Neurodermatosis - your derma calls "03".
This phenomenon, like neurodermatosis, is said in cases when the skin comes to a state of painful irritation caused by excessive sensitivity of the nervous system to factors, either acting from the outside or appearing in the internal environment of the body.
Skin( or dermis) is a structure of a complex structure, in addition to connective tissue and epithelium, which includes hair bulbs, sweat and sebaceous glands, blood and lymphatic vessels and a densely branched nervous system represented on the surface by nerve endings-receptors.
Occurrence of various disorders outside or inside the body causes a reaction from the nervous system on the skin leading to a change in the state of the blood and lymph vessels. Due to the development of their spasm or the condition of paresis, ischemia of the dermis cells comes, which is accompanied by a trophic disorder.
With a deep degree of damage to the dermis, due to the processes occurring in it, leading to its inflammation, neurodermatosis passes into 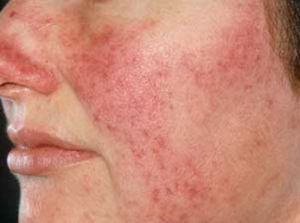 neurodermatitis.
neurodermatitis.
If compared with something familiar, dermatosis is similar to that of a dirty and pretty rubbed sofa, dermatitis is the same sofa, but with the already broken skin and springs outwardly protruding.
Like the process of its layer-by-layer transformation with the passage of a whole series of stages, the process deepening and expanding in the skin has many intermediate phases, when changes in it can not be correlated with any of the diagnoses. Therefore, the systematics of neurodermatoses is simply inconceivable to give a complete look. But we will try to do it as fully and as completely as possible.
Contents
- Classification - maximum
- Skin itching
- Features of the
- clinic About diagnosis, therapy and prevention
- Manifestations of urticaria
- Features of the
- Clinic
- Diagnostic methods, treatment, prevention
- Clinic of the disease
- About the general principles of treatment
- About the prognosisand prophylaxis
- Features of the
- Clinic Diagnostic features and approach to therapy
- Features of the clinical picture
- Diagnostic and treatment methods
- Symptomatic features
- About diagnosis and treatment
- Clinic of illness
- About diagnostics and treatment
Classification is maximum but incomplete
If we take as a basis the classification of depthlesions of the skin and the degree of complexity of the fight against the disease, the systematics of neurodermatoses has the following form.
- skin itch , the maximum manifestations of which are calculi;
- urticaria , which can confine itself to the appearance of blisters;
- pigmentary urticaria( mastocytosis) - a condition both passing with age, and persistent throughout life;
- neurodermatitis , accompanied by the appearance of papules and ending with lichenification;
- prurigo - polymorphism of the rash accrues with the depth of damage to the dermis;
- atopic neurodermatitis with polymorphic rash and with a propensity to complications;
- eczema - severe, chronically( for life) leaking deep skin lesions with recurrent-recurrent nature.
Skin itch
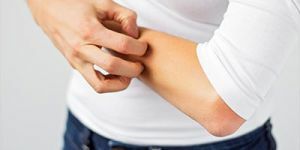 The condition named for the main sign of the lesion is itching, which occurs in response to a variety of causes and, as a rule, passes after their elimination.
The condition named for the main sign of the lesion is itching, which occurs in response to a variety of causes and, as a rule, passes after their elimination.
The causes may be both local and common skin irritation. Hence the division into two types of disease:
- generalized ( common);
- localized ( limited).
If the basis for a limited skin itch areas around the natural openings( anus, vulva or scrotum) is irritation of the skin with microbial, protozoan or helminthic poisons, then for itching the generalized causes are much greater.
These can be:
- disorders in the neuro-psychic and vegetative sphere, including such a kind of psychogenic itch, as acarophobia;
- metabolic diseases( liver and kidney pathology), endocrine diseases and disorders( diabetes, menopause);
- helminthiases;
- connection with staying at an altitude of over 6-10 thousand meters;
- seasonal pathology( itching cold, warm, sunny);
- a perverted reaction to certain types of products, such as chocolate, strawberry;
- association with metabolic disorder due to age( senile itching).
