What is it? Duodenitis is an inflammatory process in the mucosa of the duodenum( duodenum), causing structural changes in the mucous membrane, and leading to functional organ impairment. According to statistical data, more than 10% of the population experienced the symptoms of duodenitis - this is the most common pathology of the initial section of the small intestine.
People of different age categories are exposed to the disease. Twice more common in men who have a predilection for alcohol and are prone to a "binge" lifestyle. It is difficult to transfer the pathology of a woman. In them, it is accompanied by pathological processes in the endocrine glands and the central nervous system.
Provoke the development of duodenitis:
- food poisoning and infection;
- frequent use of provocative food( fried, fatty, salted, smoked);
- alcohol or its agents;
- food is dry and the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall is damaged by a foreign body.
In addition, inflammation reactions in the mucosal cover of the walls of the duodenum can be a consequence of ascariasis, lamblia, or tuberculosis, ENT infections and gallbladder infections.
A consequence of possible complications of certain diseases( lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach, inflammatory pathologies in the gallbladder, ulcerative renal failure).Most often, an impetus for the development of duodenitis, is gastritis, although the influence of food allergy is also possible.
Contents
- 1 Symptoms of duodenitis, clinical signs
- 2 Treatment of duodenitis, drugs
- 3 Prognosis and prevention of duodenitis
Symptoms of duodenitis, clinical signs
According to the stage and duration of clinical signs, duodenitis is characterized by acute and chronic course.
Acute duodenitis
The prerequisite for the rapid development of acute duodenitis is poisoning, or love of oriental spicy dishes. Against this background, inflammatory reactions on the mucosal surface of the duodenal ulcer provoke the formation of ulcerative and erosive lesions, sometimes ulcerous cavities filled with pus( phlegmon) are formed on the surface layer of the intestine. Symptoms of duodenitis in adults at the acute stage are:
- Acute pain in the stomach;
- Digestive disorder;AS Vomiting, nausea and weakness.
The development of an acute process almost always provokes inflammation in the intestine or stomach. Often this is diagnosed as gastric duodenitis, which is not true at the root, the inflammation of the mucous cover of the stomach cavity has its name - gastritis.
A provocative role contributing to the development of pathological reactions of inflammation in the mucosa of the PDC is the disturbance of mobility or peristalsis, which makes it difficult to move the condensed contents of the small intestine to the outlet( duodenostasis).
If the treatment is properly selected and the patient complies with a sparing diet, the inflammatory process in the DPC is stopped quite quickly. But, in case of repeated inflammation of the intestinal wall, the stage of the chronic course of the disease develops.
Chronic duodenitis - CD

The chronic stage of the disease is characterized by prolonged inflammatory reactions in the lower part of the small intestine. The disease periodically exacerbates or flows with mild symptoms, sometimes with complete absence.
May flow independently( exogenously), as a primary disease, or be secondary( endogenous), against a background of various provocative factors( malnutrition, bad habits, inflammatory pathologies of the digestive tract).
The disease is classified according to the nature of the lesion:
- Non-atrophic( superficial).
- Hypertrophic( erosive).
- Atrophic.
According to localization - affection of the proximal( central) and distal parts of the PDC.It is manifested by multiple clinical species:
- gastritis-like;
- is ulcerative;
- cholecystiform;
- is pancreatic;
- mixed and asymptomatic.
The most distinct symptoms of chronic duodenitis are manifested in the phase of severe exacerbation of the disease. Allocate: pain syndromes associated with gastrointestinal pathologies( abdominal), with intestinal and gastric disorders( dyspepsia), due to common disorders.
The genesis of pain symptoms is closely related to duodenostasis syndrome - a pathological change in the motor-evacuation function of the duodenal ulcer, which provokes an increased sensitivity of the mucosal walls of the intestine:
- with acidic remains of stomach contents, with insufficient treatment;
- changes in the hydrolysis of the biliary and pancreatic secretions;
- functional disorders of the biliary and virzungian duct( pancriotic);
- exposure to toxins of bacterial microorganisms.
The pronounced nature of exacerbations of HD is almost always accompanied by signs of the "lazy stomach" syndrome caused by concomitant processes - chronic gastritis, local defects( JBW) of gastroduodenal ulcers and duodenitis reflux. Common symptoms of chronic duodenitis are:
- Malady and chronic fatigue;
- Impairment of operability;
- Apathy to food and aversion to some group of products;
- Violation of coordination of movements and migraine;
- Irritability and unstable mood
- Sleep disturbance and anxious feeling;
- Increased sweating or chilliness;
- Hypotension and abnormal heart rhythm disturbances.
The abdominal symptomatology of DNA itself depends on the location of the inflammatory processes and has its own characteristics.
Superficial non-atrophic duadenite
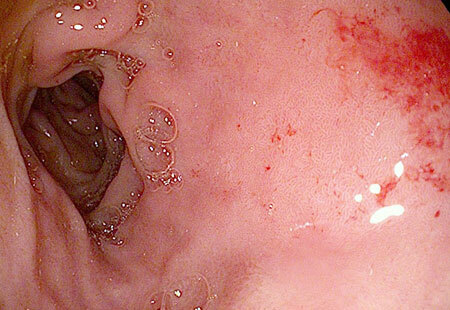
duadenite photo
Due to insignificant inflammatory reactions in the mucous membranes of the distal small intestine for more than three months. The pathogenic factor causes structural compaction in the walls of the intestine and the formation of corrugated folds on them.
