1 The essence of the pathology
Erosive gastritis or erosive-ulcerative gastritis is one of the forms of the inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa that results in the formation of small surface defects in the form of erosion. From other varieties of gastritis, the erosive type is distinguished by the appearance of extensive erosion areas against the inflamed reddened surface. Such damage sometimes covers the entire stomach surface. The development of erosive gastritis of the stomach begins with the formation of small wounds on the external surface of the stomach and gradually covers more and more territory.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method is to write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
- We recommend to read
- Diet for gastritis
- Stomach stop
- Causes and treatment of chronic gastritis in adults
- Effective remedy for gastritis and gastric ulcer
2 Types of the disease
Depending on the location of the pathology and the nature of the process, the disease is divided into the following main varieties:
- Acute erosive gastritis, developing very rapidly, covering a large area of the stomach with shallow manifestations and considered one of the most severe forms of pathologyand. This type of disease is caused by trauma, chemical or thermal burns, blood loss, sepsis, kidney or liver failure. The causes of acute manifestations can be associated with the ingress of aggressive chemicals( pesticides, acids).Defining signs are vomiting with blood and tarry stool.
- Chronic erosive gastritis, which is the most common type. The pathogenesis of this type of disease is based on a change in the secretory function with a violation of blood microcirculation and excessive release of aggressive components of gastric juice. Gradual development of the process leads to the formation of large erosions( up to 6-7 mm) on the mucosa. The chronic form is characterized by a prolonged inflammatory reaction of the inner integument. The most important reasons are: abnormal eating, alcohol abuse, smoking, taking some medications( nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), a viral infection. Long term such a course of the disease can occur with mild symptoms.
- Erosive antral gastritis, provoked by pathogenic bacteria Helicobacter pylori, which prefer the lower gastric and alkaline environment. After bacterial damage, mucosal tissues are difficult to regenerate.
- Erosive reflux gastritis, a serious lesion with deep penetration. As a result of casting the composition from the duodenum( reflux), large ulcers appear. Under the influence of an aggressive substance, detachment of the shell tissue can occur, and the exfoliated fragments come out with vomiting. On the gastric mucosa there is swelling. In place of healed ulcers, scars form which narrow the lumen of the esophagus.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
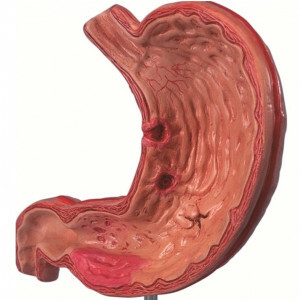
3 Manifestation of
When an erosive gastritis occurs, the symptoms are almost identical to other varieties of this gastric disease, and it is very difficult to differentiate it from external signs. Only the transition of pathology to the neglected stage facilitates the task, in connection with the appearance of characteristic gastric bleeding. The following signs of the disease can be distinguished:
- Pain syndrome, most often developing in the epigastric zone of the upper gastric department. The acute form is characterized by constant pain or pain in the form of seizures with an increase after eating. In the chronic course of the disease, pain is less pronounced, but becomes more intense as the pathology progresses. Pain can become stronger in the morning on an empty stomach, when gastric juice acts on pain receptors.
- Heartburn, more markedly manifested in case of erosive gastritis with motor dysfunction of the stomach. It is a characteristic symptom of reflux.
- Nausea and vomiting, especially noticeable in acute forms of pathology. Nausea usually occurs after eating. In the flow of vomit after the release of food residues, mucus secretion and gastric juice are fixed. In complications with vomiting, blood clots may appear.
- Dyspeptic symptoms that characterize gastric disorders: diarrhea, bitterness and dryness in the oral cavity, discomfort and heaviness in the stomach.
-
 Gastroenterologist. VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gas in any way. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. VAZHENOV: "I beg you, if you started to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not do gas in any way. .."Read more & gt; & gt;

4 Complications in the course of
disease The long-term chronic course of the disease often leads to latent gastric bleeding from erosion. Pathology with concomitant hemorrhage was called erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis. Surface foci on the anterior and posterior wall, as well as the gastric day, rarely produce blood. Dangerous in this regard are large in size, numerous, sufficiently deep erosion and ulcers with reflux. The most likely bleeding is when the lesion is localized in areas of low curvature, where larger blood vessels lie. Increase the likelihood of hemorrhagic appearance of the presence of hypertension and poor blood coagulability, as well as the reception of certain medical products( Aspirin, Heparin, Diclofenac, etc.).
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read testimonials & gt; & gt;
Erosion-hemorrhagic gastritis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- decreased intensity of pain as bleeding appeared;
- vomiting with bloody impurities, most often with a brown discharge;
- signs of anemia: dizziness, pallor of the skin, lower blood pressure, tachycardia;
- is a darkening of the stool caused by the presence of blood after exposure to gastric juice.

