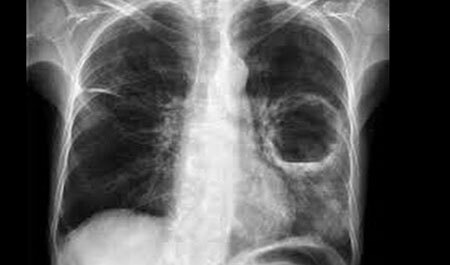
The disease is classified as a systemic lesion. The second name is "Schauman's disease - Bénier-Beck" or simply "Beck's disease".
In sarcoidosis, specific granulomas are formed in the lung tissue, and the disease itself can occur with the defeat of a variety of internal organs - but the defeat of the bronchopulmonary system accounts for more than 90% of all cases of primary sarcoidosis.
Contents of
- 1 Sarcoidosis of the lungs - what is it?
- 1.1 Causes
- 2 forms and mechanisms of sarcoidosis development
- 2.1 stages of the disease
- 2.2 process activity
- 3 Symptoms and signs of pulmonary sarcoidosis
- 4 diagnosis of lung sarcoidosis
- 5 Treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis
- 5.1 Complications pulmonary sarcoidosis
- 5.2 Diet and eating habits
- 6 Preventionsarcoidosis of the lungs
- 7 Classification according to the ICD 10
Sarcoidosis of the lungs - what is it?
Sarcoidosis of the lungs - what is it?
The disease is based on granulomatous inflammation, which is manifested by the formation of a number of nodules in the lungs. These granulomas can be considered superficially for the manifestation of pulmonary tuberculosis, and usually, patients are first suspected of having pulmonary tuberculosis.
Sarcoidosis is an absolutely contagious disease.
Characteristically, sarcoidosis manifests itself at a young age, from 25 to 45 years, and its prevalence in females is higher than that of men. Nodules with sarcoidosis are characterized by a tendency to merge, which leads to the formation of large foci, and often changes the radiographic picture of the disease.
Separate and rarely located nodules do not cause any symptoms, and such a latent flow can only be detected by radiography of the lungs.
Sarcoid granuloma can spontaneously "resolve", but more often it results in fibrosis, which is the replacement of granulomas with scar tissue. It also disrupts the lungs.
In addition to lung damage, sarcoidosis of the skin, liver, spleen and eyes is possible. In more rare cases, affected bones, joints, heart, kidneys and even salivary glands. Therefore, sarcoidosis can occur in any organ and tissue, except for the teeth.
Causes of
 Beck's disease has an unclear origin, as doctors say - "cryptogenic nature" and "unclear etiology."There is no firmly established reason for its development.
Beck's disease has an unclear origin, as doctors say - "cryptogenic nature" and "unclear etiology."There is no firmly established reason for its development.
Many researchers tend to the autoimmune theory, the influence of microbes and viruses. Some associate the occurrence of sarcoidosis with the destruction of lung tissue in persons of certain professions: pharmacists, workers in chemical industries and other kinds of activities.
Forms and mechanism of development of sarcoidosis
Unclear reasons led to the fact that the cause of the disease should be considered a complex of different factors that triggers the process of granulomatous inflammation.
The first symptoms of Beck's disease are the defeat of respiratory acini with the development of alveolitis, as well as peribronchitis. Then hypoventilation develops, and the disease begins to manifest itself as a characteristic clinical picture.
Sarcoidosis of the lung has several forms:
- lesion of the intrathoracic lymph nodes;
- lesion of alveolar tissue - sarcoidosis of the lung itself;
- mixed form, in which both alveoli and lymph nodes are affected;
- generalized form, in which other organs, for example, skin or liver, are affected in addition to the bronchopulmonary system.
The two most common forms of damage to the bronchopulmonary system are most common.
Stages of the disease
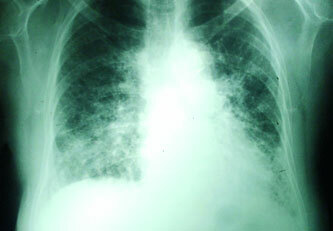
There are three stages of lung sarcoidosis, which can be called "degrees".
Their names are rather arbitrary:
- At the first stage, only the lymph nodes are affected, and the lung tissue is not affected.
- Sarcoidosis 2 degrees of the lung already, except the lymph nodes, affects the lung tissue. At this stage, there may already be symptoms that indicate the development of respiratory failure;
- The third stage is characterized by pronounced pneumosclerosis or pneumofibrosis of a significant proportion of lung tissue, due to the granulomatous outcome in scar tissue, as well as the appearance of discharge foci from both sides.
Activity of the process
There may be three types of sarcoidosis along the way, however, like any chronic disease:
- active phase or exacerbation phase - new outbreaks are characteristic;
- phase of process stabilization;
- the phase of regress of inflammation. The most favorable outcome is the complete dissolution of granulomas. Other forms - fibrosis, as well as the formation of calcinates.
In addition, the rate of development of the disease is important - it can have an erased or delayed pattern, a fast or slow progressing variant of the development of inflammation.