Features of the
Clinic Characteristic of any age, a condition characterized by a scratching reflex, a slight expression of which leaves a maximum trace on the dermis in the form of abrasions( excoriations).With prolonged and persistent flow, the skin becomes dry, and abrasions can be suppurated, the nail plates scratching the polished nails.
In an itch of a widespread discomfort, starting with a small area of the skin, rapidly seizing all the new zones, spreading throughout the skin surface.
Gradually, "creeping crawling" and tingling becomes permanent, the itching becomes obtrusive, leading to combs until burning and protruding blood drops, after which the itching fits temporarily.
With a limited process, the same changes are of a local nature. Chronic( as in the elderly) existence leads to the appearance of areas of hyperpigmentation with shiny, linear-shaped scars on the grayish background of the dermis cells.

About diagnostics, therapy and prophylaxis
When diagnosing, as with differentiation from similar pathology, take into account the alleged cause of pruritus and characteristic complaints, accompanied by the scarcity of cutaneous manifestations.
Most often, the skin itch passes on its own after the effect of the factor that provoked it( cold, height), while persistent "scabies" continue to take measures to stop the irritating effect, for example, wearing cotton clothing free cut.
If necessary, therapeutic measures are used referral tools:
- sedative or psychotropic;
- antihistamine;
- improves microcirculation and healing( including, softening ointments and creams, like Dardia Lipo, Emolium and the like).
Prognosis for uncomplicated course of the disease is favorable, the consequence of the same persistent chronic course may be the neuroticization of the patient.
With the goal of prevention, timely treatment of provoking diseases, revealing of hidden pathology and timely examination should be observed in the event of disturbing symptoms.
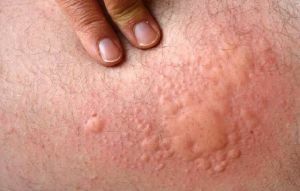
Manifestations of urticaria
The second name is urticaria rash, which tends to volatilize with an acute and first occurring case of the disease.
However, the abundance of etiological factors makes the pathology regularly manifested, in 25% of cases acquiring a chronic course.
The provoking factors include:
- nutritional supplements and products;
- medicinal substances;
- auto-allergens and other.
The classification includes two forms of the disease:
- allergic;
- is pseudo-allergic.
 The pathogenesis of the first form is an immediate type of allergic reaction to any substance( food, household chemicals) by means of IgE.Either the formation of immunocomplexes activating complement, which leads to the release of mast cells from their contents( with blood components transfusion, immunization).
The pathogenesis of the first form is an immediate type of allergic reaction to any substance( food, household chemicals) by means of IgE.Either the formation of immunocomplexes activating complement, which leads to the release of mast cells from their contents( with blood components transfusion, immunization).
With pseudoallergic urticaria, the provoking factor is histamine releasing( radiopaque) substances, inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis( salicylates), cooling, and the like.
Features of the
Clinic On the background of unbearably severe itching, a rash appears in the form of a flaming red or white color, then blisters of a round or oval shape ranging in size from 3-5 mm to 12-15 cm with even or fancifully scalloped edges appear.
The period of existence of blisters until the last disappearance is from 20 minutes to 1 day. When the rash lasts for up to 30 days, it is said that acute, with a duration of over 30 days, chronic hives.
The localization of the rashes is diverse. Acute urticaria is a reaction of an immediate type, characterized by a massive edema with large blisters with a grip of the face and neck with the transition to the trunk.
In the genesis of chronic urticaria( which women suffer more often) a significant role is assigned to stress factors.
Methods of diagnosis, treatment, prevention
For anamnesis, the history and dynamics of the clinical picture are important. It is necessary to differentiate from insect bites, scabies and herpetiform dermatitis.