5 Principles of treatment
How to treat erosive gastritis? The doctor can answer this question after carrying out necessary inspections. Do not self-medicate. Only a specialist can properly diagnose the disease, decide how and how to treat the pathology. When an erosive gastritis is established, the treatment is made taking into account the type and stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the organism, the presence of complicating factors.
The general treatment regimen includes:
- elimination of the causes of the disease;
- providing a diet as the most important factor;
- medical treatment.

In its turn, the task of therapy is:
- elimination of the inflammatory process, reducing the aggressiveness of gastric juice;
- normalization of secretory and motor function of the stomach;
- symptomatic treatment( anesthesia, stopping bleeding, removing edema, etc.);
- recovery of diseased tissue and prevention of recurrence in the future.
6 Medication Therapy
Treatment of erosive gastritis is based on complex drug therapy. First of all, in the presence of defeat Helicobacteria antibiotics should be prescribed antibacterial. Usually, a medication such as Tetracycline, Levofloxacin, Clarithromycin, Amoxicillin with a long course of admission, or universal antibiotics is prescribed: Pylobacter Neo, Clatinol.
As the basic treatment of erosive gastritis, the following types of drugs are used:
- antisecretory agent to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid: histamine receptor blockers( famotidine, ranitidine, Kwamatel) and proton pump blockers( Omez, Lansoprazole, Controlol, Proxium);
- antacids to reduce the aggressiveness of the gastric composition: Rennie, Maalox, Almagel, Fosfalugel, Venter;
- preparations for the normalization of digestion in conditions of lowering the production of hydrochloric acid: enzymatic agents such as Creon, Mezim, Festal, Panzinorm, Pangrol;
- medications for the normalization of motor function: Metoclopramide, Cerucal, Motilium, Domperidone;
- Haemostatic agents for erosive hemorrhagic pathology: Etamsilate, Dicinone, Vikasol, thiectic acid( in the form of injections);
- restorative preparations for tissue regeneration: Iberogast, Trental;
- antispasmodics as symptomatic therapy: No-sppa, Papaverin.
7 Food Optimization
An important element in the treatment of erosive gastritis is a diet. During the course of the active inflammatory process, diet No. 1 is recommended, and as the manifestation of restriction calms down, the food is transferred to diet No. 5.Basic dietary rules for chronic erosive gastritis:
- Foods that increase the secretion of gastric juice and are able to irritate the mucous membrane - fried and fatty foods, spicy seasonings, spices, smoked products are excluded.
- Only fresh products are used, and they are cooked by steaming or by cooking.
- Food should be frequent and divided - 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- When consumed, the food should have a comfortable temperature( not hot and not cold) in a liquid state or in the form of porridge.
- Prohibited products: fresh baked goods from flour, biscuits, chocolate and sweets, animal fats( pork, lard, home-made sausage with spices).
- Recommended products: yesterday's white and black bread, rusks, bran, potatoes in puree or soup, porridges( except wheat and barley), vegetable oil and a small amount of butter, meat of dietary species( rabbit, chicken, veal), fish,fermented milk products.
8 Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine can be a good aid for drug therapy in the restoration of tissues and the normalization of stomach functions, but with its proper application. It is best if the people's funds are agreed with the doctor. The following folk methods are widely used:
- Cabbage juice is taken 100 ml 3 times a day for 20-30 days.
- Potato juice is taken 3 times a day before meals, and the dose gradually increases from 25 ml to 100 ml, the course of treatment - 15 days.
- Seabuckthorn in the form of berries.
- Sea buckthorn oil is taken 3 times a day for 1 tbsp.l.
- Sea buckthorn infusion: berries are poured with boiling water( in a ratio of 1: 5) and infused for 2 hours, honey is added to the cooled composition, it is drunk in a volume of 0.8-1 l during the day.
- A mixture of flaxseed with water( 2 tablespoons per 0.5 liters of water), is used 60-70 ml 3-4 times a day before meals for 15-25 days.
- Honey can be used alone or added to any composition.
Long since infusions and decoctions from chemist's camomile, St. John's wort, yarrow, oak bark have also been applied.
Erosive gastritis refers to quite dangerous diseases and is one of the most severe varieties of gastritis. The effectiveness of treatment largely depends on the timeliness of the initiation of treatment. At the first signs it is necessary to consult a doctor, since self-diagnosis is very difficult due to the similarity of symptoms with many other diseases.
- 1 The nature of the pathology
- 2 Varieties of the disease
- 3 Manifestation of
- 4 Complication in the course of the disease
- 5 Principles of treatment
- 6 Medication therapy
- 7 Food optimization
Erosive gastritis is a fairly common stomach disease, the degree of danger of which depends on the neglect of the pathology. It is very important that symptoms are diagnosed in a timely manner, and the treatment of erosive gastritis is performed by a professional. If at the initial stage the disease can be cured easily enough, then as the erosive gastritis of the stomach progresses, it becomes an extremely dangerous disease and can cause serious complications.