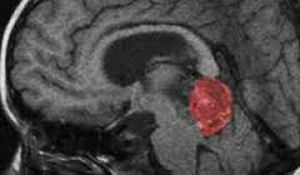
 Cavity of the brain( most often diagnosed with cavernous angioma and hemangioma) - cavernous malformations, consisting of a vascular tissue with cavities that are empty or filled with blood.
Cavity of the brain( most often diagnosed with cavernous angioma and hemangioma) - cavernous malformations, consisting of a vascular tissue with cavities that are empty or filled with blood.
A cavernoma can usually occur without symptoms or with neurological symptoms and syndromes, the consequences depend on the size of the lesion and its position.
The tumor is mainly located in the cerebral cortex, but is sometimes located in the corpus callosum, basal nuclei, brainstem, brain ventricles and thalamus.
Cavernoma is a neoplasm of cyanotic color, it consists of a vascular tissue in which cavities are present. Cavities are empty, and also filled with blood clots, blood or scar tissue.
This vascular neoplasm undergoes hemorrhages, so the brain tissue next to the tumor is yellowish in color. The partitions between the cavities are made of collagen fibers or coarse fibrous connective tissue. After hemorrhage, traces of calcification and healinosis remain.
Contents
- Provoking Factors
- Features of the clinical picture
- How to recognize the disease?
- Diagnosis of
- What does modern medicine offer?
- Operative therapy
- Radiosurgery is modern and effective
- Complementary therapies
- Prophylaxis and prognosis
Aggravating factors
The cavernoma is mainly a congenital disease, although sporadic cases also occur. Neoplasm is a benign tumor that has a spongy structure, when pressed they are soft and elastic. 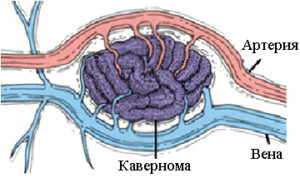
Because of the pressure on it, the formation may disappear, but then it will assume the same size. Cavernous malformations often bleed, resulting in infection.
Predominantly, cavernous angiomas and hemangiomas are formed in the womb due to changes in the processes of differentiation of tissue cells. Fetal anastomoses that connect arteries with veins give rise to tumor development.
When the vessels proliferate, the growth increases in size. Cavernoma can also appear with a soft tissue injury that can trigger the development of vascular formations.
Features of the clinical picture
Symptoms of this disease depends on the location of the vascular formation. The first sign may be an epileptic seizure with a neurological disorder.
Symptoms are manifested by the presence of:
- headaches, which at the initial stage of development are mild, although periodic, but with the development of the disease the pain becomes stronger and the medications do not help;

- convulsions having an epileptic form;
- noises in the ears or ringing in the head;
- of uncertain gait, dizziness, and impaired coordination and motor activity;
- dyspeptic disorders in the form of vomiting and nausea;
- the appearance of weakness in the limbs, as well as numbness and paralysis;
- dysfunction of vision, speech and hearing, as well as impaired memory, attention and the appearance of confused thoughts.
How to recognize the disease?
The manifestation of symptoms depends on the location of the tumor. The vascular tumor appears in the upper cerebral areas in 80% of patients, in the cerebellum - in 8%, and the rest is observed in the spinal cord.
Symptoms depending on the location of the tumor:
- The temporal fraction of is hearing and speech dysfunction. The patient does not recognize the voices of friends.
- Frontal lobe of - memory deteriorates, patient is unable to perform small movements, and handwriting also changes. Possible periodic apathy and depression, or, conversely, inadequacy and euphoria. Speech worsens( vocabulary depletion or excessive talkativeness may occur).
- The dark area of the is an intelligence disorder.
- Cerebellum - unstable gait, speech disorders and strange movements( head turns, strange postures and inclinations).
Diagnosis of
For the diagnosis of tumor processes, the following methods are used:
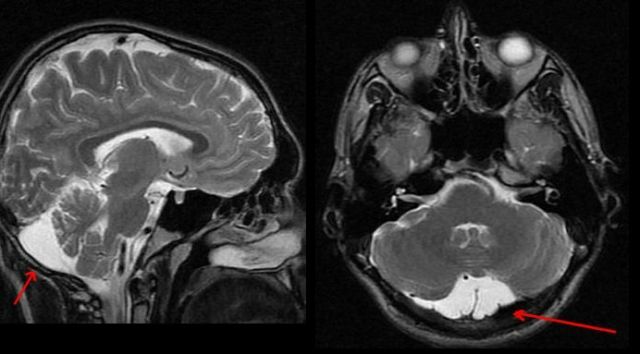
- Magnetic resonance imaging and in our time remains the gold standard and the most accurate method of diagnosis. According to
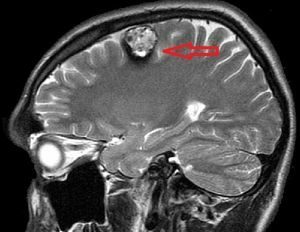 , the ratio to cavernoma of the brain MRI has 100% sensitivity and 95% specificity. In order to determine the maximum enterprise for small tumors, a regimen is prescribed that is weighted according to the degree of heterogeneity of the electromagnetic field. The application of such rules in practice gives a good result in the identification of various cavernous formations in the brain.
, the ratio to cavernoma of the brain MRI has 100% sensitivity and 95% specificity. In order to determine the maximum enterprise for small tumors, a regimen is prescribed that is weighted according to the degree of heterogeneity of the electromagnetic field. The application of such rules in practice gives a good result in the identification of various cavernous formations in the brain. - Functional Magnetic Resonance Tomography is also used before the operation of patients whose tumors are located in a significant area of the cerebral cortex. But the use of this method of diagnosis is limited, because the symptoms are distorted due to the presence of hemisiderin in the surrounding tissues.
