 The nervous system has been a mystery to the medical profession for many centuries. People slowly approached the understanding of terms known to us, such as: axon, dendrite, reflex, nervous impulse.
The nervous system has been a mystery to the medical profession for many centuries. People slowly approached the understanding of terms known to us, such as: axon, dendrite, reflex, nervous impulse.
However, in any area there are people who actually "turned" everything from head to foot and made a very significant contribution to the development of this or that branch of medicine.
Such a scientist was Academician Pavlov, who explained the physiology of human reflexes, thereby giving the world the opportunity to take a fresh look at the familiar things.
Thanks to his discovery, neurology and psychiatry began to develop actively, and outstanding scientists, such as Oppenheim, further developed this branch of medicine.
Pathological reflexes in neurology
Oppenheim's symptom is a pathological reflex in neurology. This means that a healthy person, given a symptom, does not have 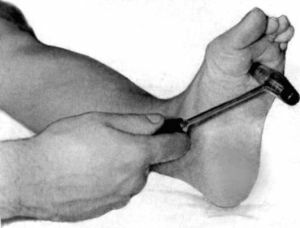 .
.
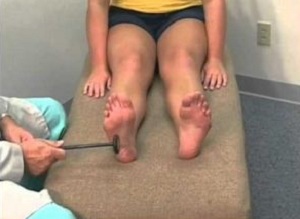
To check it it is necessary to push the thumb of the thumb on the tibia from below upwards, after which the big toe will begin to contract and stretch upward. This symptom recalls the Babinsky reflex( it is caused by stroking the back surface of the foot, after which exactly the same phenomenon occurs).
In neurology, all pathological reflexes are examined in pairs, for example, the symptoms of Babinsky and Oppenheim. There are many other symptoms( Hirschberg, Poussep, Gordon, Zhukovsky), but in practice all these symptoms are rarely checked by a neurologist, it is enough to check a maximum of three.
What does the Oppenheim symptom indicate?
The pathological reflex of Oppenheim is associated with a violation in the vasomotor cortex of the cerebral hemispheres( precentral, central gyrus) and indicates a violation of the efferent conduction of the nerve impulse, from the nerve trunks to the organ-reflectors.
Often, the Oppenheim symptom occurs when a violation in the extrapyramidal system. Based on this, we can assume an initial neurodegenerative dementia.
This makes it possible to begin treatment as soon as possible and to "keep" the disease at the initial stage. Most often, such a disease is Parkinson's disease, which causes damage to efferent innervation, up to the paralysis of skeletal muscles, and then the cardiac and diaphragmatic muscles.
It is important to know that Parkinson progresses and affects the motor nuclei from the bottom up.
What does the symptom mean at the physiological level?
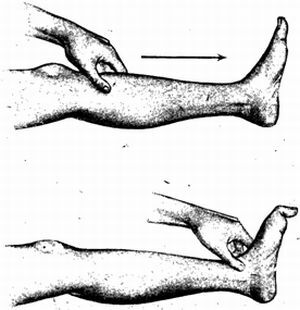
Response to the Oppenheim symptom in a healthy person. ..
This simple symptom indicates irreversible changes in efferent innervation. And this phenomenon manifests itself in this way, because when you press your finger on the tibia, the signal is perceived by the sensory receptors that give signals to the brain, but first they pass through the hindbones of the spinal cord and only then along the ascending paths to the motor neuron portion of the brain.
"Focus" is that during the passage of a nerve impulse, due to neuronal degeneration, the body must respond.
Since the neurons of the extrapyramidal system are affected by the efferent signal from the brain, it can not completely pass to the organ of the performer, therefore the spinal reflex is included in the work, which consists in the extension of the big toe.
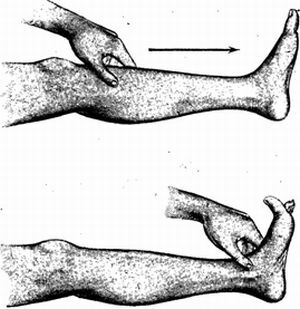
. .. and pathological reflex
There is another version of the pathophysiology of Oppenheim's symptom. It consists in the following: since the nerve cells of the extrapyramidal system synthesize dopamine( a neurotransmitter involved in conducting a nerve impulse between neurons), then with neuronal dementia, the necessary amount of its synthesis simply does not occur.
Accordingly, the signal of motion from the central nervous system is impossible, and the work includes "ancient" spinal reflexes of a person, which normally do not manifest.
Oppenheim's symptom is actively used in differential diagnosis of lesions of the vasomotor regions of the brain. Due to its simplicity and general availability, any neurologist is given the opportunity to "move in the right direction" on the way to establishing the correct diagnosis.



