wellander disease
- Adult disease
- Other types and types of AGA
- Differential analysis
- Objectives and methods of treatment
- Prevention
Historical facts
In 1891, the SMA in children was first described by scientist Werdnig. He clearly described the pathomorphological changes in muscles, various groups, peripheral nerves and spinal cord, while he noted the atrophy of the cells of the anterior horns and the roots of the spinal cord.
In 1892, Hoffman noted the nosological independence of the problem.
In 1893, Verdnig and Hoffman provided evidence of degeneration of the cells of the horn of the spinal cord.
In 1956, a more recent form of AGR was presented to the general discussion, with more positive predictions.
About SMA available and informative
Interesting facts about spinal muscular atrophy:
- despite the rarity of this problem, this is the most common violation of the genetic form;
- in childhood, the disease is transmitted through an autosomalessessive line;
- this gene is mapped on the 5th chromosome and identified in 1995;
- among children, the average fertility rate with this problem is 1 per 6000 - 10,000 people;
- children 1 form of muscular atrophy do not live up to 2 years in 50% of cases;
- SMA can manifest itself not only at birth, but also in middle or old age;
- on average, every 50 people has a recessive gene;
- a child who has two of these genes, both on the part of the mother and on the part of the father, is predisposed to defeat for 25%, for normal well-being, it is enough to have 1 normal gene.
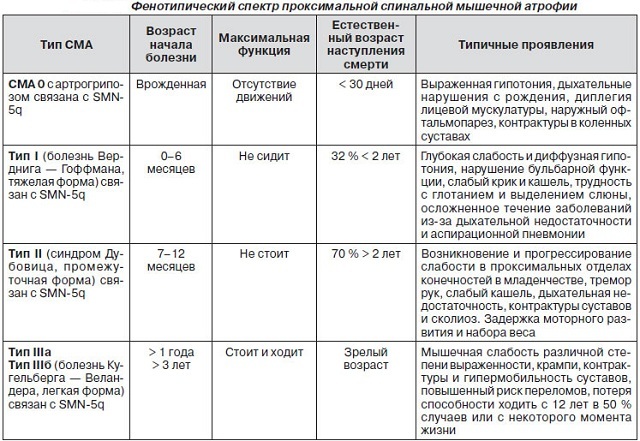
Classification and symptoms by type differences
There are several types of AGR.
Verdig-Hoffmann Amiotrophy
Type I - infant, Verdnig-Hoffmann's disease, up to six months. Very heavy appearance, these babies do not sit on their own, the head does not hold, difficulties with sucking, swallowing and breathing, the fasciculation of the tongue, bulbar disorders are manifested.
 The disease is noticeable from the first hours of birth, the lack of deep reflexes and pronounced muscular hypotension. Osteoarticular deformities are pronounced. Even in the small number of children who will be able to sit down and hold their heads, these skills soon regress.
The disease is noticeable from the first hours of birth, the lack of deep reflexes and pronounced muscular hypotension. Osteoarticular deformities are pronounced. Even in the small number of children who will be able to sit down and hold their heads, these skills soon regress.
Often such children have a malformation of the hip joint, clubfoot, the presence of "chicken" chest.
Forecast : the disease is rapidly progressing, malignant form. Death occurs before the age of 9, mostly due to problems with the cardiovascular system and respiratory failure.
Disease Oakley
II type - intermediate, Dubovits disease, up to 18 months. Such babies have already passed the first stages of development, but they will not be able to learn how to walk, the development of the disease depends on the degree of pathology of the respiratory muscles.
Usually, the symptoms of spinal muscular atrophy of this form appear in the subacute flow after the transferred stress for physical health, begins with the lower limbs and gradually shifts to the upper areas.
Fasciculation of the tongue appears, small finger tremor, bulbar paralysis.
Forecast : milder malignant course, lethal outcome occurs at the age of 14 - 15 years.
Disease of Kügelberg-Wellander
III type - juvenile, illness of Kügelberg-Welander, from 18 to 30 months. This type is less susceptible to death, the child