Treatment begins with the elimination of a hysterectogenic factor. It is necessary to conduct desensitizing therapy of  with antihistamines( Levocetirizine, Desloratadine and the like) against the background of a therapeutic diet.
with antihistamines( Levocetirizine, Desloratadine and the like) against the background of a therapeutic diet.
Intravenous infusions of sodium thiosulfate or injections of calcium gluconate in / muscularly or ivently. If necessary, resort to the use of Prednisolone( up to 100 mg iv).
In order to avoid the development of chronic urticaria, the patient is recommended to sanitize the chronoinfection foci, because exclusively external treatment of the effect does not have any effect.
Pigment form of urticaria
Pigmental urticaria, also called mastocytosis, the etiological factor of which is the effect on the dermis:
- mechanical( compression or friction);
- thermal( insolation, hot steam or water).
When influencing the cells of the dermis, the reagents of provocation from mastocytes present here in excess release the bioactive components of the allergic reaction( histamine, peptidase, heparin and others), resulting in the formation of itchy urticaria on its surface.
Clinic of the disease
Children of early age( up to 2 years) are exposed to the disease, and mastocytosis, debuted after 10 years, is prone to persisting throughout life.
The disease manifests itself as:
- of pigmentary urticaria proper;
- mastocytoma.
For pigmentary urticaria is characterized by the emergence of randomly scattered on the skin of the body of highly itchy spots of brownish-red color with a diameter of 0.5 to 2 cm. In infants, it is possible with the appearance of vesicles or blisters. Mechanical impact( friction) leads to a change in the color of the spot on the bright pink and a noticeable increase in edema - the phenomenon of Unna.
The manifestation of a mastocytoma is the appearance on the skin of the back, abdomen, forearm of one or more shaped elements - 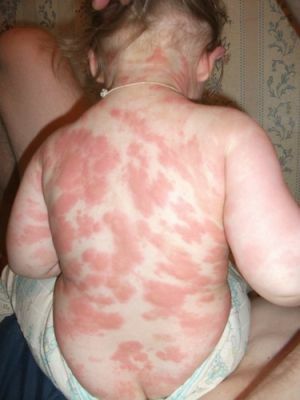 raised above the surface of plaques or papules of a brownish-yellow color, oval in shape, with a surface similar to orange peel.
raised above the surface of plaques or papules of a brownish-yellow color, oval in shape, with a surface similar to orange peel.
The positivity of the Unna phenomenon and the propensity of mastocytoma to independent regress are noted.
The disease is prognostically favorable: after the disappearance of exudative phenomena, the remaining pigment spots are reduced until reaching the pubertal period.
When kept to adulthood, the disease proceeds fairly easily. Cases of diffuse mastocytosis, as well as systemic damage, are extremely rare.
For diagnostics, in addition to the characteristic clinic, the positivity of the Unna phenomenon and the tissue biopsy data are important.
About the general principles of treatment
There are no standards for the treatment of this disease.
The use of pro-antihistamines in therapy with levocetirizine, Loratadine and the like, allows to achieve an antipruritic effect, especially in combination with a cytomidine blocker of H2 receptors.
Prolonged administration of Ketotifen helps stabilize mast cell membranes and prevents the release of bioactive substances.
Local double-daily application of glucocorticoid agents: Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone aceponate, Alclomethasone facilitates the removal of itching and inversion of the formed elements of the rash.
About prognosis and prophylaxis of
Patients should be informed of the need to avoid aggravating factors: mechanical stress and injuries that irritate the skin, thermal procedures, insolation. For already sick children, the danger is posed by insect bites and arachnids due to the possibility of anaphylaxis.
Persons of all ages are not recommended for use degranulation-causing mast cells:
- Aspirin and NSAIDs;
- codeine and morphine-containing;
- Polymyxin B;
- radiopaque substances with iodine content.
