 Among all neoplasms of the central nervous system, hemangioblastoma takes a special place. This is a fairly rare variety of vascular tumors( no more than 2-3% of the total number of intracranial volume formations).
Among all neoplasms of the central nervous system, hemangioblastoma takes a special place. This is a fairly rare variety of vascular tumors( no more than 2-3% of the total number of intracranial volume formations).
Hemangioblastoma can be single and occur sporadically in patients older than 35 years in the cerebellum, or it may be multiple with localization in different parts of the brain and spinal cord, as well as optic nerves and the retina in young and young patients up to 25 to 30 years.
In the latter case it is a hereditary Hippel-Lindau disease, and this is already a much less favorable prognosis for life. What is this pathology and how to treat it?
Species of
formations. Hemangioblastoma refers to tumors of 1 degree of malignancy( or benign) with a predominant location in the posterior cranial fossa, rarely - beyond its limits.
The study of this pathology was conducted at the beginning of the last century in connection with the investigation of a hereditary disease in which changes were detected on the retina of the eye, in internal organs by the type of vascular tumors. At the same patients at autopsy found similar formations in the cerebellum, which were the cause of death.
The disease was named after the scientists - Hippel-Lindau disease. Later, sporadic cases of vascular formations of benign origin in the cerebellum were established, and more among the male population.

The macroscopic character of the hemangioblast allows to distinguish 3 variants:
- soft-tissue ( solid) tumors in the form of a crimson node encapsulated, they have a clear localization( approximately 65% of cases);
- smooth-walled cyst with transparent contents and a small nodule on the wall( approximately 30%);
- mixed tumor variant - single unit with cysts inside( 5%).
Microscopically, hemangioblastoma is a cluster of capillaries, between which are stromal( connective tissue) cells. Here also up to 3 possible variants are identified:
- juvenile tumor - consists predominantly of their fine capillary network;
- transitional form - contains approximately the same number of stromal cells and vessels;
- is a purely cellular variant of - multiple cells are located on small damaged vessels.
Causes and mechanism of formation of
Along with other neoplasms of the nervous system( craniopharyngioma, astrocytoma, meningioma and others), hemangioblastoma often develops in individuals with established hereditary predisposition and certain provoking factors of carcinogenic effect.
These include: 
- radioactive radiation;
- excessive exposure to insolation;
- work in hazardous industries( asbestos dust, benzene vapor, phenol formaldehyde, oil and coal resins and others);
- adverse environmental situation;
- viral infections( herpes, a group of retroviruses and adenoviruses).
In the case of Hippel-Lindau disease, the cause is a gene mutation, which is inherited from one of the parents by half of its children( an autosomal dominant type).In such patients, the development of suppressor( suppressing factor) of tumor growth is disrupted.
This is why these people during their lifetime form multiple benign or malignant tumors throughout the body - in the eye retina, optic nerves, pheochromocytoma( adrenal gland tumor), cyst in the pancreas, hemangiomas in the brain and spinal cord.
Any variant of hemangioblastom squeezes certain areas of the brain as it grows, which causes the appearance of neurologic symptoms.
Clinic of the tumor process
The severity of clinical manifestations in intracranial tumors, including hemangioblastoma, depends on the size and localization of volume formation. Hemangioblastoma is very rarely located inside the substance of the large hemispheres. More than 80% of patients have cerebellar localization, in 13-15% of cases the stem part of the brain is affected and about 5% falls on the parts of the spinal cord.
Symptoms are divided into 3 main groups:
- common cerebral manifestations;
- cerebellar symptoms;
- long-term consequences.
The first group of clinical manifestations is caused by a violation of the outflow of liquor fluid and the buildup of hydrocephalus( hydrocephalus).
 A constant headache occurs in the back of the neck or over the entire head, which is not suppressed by usual analgesics. Often the phenomenon of labyrinthitis with characteristic dizziness, nausea and vomiting without relief from the condition after it.
A constant headache occurs in the back of the neck or over the entire head, which is not suppressed by usual analgesics. Often the phenomenon of labyrinthitis with characteristic dizziness, nausea and vomiting without relief from the condition after it.
In the early stages of the disease with ophthalmoscopy, stagnant spots of the optic nerves are found. To these manifestations are later blended long-term effects - paresis and paralysis of cranial nerve fibers, convulsive syndrome, disorders of skin sensitivity.
