 No matter what this phenomenon is called: symptoms of irritation of the meninges( meningeal symptom complex) or meningeal signs, it is always about the same process in the brain or spinal cord - the process of intoxication with the disorder of the course of biochemical reactions in the tissues of the higher structures of the nervoussystem.
No matter what this phenomenon is called: symptoms of irritation of the meninges( meningeal symptom complex) or meningeal signs, it is always about the same process in the brain or spinal cord - the process of intoxication with the disorder of the course of biochemical reactions in the tissues of the higher structures of the nervoussystem.
And it does not matter which agent the intoxication is caused by:
- the activity of its own chronic microbial infection, "dozing", but suddenly "awakened" from years of hibernation at the right time;
- "import" of some kind of supernovae virus;
- got into the blood stream a toxic chemical( technical or household) product or allergen.
For symptomatology will be approximately the same in all cases. And even in the form of mechanical pressure on the cerebral membranes with hemorrhages in this or that part of the brain, toxic products are formed from the destruction of their own tissues, leading to a disorder in the fine tuning of the nervous processes.
For the diagnosis of neurological pathology, there are many methods of research - both clinical, and instrumental and laboratory. In turn, among the clinical, there are several most reliable symptoms of irritation of the meninges, to the shine of "spent" by the centuries of medical practice.
The classic syndromes-reflexes of the symptom complex are the names of the "fathers" of medical science and neurology who first discovered them many years ago: Kernig, Brudzinsky, Gordon and others.

General principles and mechanisms
The essence of the process is that, in response to a chemical attack on the nerve structures located in the meninges, the reflex arc closes, accompanied by a muscular reaction from both the smooth muscle and the musculature of the  skeletal muscle. The answer on the part of the latter is especially strong and grossly noticeable, and therefore can not be ignored simply.
skeletal muscle. The answer on the part of the latter is especially strong and grossly noticeable, and therefore can not be ignored simply.
Against the backdrop of mandatory headaches, excessive sensitivity to sound and light, nausea and vomiting, general weakness and muscle pain, as well as fever and consciousness disorders( symptoms not absolutely necessary for meningitis) - phenomena aggravated by tapping on the skull, spine, as well as by touching the body, the opisthotonus is also inevitably formed.
This is the classic pose found and accepted by the patient to alleviate the suffering caused by edematic and inflammatory changes in the affected meninges.
Its appearance means that the time for revealing pathological reflexes has come.
Symptoms of Brudzinsky and neck stiffness
To assess the degree of rigidity of the occipital muscles, placed under the back of the patient's hand by a neurologist diagnosed, the neck of the patient is bent to reach him with the chin of the breast surface;the result of the test is estimated from the distance "traversed" the head to the specified body level.
This test may not be reliable enough for elderly people - they have stiff neck because of age, and also in children.
In addition to the rigidity of the occipital muscles, the reflex resistance exerted by the cuffed tension of the cervical and occipital muscles, attempts to bend the patient's head to the chest, the meningeal symptom complex is manifested by the syndromes of Brudzinsky.
There are four symptoms of Brudzinsky:
- Positive upper occipital symptom is manifested by flexing the lower extremities in the knee and hip joints
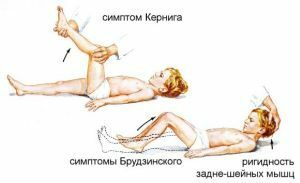 with their reduction to the body with an effort to bend the neck and tilt the patient's head forward.
with their reduction to the body with an effort to bend the neck and tilt the patient's head forward. - Brudzinsky's symptom pubis median - manifests by bringing to the trunk and flexion of both lower limbs in both the hip and knee joints when pressing on the pubic region.
- Contralateral ( literal translation: on the other hand) or the lower variant of the symptom is the reflex of flexion of the second limb when the thigh of his leg, bent by the diagnostician in the knee joint at a right angle( not to the end), is brought to the abdomen of the patient.
- With cheek variant of the symptom, pressure on the cheek under the zygomatic arch causes a reflex rise of both shoulders and folding-flexion in the elbow joints of both hands of the patient. In the variant with a tapping along the zygomatic arc, a reflex involuntary bending of the legs in the knees occurs.