Developmental peculiarities and principles of therapy of neurodermatitis
The neurodermatitis, also known as neurodermatitis, is a chronic disease characteristic of older children and adults, characterized by the lichenification of dermis cells.
Etiological factors and pathogenesis have not been fully investigated. Presumably, the disease is caused by dysfunction of the central nervous system with a modification of nerve fibers and receptors of the skin of an organic property. The connection with endocrine disorders and pathology of the gastrointestinal tract was noted.
Neurodermatitis is divided into three types:
- limited;
- disseminated;
- diffuse.
Features of the
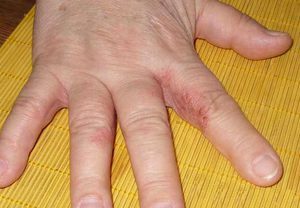
clinic In the photo, the limited neurodermatitis of the palms
The disease is characterized by a painful itch, resulting in permanent scratching, resulting in its lichen-plaque-flat, small, shiny diamond-shaped papules, at first flesh-colored, followed by pinkish-brownish.
The surface of plaques is formed by excoriations, scales, blood crusts, the boundaries are blurred.
For limited neurodermatitis, the localization of the surface lesions is typical:
- of the neck( posterior and partly lateral);
- of the shins;
- zones of ankle joints;
- folds of hip and interannual;
- perineum, scrotum or labia.
In a focus with dimensions from 5 × 10 cm and more clearly identified three zones: the central - the zone of lichenification, the middle - the area of small lichenoid papules and the zone of hyperpigmentation at the periphery.
Disseminated neurodermatitis is the simultaneous existence of several foci with the described changes.
The concept of diffuse neurodermatitis includes massive damage to dermal integuments with the presence of large areas of its lichenification zones and flat-papular fragments on a common, sallow skin background.
Diagnostic features and approach to therapy
For diagnosis and subsequent treatment, the typical for neurodermatitis symptoms, the timing of its existence, and in part anamnesis, which allows to exclude:
- eczema;
- atopic dermatitis;
- pruritus of adults.
The choice of treatment methods directly depends on the form of the neurodermite. With limited lesion, cutaneous  will be effective in the use of glucocorticosteroid ointments( Betamethasone in pure form or in combination with salicylates, Fluticasone, Clobetasol), ointments with naphthalan oil, special creams, gels and the like.
will be effective in the use of glucocorticosteroid ointments( Betamethasone in pure form or in combination with salicylates, Fluticasone, Clobetasol), ointments with naphthalan oil, special creams, gels and the like.
The diffuse form requires a long-term use of desensitizing agents, including the use of Prednisolon short courses in combination with antihistamine combinations.
During the periods of remission of the disease, therapeutic therapy in the resort, in particular, hydrogen sulphide baths, as well as physiotherapy including selective phototherapy and electrosleep will be useful. Externally, the same remedies are used as with the rest of the disease.
The prognosis and consequences depend on the severity and extent of the process, the duration of the disease, the success or failure of the treatment - deep and extensive skin damage prevents freedom of movement and limits the perception of sensations.
Prevention measures are the protection of skin from damage, the fight against stress and foci of infection in the body, the passage of regular examinations by a dermatologist.
Pruritus, she is prurigo
Both adults and children are affected. Pochemuha includes several conditions accompanied by itching, with a different morphology of the formed elements of the rash:
- papules;
- papule-vesicles;
- Urticaria;
- nodes.
Presumptive etiological factors are various variants of autoallergization and autointoxication, enzymatic insufficiency of the intestine.
Features of the clinical picture
The disease includes prurigo:
- nursery;
- is an adult;
- is a knotty species of Gayd.