External provoking factors with accompanying signs of a fundal( defeat of a body or a bottom of a stomach) a gastritis provoke disease.
Symptoms of superficial duodenitis are expressed by a pain syndrome that occurs usually when eating or immediately after eating. Accompanied by:
- temperature increase;
- tenderness in the abdomen and around the umbilical zone;
- intoxication symptoms( vomiting, nausea).
Hypertrophic( erosive) duodenitis
It is distinguished by a superficial defect of the mucous membrane of the intestine due to erosive lesions. In addition to external factors, the developmental catalyst can be surgical interventions on internal organs, sepsis, thrombotic lesions of veins, diseases of the central nervous system and blood.
In the phase of exacerbation of superficial antral gastric gastritis, in the proximal part of the PDC, the pain symptom can manifest as an ulcerative symptom, after one and a half, two hours after eating, in a state of hunger, or in the night sleep period. Another portion of food and treatment of symptoms of duodenitis, stop pain( mainly antacid drugs).
With lesions of the distal parts, the disease manifests itself with pain symptoms similar to those of pathological lesions of the pancreas and bile ducts. Soreness manifests itself in the epigastric zone, manifested by increased symptomatology after eating meat, milk or sweets.
Cholecystlike variant of the disease is characterized by pain in the right zone from the navel irradiating to the zone of the hypochondrium of the same side, and the pancreas-like variant is painful in the epigastric region or in the left zone from the navel, gradually spreading in the lumbar region.
Reduces the pain syndrome of this form of erosive duodenitis, treatment with myogenic spasmolytic drugs and a special diet.
If motor-evacuation disorders are present, the pain syndrome may appear paroxysm or be present permanently. It is localized in the right umbilical zone or in the epigastric zone, accompanied by a rumbling and a sensation of bloating.
Particularly clearly manifested pain in the defeat of the serous cover of the DPC.They are constantly present and exacerbated by movement and shaking.
Duodenitis with atrophic flow
Causes lesions of the glands in the upper part of the small intestine, which causes disorders in the secretory function of the duodenum and a decrease in the production of digestive juice. The mucous membrane of the intestine is very thin.
The incorporation of enteritis with manifestations of imbalance of microflora and impaired patency in the upper part of the intestine( duodenosis) is almost always expressed by gravity in the stomach and a feeling of overflow, swelling, gas formation and weak stool.
With pathological processes in the pancreas, digestive disorders and severe atrophic gastritis, the symptoms of duodenal duodenal atrophic flow are noted by signs of irregularities in metabolic processes and symptoms of vitamin deficiency - weight loss, dry skin, brittle nails and hair.
In severe bile duct function, yellowing of the skin and sclera occurs. On the surface of the tongue appears a yellowish, or yellowish-white tinge.
Treatment of duodenitis, drugs

Diagnosis of the disease based on the results of gastroscopy. Additional techniques include:
- X-ray contrast examination of the stomach and upper part of the large intestine;
- biochemistry of blood and gastric secretion;
- determination of acidity;
- The Koptogram;
- analysis of a biopsy specimen if a malignant process is suspected.
Treatment of chronic duodenitis is carried out depending on the clinical manifestations.
Patient recommended rest and "hungry" diet for two days. If necessary, gastric and intestinal rinsing is performed. Recommended preparations are adsorbing properties, and the therapeutic diet - mashed and steam dishes - not hot and not cold. With phlegmonous flow, antibiotics or surgical intervention.
In a stage of exacerbation, patients with chronic duodenitis are treated in a hospital setting. Therapy is selected by the presence of background pathologies that caused the disease.
- When parasitic pathologies - therapy with drugs "Flagil", "Furazolidon" or "Chloksin."
- Treatment of helicobacter pylori infection is carried out by antibiotic therapy( Metronidazole).
- Acidity is regulated by drugs - "Omeprazole", "Ranitidine" and their analogues.
- Intestinal mucous membrane is protected with enveloping agents - "De-nol" or "Sulfacrate".
- For the restoration of digestive functions, enzymes are used - Penzinorm, Mezim, Festal, Creon, Pancreatin.
- Prevention of inflammatory reactions is carried out with decoctions of yarrow or chamomile.
- In case of motor dysfunction of DPC, due to digestive disorders, the cause is eliminated by a conservative way - a balanced balanced diet, choleretic preparations or probing and washing of WPC.
Prognosis and prophylaxis of duodenitis
The main prevention factor is a correctly balanced diet and moderation of bad habits. Contribute to the prevention of disease - timely examination and treatment of pathological processes in the gastrointestinal system, use of medicines only for the intended purpose.
Prevention of relapse is possible only with regular examination and monitoring by a doctor.
With all the recommendations of the attending physician, the prognosis is favorable.