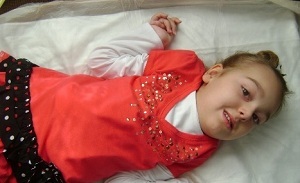
In the photo, the programmer Valery Spiridonov from Russia - the diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy
alone stands, however this process is very painful for him, in the future he will be disabled, without a stroller or walking stick it does not move.
The disease begins imperceptibly, the kid starts walking with the gait of the "clockwork doll", stumbles and falls, the movements become uncertain. Atrophy of the muscles is initially poorly visible due to the presence of developed subcutaneous fat.
However, there are all the same symptoms of tremor of fingers, fasciculation of the tongue, bulbar disorders. Even in the early stages of the disease, well-developed reflexes disappear.
Joints and bones are deformed, especially in the chest area.
Forecast : babies lose the ability to walk to 10 - 12 years, and live up to 20 - 30 years.
Disease in adulthood
IV type - adult, after 35 years. Due to atrophy of tendon reflexes, decrease in proximal muscles, a person is deprived of the ability to move independently.
Forecast : the course has no effect on life expectancy.
Other types and types of AGA
In addition to spinal muscular atrophy transmitted at the genetic level, there are still a certain number of related diseases:
- 1 type X-linked amyatrophy - beginning at 40 - 60 years;
- 2 - congenital, very aggressive form, leads to death up to 3 months;
- 3 - all limbs are affected, in almost all cases the boys suffer;
- distal spinal amyotrophy type 1 - since birth, sometimes in utero, upper limbs are affected;
- 2 and 4 types - this disease was described only in one family;
- 3 is a slowly developing disease;
- 5 typical - slowly developing at a young age;
- VA and VB-type - upper limb defeat;
- lesion of shins - appears in adolescence, develops slowly with weakness in the knees;
- lesion of the vocal cords - paralysis of ligaments in adults;
- autosomal dominant spinal amyotrophy - appears in adulthood, and its juvenile form in adolescence;
- is an innate character - a disease from the first moments of life;
- scapular-fibular species - a very rare disease of the lower extremities with the curvature of the foot;
- Juvenile segmental view of spinal cord injury - a very rare case, manifested in adolescence with progress 2 - 4 years, after the affected hands;
- Fenkel's disease - develops mainly around 37 years, but there are cases of appearance at the age of 12;
- Jockel's disease is a late and slow onset;
- spinal amyatrophy with myoclonic epilepsy - the extremities are affected, mostly due to myoclonic seizures;
- spinal form with congenital fractures of bones - severe form of muscle exhaustion;
- pontocerebellar hypoplasia - there are 8 types of it;
- asymmetric segmental form - a disease of 15 - 25-year-old people.

Differential analysis of
Prediction is possible due to the obtained data resulting from:
- genetic analysis;
- features of the clinic( type of disease, location of localization);
- associated symptoms, for example, fasciculation of the tongue;
- results of ECG and skeletal muscle biopsy data.
Differentiation of infant and early SMA can be made on the basis of problems with congenital muscle hypotension - the syndrome of "flaccid child", amyotonia, the congenital nature of benign muscular dystrophy, heredity and chromosome analysis.
The juvenile appearance differs from the spinal amyotrophy of Kugelberg-Weelander and various types of muscular dystrophies.
Objectives and methods of treatment
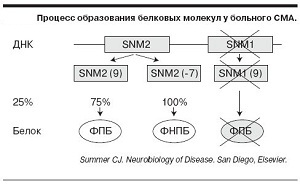 Since this disease occurs mainly due to a lack of SMN protein, the main goal of treatment is to increase its level. Today, active research is being conducted in this direction in the institutes of the United States, Italy and Germany.
Since this disease occurs mainly due to a lack of SMN protein, the main goal of treatment is to increase its level. Today, active research is being conducted in this direction in the institutes of the United States, Italy and Germany.
Thanks to a group of volunteers, a clinical study of CMA therapy with valproic acid, butiran sodium and other medicines is being conducted. Data on the use of stem cells have not yet been made public.
The patients are positively affected by:
- massage;

- neuromuscular stimulation;
- physiotherapy, any physical activity have only a positive effect.
- patients with SMA need a diet;
- course of drugs, which include vitamin complexes, analgesic drugs, improving the metabolism of nervous tissue and muscles, stimulating them.
Today, the patient's condition can be maintained and a little easier, but spinal muscular atrophy remains incurable.
Prevention
Prophylactic measures are passive actions - consultations of future parents who have the AGR gene on possible risk, prenatal DNA diagnosis before 14 weeks of pregnancy, chorionic villus biopsy for final diagnosis and parents' decision on further action.