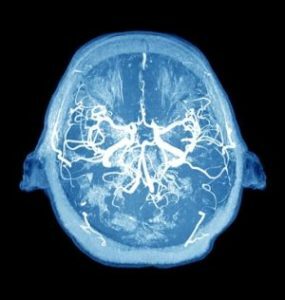
- angiography is also used, a common method for examining vessels, but it is not informative in the study of cavernous angioma. It is used in differential investigation of peripheral aneurysm and cavernoma.
- The is used for observation before surgical intervention of deep tumors, and when calculating the dose of radiation that the patient receives in stereotactic methods of surgical intervention.
- Computed tomography is a method that allows finding individual malformations that are not detected by angiography. But relying only on the results of computed tomography, to identify the exact disease is very difficult. Therefore, CT is used to detect haemorrhage from the cavernoma when there is no possibility of an MRI.
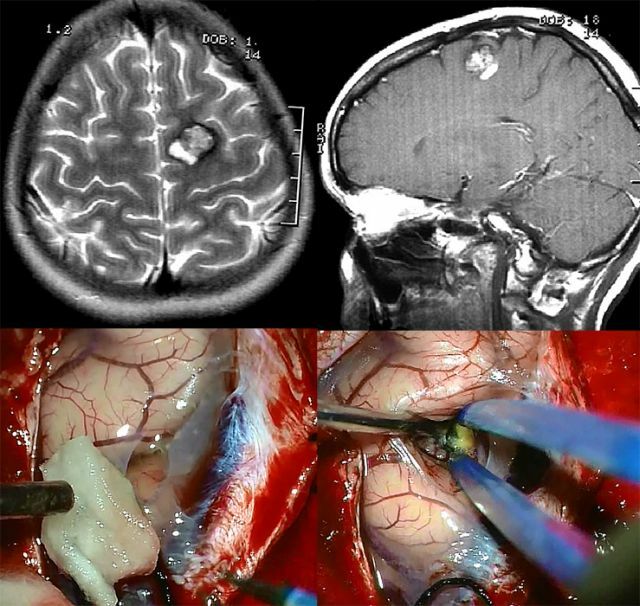
On the photo of a cavernoma on the MRI from above and its removal from below
What does modern medicine offer?
Many patients with this diagnosis are offered to remove the tumor. In this way it is possible to prevent such a complication as intracerebral bleeding.
Operative method of therapy
For the treatment of cavernoma, surgical intervention is used. The operation is most often used only if the patient has a symptom such as an epileptic seizure. Elimination of education in many patients with epileptic syndrome provides complete cure or decreases epileptic seizures.
 The result of the operation depends on how long the patient has been troubled by seizures. Patients with the least experience of disease development have a greater chance of recovery. If the disease develops for quite a long time, then a deep pathological lesion of the brain material occurs, which leads to the appearance of distant epileptogenic foci.
The result of the operation depends on how long the patient has been troubled by seizures. Patients with the least experience of disease development have a greater chance of recovery. If the disease develops for quite a long time, then a deep pathological lesion of the brain material occurs, which leads to the appearance of distant epileptogenic foci.
The tumor removal operation is individual for each patient and depends on the structure and localization of the tumor. When surgical intervention, a special microscope is used, due to which the operated area is increased several times.
In pre-and post-operative treatment, it is possible to achieve an early cure and reduce hospitalization.
Removal of cavernous angioma:
Radiosurgery is modern and effective
Also used is a method of treatment like radiosurgery. The tumor is exposed to a directed beam of radiation energy. By its results, the method is almost similar to surgical intervention, but it has fewer consequences than with surgical removal of the cavernoma.
In this case, irradiation does not have an effect on surrounding brain tissue located side by side, and does not cause side effects that are peculiar to radiation therapy.
Special Cyber-knife and Gamma-knife devices are used for the procedure. With their help, the tumor has an effect of ionizing radiation from different angles. To recognize the exact coordinates of the finding of education, make a special map of the patient's brain. For the card, the results of MRI are used.
Radiosurgery lasts for 1-5 days. The irradiation session lasts up to an hour. Although epilepsy in this case is not completely cured, this method only reduces the number of attacks.
Complementary therapies for
In the treatment of the cavernous region of the brain, modern physicians also apply the following methods:
- Laser therapy .With the help of laser exposure, tumor tissues are removed layer by layer. The advantage of this method is
 minimal risk of scarring and bleeding. Use it for superficial location of the cavernoma.
minimal risk of scarring and bleeding. Use it for superficial location of the cavernoma. - Diathermocoagulation is used in the treatment of inclined to bleeding tumors of small sizes. The tumor is removed under the influence of an electric current.
- Sclerotherapy .It is an injection into the tumor cavity of the drug of sclerosing action, as a result of its walls stick together, the vessels fall off and become empty. With this method, the tumor size decreases without surgery.
- Hormone therapy .It is used for rapid growth of the tumor, due to the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect of hormonal drugs, growth is suspended until regression. Such therapy can reduce the tumor or stop its rapid growth.
- When cryolemic treatment of , the tumor is removed by liquid nitrogen. Due to low temperatures, the tissues of the formation become frozen.
Prophylaxis and prognosis
If the diagnosis was made before complications appear( vascular rupture or hemorrhage), then the prognosis is quite favorable. Patients recover quickly and return to normal life.
With a cavernous brain, unfortunately, prevention is impossible, since the diagnosis is innate, one can only prevent the consequences.

Thanks to modern diagnostic methods, it is possible to identify the disease at an early stage of development and eliminate cavernous malformations, which prevents complications( hemorrhage and death).