Pochesu of pediatric( strobulus) is often affected by persons of age from 2 to 6 years due to the presence of helminths, foci of chronoinfection, 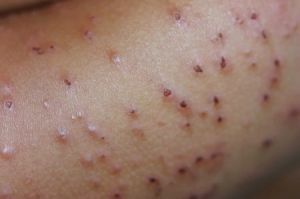 disorders in the liver and gastrointestinal tract, development of toxic and allergic reactions. Children older than 5-7 years do not get sick.
disorders in the liver and gastrointestinal tract, development of toxic and allergic reactions. Children older than 5-7 years do not get sick.
Having seized the face, trunk, buttocks, flexor surfaces of the extremities, the eruption in children has undergone a number of changes: a blister with a bubble or dense papule in the center disappears after a half-day, leaving the papule, the vesicles dry out to form crusts.
On the face there is the formation of scattered papillae of light pink in color with the head of a pin with papulevezicula in the middle, turning into a vial, on the opening of which a blood crust is formed. The disease lasts from 2 weeks to 3 months. Acute pruritis in adults is characterized by the appearance on the trunk and extensor zones of the limbs of compacted hemispherical formations against a background of severe itching.
For Gaida's prurigo are characteristic:
- lesion concerns women 40-60 years old;
- presence of an isolated papular rash or nodes up to 1 cm in circumference, dense, dirty-gray hue, localized at the rear of the hands, shins, extensor zones of the extremities, with pronounced biopsy pruritus;
- duration of leak;
- Torpidity for treatment.
Methods of diagnosis and treatment
For the diagnosis is important, the history and the clinic, which allows you to differentiate the disease from hives and red flat lichen.
Desensitizing agents are used for treatment, including glucocorticosteroid ointments, with Gaida pruritus with occlusive dressings.
Prevention is to eliminate trigger factors and dynamic observation by a dermatologist.
Atopic dermatitis
The disease with a chronic recurrent nature and hereditary conditionality is one of the category of atopic disorders.
Etiological factors are:
- gene predisposition;
- immune deficiency;
- dysfunction of endocrine structures;
- dysfunction of higher nervous and autonomic functions;
- pathology of the digestive tract. Thus, genetically determined dry skin( xerosis) and sebostasis( insufficiency of sebaceous glands) leads to a breakdown in the function of the skin as a barrier, which causes the ingress of allergens from the external environment that trigger allergic reactions.
Atopic dermatitis is subdivided by age categories:
- from 3 months( in infants);
- from 2 to 13 years( for children);
- from 13 years( adult);
According to the nature of the course of the disease there is:
- period of exacerbation;
- remission;
On the vastness of the area, atopic dermatitis happens:
- limited( localized), up to 10% of the skin area;
- common, up to 50%;
- diffuse, more than 50%;
- generalized type( erythroderma), about 100%.
Due to the severity of the process, atopic dermatitis happens:
- is mild;
- medium-heavy;
- heavy.
There is also a division in morphology with a predominance of manifestations:
- exudative;
- erythematous-squamous;
- erythematous-squamous with signs of lichenification;
- lichenoid;
- pruriginosic.
Symptoms of
As itching of neurodermatoses, the disease is characterized by a large polymorphism of the elements:
- of primary , characterized by spots( erythematous, erythematous-edematic, erythematous-squamous);vesicle;papules( from follicular to lichenoid and pruriginous);
- secondary : scales;crusts;erosion;cracks;lichenification.
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by the symmetry of rashes and dyschromia in the form of white pityriasis.
Exudative form is characterized by dying rashes, the appearance of edematous erythema, vesicles, serous crusts and red dermographism. Erythematous-squamous manifests itself as the formation of zones of hyperemia and infiltration, exfoliation and mixed dermographism.
Severe course is manifested by erythematous-squamous variant with lichenification, pronounced itching, multiple calculi and white dermographism.