Symptoms and signs of lung sarcoidosis
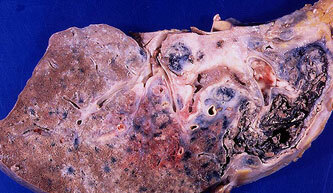
Signs of lung sarcoidosis are nonspecific. This means that instead of granulomatous inflammation, there could have been any process-the character of the disturbances caused only by the fact that the nodes "interfere" with the work of the lungs by the fact of their presence.
It is impossible to diagnose Bek's disease by symptoms alone, since they can be interpreted too broadly:
- lethargy, weakness;
- reduced performance;
- causeless weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- night sweats;
- subfebrile fever;
- disturbances of falling asleep.
As can be seen from the list - these symptoms are characteristic of a large group of various diseases, from myocarditis to HIV infection.
With significant development of the process, there are symptoms that speak of the defeat of the bronchopulmonary system:
- the appearance of cough and various rales;
- occurrence of dyspnea;
- appearance of joint pain;
- periodic chest pain and feeling of squeezing or foreign body behind the sternum.
As a rule, these are the symptoms that cause the doctor to send the patient to a radiological examination, where "suspicious shadows" are found.
But there is also a completely asymptomatic course of sarcoidosis of the lungs, especially in the early stages or in the case of isolated lesion of one group of lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of lung sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis of the lungs and intrathoracic lymph nodes refers to diseases that can be exposed immediately following an X-ray examination, but require continued confirmation.
The decisive "point" in the diagnosis allows you to put a biopsy of the lungs.
The main "reference points" of diagnostics are:
- detection of the inflammatory process in the blood;
- change in the number of γ-globulins;
- characteristic radiographic pattern in lung examination;
- biopsy, performed, as a rule, during bronchoscopy.
The histological picture shows epithelioid granulomatous inflammation.
Therefore, those who think that lung sarcoidosis is cancer, are mistaken. No tumor cells are detected in Beck's disease.
Treatment of
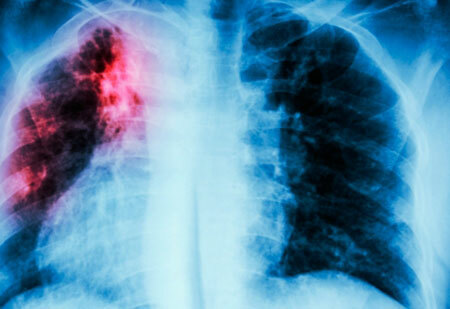
sarcoidosis Most often, after the diagnosis is established, the patient is simply observed, as spontaneous remissions are possible. Prescribe treatment only in severe cases, as well as with significant progression of the disease.
Because sarcoidosis of the lungs is similar to tuberculosis, therapeutics of this disease are dealt with by doctors - phthisiatricians and rheumatologists.
The main drugs that are shown in this disease are corticosteroid hormones, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect( indomethacin).
In resistant cases, cytostatics and immunosuppressants are prescribed.
Since all these drugs have a harmful effect on the stomach, during treatment it is necessary to take drugs - blockers of the proton pump to prevent ulceration, for example, omeprazole.
With a favorable outcome of treatment, the patient after two to three years is removed from the dispensary.
Complications of
sarcoidosis of lungs Contrary to rumors, lung sarcoidosis does not translate into cancer, but the inflammatory process can be complicated by the following conditions:
- development of chronic respiratory failure;
- appearance of "pulmonary heart" in connection with stagnant phenomena in a small circle of blood circulation;
- because the development of inflammation weakens the immune system, sarcoidosis can be the cause of tuberculosis adherence;
- marked outcome in fibrosis can significantly reduce the lung area, this phenomenon is called "honeycomb".This condition is manifested by the appearance in the lung tissue of small cavities, which are manifested by respiratory failure.
You should quit smoking when treating sarcoidosis.
Diet and nutrition features of
Beck's disease refers to those conditions in which the concentration of calcium ions in the peripheral blood increases. Therefore, the risk of stone formation in the kidneys, the bladder may increase.
It is necessary to refrain from those products that contain calcium - for example, from milk and cheese. In the rest, the food should be full and easily digestible.
Prevention of sarcoidosis of the lungs
 Because the causes of the disease are not clear, it is impossible to "aim for prevention".
Because the causes of the disease are not clear, it is impossible to "aim for prevention".
As the groups of occupations that are more prone to developing the disease are known - the main instrument is the annual conduct of fluorography, spirography and timely visit to the doctor at the appearance of incomprehensible and "insignificant" symptoms described above.
Compliance with occupational health standards and the use of personal respiratory protection are important.
Hardening, swimming, increasing the body's immunity, timely intake of vitamins - all this increases the chances that a person will not get sick with sarcoidosis.
Classification by ICD 10
According to the existing classification of diseases, 10 revision, sarcoidosis of the lung( ICD 10) is coded as D 86.
The section to which it was placed is called "individual disorders affecting the autoimmune mechanism."This is evidence of confusion, due to the uncertainty of the causes of the onset of the disease.