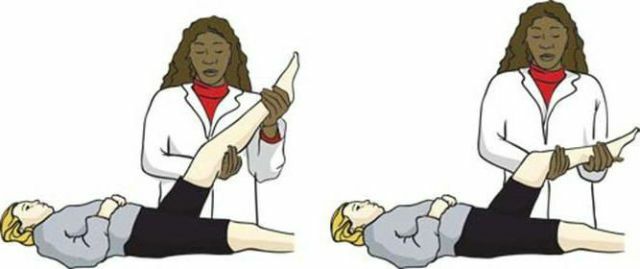
Reflexes of Kernig
Strengthening of the irritation of the meninges occurs when the symptom of Kernig is tested in two stages.
After the patient is laid on his back, in the first stage the neuropathologist explores the patient's leg at a right angle in both the hip and knee joints.
Then the patient is asked to attempt to straighten the leg in the knee, which causes a reaction of the sharp resistance of the muscles flexing the shin. Sharp exacerbation of pain in the patient is noticeable to the researcher even when the patient is in an unconscious state - in this case the second phase of the test is performed by the examining physician.
In addition to irritation of the meninges due to meningitis, the Kernig symptom can also be positive:
- with excessive intracranial pressure;
- with trauma to the skull;
- in the presence of a hematoma in the brain tissue.
Other symptoms of irritation of the meninges
If necessary, also take:
- Meningean Guillain test is a reaction in the form of an involuntary contraction of the quadriceps muscle of the femur( m. Guadriceps femoris) of the second leg, as a response to squeezing the body of the opposite leg muscle of the same name. Is pathognomonic
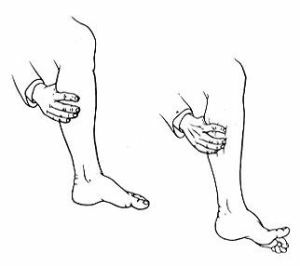 for meningitis, in a healthy person this reflex is absent.
for meningitis, in a healthy person this reflex is absent. - Diagnosis and evaluation of of Gordon's symptom , manifested by extensor-or back flexion-extension of the large( I) toe when the examining physician of the muscles of the shin of the patient is diagnosed and valuable.
- In addition to reflex muscle - flexor and extensor reactions, strengthening painful painful sensations when the patient is in consciousness is achieved by pressing the Kerer points on .When the meningeal state is of diagnostic significance, there are both trigeminal points( according to the names of outlets under the skin of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, these are respectively supraorbital, infraorbital and mental), and the occipital ones are occipital. In case of massive, bilateral diffuse damage to the meninges, the pain will be intensified by pressing on the indicated points on both sides of the body, with a one-sided one on only one side of the body.
Other "milestones" on the way to the diagnosis
In addition to the classic signs, there are other signs of symptoms of irritated meninges, such as:
- Lobzin test - pain enhancement when exerting pressure on the wall of the external auditory canal;
- phenomenon of Flatau - when the head is tilted forward, the pupil's pupils widen;
- Bekhterev's test : with a percussion of the zygomatic arch, the headache intensifies and a reflex reduction of the facial muscles occurs;
- Pulatsky, or craniophacial reflex - the appearance of grimaces of pain even with the most gentle percussion of the skull.
As for the children, the most revealing are:
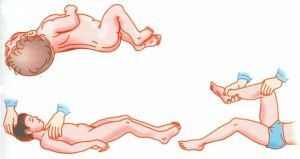
- symptom of Lesage ( or suspension symptom) - a child with a meningitis, lifted by the armpits, pulls the legs to the abdomen, holding them in this position until it is lowered;
- is a symptom called "the sound of a cracked pot" , which occurs when percussion of a large fontanel in infants, as well as its painful tension and unjust swelling.

One symptom is always not enough
Despite the "iron" reliability of the above signs - meningeal signs, it is not necessary to be guided by the diagnosis, because incorrect diagnosis leads to mistakes in the tactics of patient management.
Only a specialist - neuropathologist - can confirm or reject the diagnosis on the basis of analysis of the data of the complex of studies carried out.