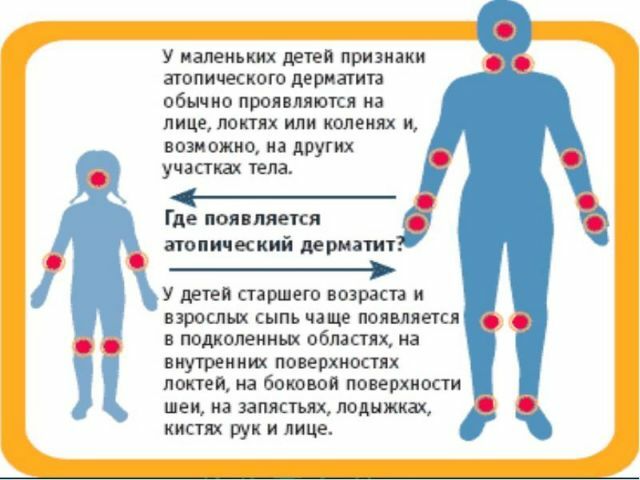
 Infant localization is characterized by localization of rash on the face, extensor zones of the extremities, abdomen, breasts, formation of "milk crusts" on the cheeks, childlike location in elbows and popliteal folds, back of neck, in areas behind ears."Adult" rashes are located on the neck, face, top of the trunk, hands.
Infant localization is characterized by localization of rash on the face, extensor zones of the extremities, abdomen, breasts, formation of "milk crusts" on the cheeks, childlike location in elbows and popliteal folds, back of neck, in areas behind ears."Adult" rashes are located on the neck, face, top of the trunk, hands. With prolonged existence of the process - with atopic erythroderma and secondary infection, lymphadenopathy develops involving the areas of the neck, neck, underarms, and groin in the affected area of the lymph nodes.
Atopic dermatitis often causes associations with ichthyosis, xerosis, follicular keratosis due to the considerable dryness and exfoliation of the skin.
Complicated forms include attachment of infection:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- fungal.
On the diagnosis and treatment of
In addition to the clinical picture in favor of the disease, the data of laboratory studies speak. A general blood test reveals leukocytosis with eosinophilia, serological test - excess IgE, coprology - signs of fermentative-putrefactive dyspepsia and helminthic invasions.
Differentiation is also made from scabies, pink lichen, seborrheic and contact dermatitis.
The general therapy includes funds with the action:
- antihistamine( class of Chloropyramine and Clemastine);
- membrane-stabilizing( Ketotifen);
- desensitizing( calcium gluconate, sodium thiosulfate);
- sedative or psychotropic( Bellataminal, Persen);
- enterosorbent and corrective work of the digestive tract( Lignin hydrolysis);
- immunocorrective( Methyluracil).
Severe course of the disease requires the use of infusion therapy, plasmapheresis, hemosorption, glucocorticoids( Prednisolon IV and in / muscularly) in short courses.
In the case of secondary infection, antibiotic treatment( Erythromycin, cephalosporins) is used, antiviral( Acyclovir) and antifungal( Fluconazole) are prescribed.
The preparations for external therapy include anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects:
- glucocorticoids of Prednisolone in creams and lotions( including antibiotics);
- lotions with preparations of astringent and antimicrobial action( solutions of Zinc sulfate, Tannin) and other means.
Effective administration of solutions of local antimicrobial agents: Potassium permanganate, Nitrate silver, diamond grun,
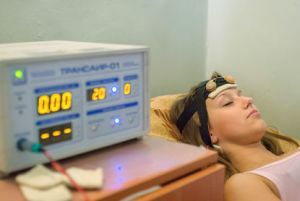
Electrosleep - an effective tool in the fight against numerous forms of neurodermatosis
Castellani and antimycotics( Clotrimazole).
Physiotherapy uses electrosleep, UFO, paraffin and ozocerite locally, baths, effectively climatotherapy, radon and hydrogen sulfide baths.
Prevention of the disease is the elimination of allergens, a decrease in the level of emotional and psychological overload, compliance with the regime of the day.
About eczema
Eczema is a polyorganic-borne chronic inflammatory disease with a tendency to recur, with polymorphism of the rash. The pathognomonic sign is serous wells.