The severity of general cerebral symptoms can be so strong that it masks cerebellar manifestations, among which the main is cerebellar ataxia. It can be dynamic when the function of coordination of movements is broken( the tumor is in the hemisphere of the cerebellum) or static, when there are disorders of the habitual posture and walking( a tumor in the cerebellum worm).
Typical are excessive hand waving, very large sweeping handwriting, the inability to rapidly change movements, slow speech, nystagmus( rapid eyeball movements), muscle hypotension, tremor.
Unilateral disorders as the tumor grows and the opposite side of the cerebellum becomes bilateral up to complete cerebellar syndrome.
In the late stages of the disease, neuropsychic disorders - asthenia, depression, deafness of consciousness, are often attached.
With the location of the hemangioblastoma in the oblong and spinal cord, the clinic manifests itself in the sensory and motor spheres in accordance with the location of the tumor, as well as functional disorders from the intestine and urinary system.
Diagnostic and treatment measures
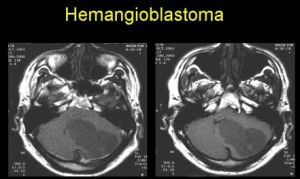
Diagnostic measures for suspected brain tumors include general neurological examination and special research methods. The neurologist at the reception evaluates reflexes and skin sensitivity, it is often necessary to conduct an ophthalmoscopy( examination of the fundus).The main place in diagnostics is occupied by such research methods as CT and MRI.
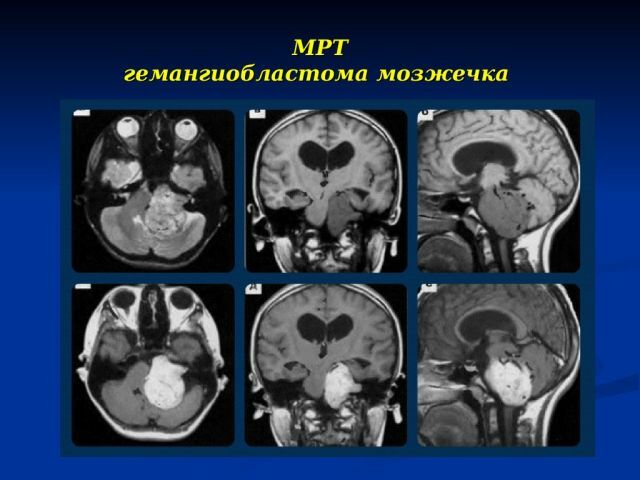
Tumor of the cerebellum on MRI
The final diagnosis is usually made after a histological analysis of a sample of tumor tissue taken during surgery. In a number of cases, ultrasound of the brain and contrast angiography are used. Patients with hereditary complications in the history are shown medical-genetic consultation.
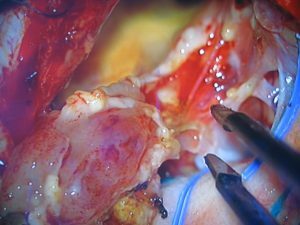
The standard of treatment is surgery for radical removal of the tumor. Isolation and excision of volumetric education is carried out with the help of modern neuronavigation systems. In cystic hemangioblastoma of the brain, first suck the contents of the cyst with a syringe, then remove the tumor.
With a sharp increase in intracranial pressure and compression of the brain substance, emergency surgical intervention is performed - ventricular puncture and excision of hemangioblastoma.
Removal of hemangioblastoma 4 ventricles:
For inoperable tumors, palliative operations are carried out to alleviate the patient's suffering, for example, shunting, to ensure the removal of excess liquor fluid.
 Tumor irradiation can be used as a preparation for surgery or as maintenance therapy in the postoperative period, as well as independently with inoperable form of hemangioblastoma.
Tumor irradiation can be used as a preparation for surgery or as maintenance therapy in the postoperative period, as well as independently with inoperable form of hemangioblastoma.
Chemotherapy in an intrathecal way( medication in the spinal canal) is used as part of a complex of measures for the treatment of hemangioblastoma. Alternative to date, the method is rightly considered radiosurgery, but the limitation is the large size of the tumor, in addition, the effect occurs after weeks or even months.
Sporadic benign hemangioblastoma has the most favorable prognosis for radical tumor removal, which is possible in more than 82% of cases. Subtotal( incomplete) removal of tumor growth from a solid node often leads to the occurrence of postoperative relapses. The worst prognosis for the genetic mutation of Gippel-Lindau.