The maximum is often found in persons 20-50 years old, for the most part - women.
In etiology, endogenous and exogenous stimuli play a decisive role. The first include genetic factors, intoxication due to diseases, to the second - neurological failures, allergens of physical or chemical nature.
To types of eczema, according to the classification, are:
- true( idiopathic);
- microbial;
- child( not recognized by all);
- seborrhoea( attributable to seborrheic dermatitis);
- professional( contact).
According to the type of current, eczema differs acute, subacute, chronic with a course of 2-6 months or indefinably long.
Clinic of the disease
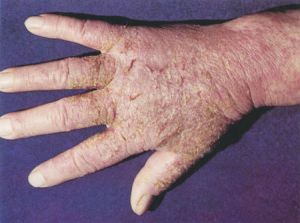 The development of acute true eczema occurs in this order.
The development of acute true eczema occurs in this order. Originally, the red and pink spots appear in number and size, then, merging together, create an erythematous rash that becomes diffuse erythema, which rises above the skin level( erythematous stage).
It is followed by Papular( due to the formation on the erythematous background of many small, edematous-juicy exudative papules of red and pink color with the consistency of the test).
Due to the increase in the inflammation process, edema increases with the transformation of papules into vesicles( the vesicle stage), which contain a sterile serous fluid. When the vesicles are opened, bright red erosions are produced, constantly producing colorless serous exudate - serous( eczematous) wells.
When merging serous wells, large fires of a glowing red color appear with serous wells against their background. Deprived of the cornified layer of the zone intensively produce exudate impregnating the laundry( the stage is wetting).This is the peak of the evolution of acute eczema.
Subsequent, cholastic stage is characterized by the absence of occurrence of the following vesicles.
Undisturbed vesicles shrink to the degree of crusts, within which there is a slow restoration of the cornificatory layer with a change in the color of the foci on the cyanotic pink and the fall of the crust with the onset of otreparid peeling - squamous stage.
The gradual acquisition of body skin with the termination of exfoliation indicates a reverse process.
Next comes the recurrence with a jerky evolution - a layering of stages and the presence of all elements simultaneously.Squamous eczema
True eczema is fraught with the attachment of a pyococcal infection.
Species of true eczema are dishydrotic, damaging the skin solely from the palms and soles, and microbial, caused by the activity of microorganisms.
Varicose eczema affects the entire thickness of the skin, including the hypodermis, leading to lymphangitis and lymphadenitis.
In the list of causes of contact eczema, the main role belongs to monovalent sensitization of production or household character.
About diagnosis and treatment of
Finding serous wells( pathognomonic sign of eczema) is an evidence-based argument in diagnosis.
Laboratory tests with skin tests reveal a monovalent sensitization and allow differentiating eczema from a similar cutaneous pathology.
The combination of etiopathogenetic and cutaneous therapy makes it possible to minimize inflammatory-exudative phenomena and achieve a temporary remission.
Principles of therapy are similar to those for all types of cutaneous pathology, the following medicines are prescribed:
- antihistamines;
- adsorbing;
- detoxifying agents.
If necessary, antimicrobials of the appropriate category are also prescribed.
The basis for the success of treatment is a strictly adjusted diet( hypoallergenic table).
External therapy should take into account the phase of the inflammation process, it is necessary to limit the volume of water procedures - the application of lotions and bandages.
Treatment for the remission of chronic eczema begins with the use of ointments with glucocorticoids for cutaneous application, later - in combination with antibiotics and salicylates.
The duration of the inter-recessive interval depends not only on the use of different methods of treatment, but also on the patient's self-discipline and strict adherence to the prescribed regimen and diet.
Despite the insufficient effectiveness of treatment of certain types of neurodermatoses, the general level of knowledge about their etiology and pathogenesis, steadily increasing, already today allows you to heal the most persistent skin diseases.