 Violation of muscle tone of a neurological nature is called torsion dystonia. This disease can develop with violations and lesions of the brain nuclei.
Violation of muscle tone of a neurological nature is called torsion dystonia. This disease can develop with violations and lesions of the brain nuclei.
Under the influence of certain factors, the brain ceases to function normally, because of which involuntary and unconscious contractions of muscle groups can occur, while the person is forced to unconsciously assume a certain posture.
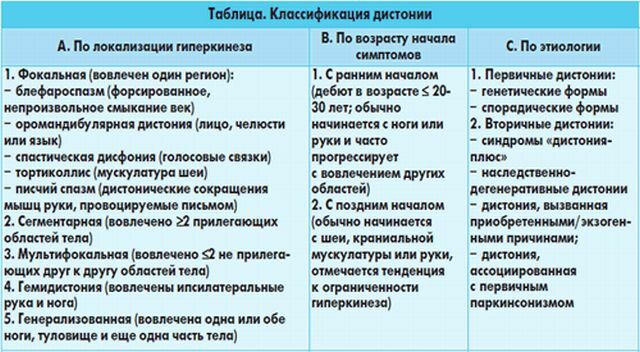
Torsional dystonia is a rare disease, with 3 people per 100 people. Most often this disease has a beginning at a young age of up to 20 years. With the process of growing up, the disease can progress, moving from one stage to another.
Varieties of violation of
Torsion dystonia is characterized by uneven muscle tone of body parts, and often there are rotational movements. The disease most often manifests itself in the form of spasms of individual muscle groups - a focal form.
With this form, involuntary closing of the eyelids occurs due to the stress of the circular muscle of the eye. Also there is a contraction of the muscles, cheeks, mouth and tongue, swallowing is difficult, in some cases with spastic dystonia the patient can not talk.
Torsional dystonia, depending on the manifestations, is divided into 2 types:
- Symptomatic etiology of is a consequence of diseases or brain damage( cerebral tumors, cerebral palsy,
 encephalitis, with craniocerebral trauma).
encephalitis, with craniocerebral trauma). - Hereditary etiology of - is transmitted by hereditary pathway. Transmission can be carried out in different ways. In some people, the disease is transmitted by a dominant type( the disease can be traced in 2-3 generations), others are recessive( the disease is traced in 4-5 generations, and there are cases when the parents had a relationship).
Also the disease is divided into the following types depending on the extent of the lesion:
- Local .Not all groups of muscles are affected, but some( spasm of writing, buccal or facial dystonia, blepharospasm).When the muscles of the neck are affected, spasmodic torticollis occurs.
- Segmental .There are spasms of several adjacent muscle groups.
- Generalized .With such a violation, the muscles of the pelvis, back, trunk and extremities are affected.
Causes of the disease
No clear answers have yet been received as to why this disease occurs. Only types and types of torsion dystonia were studied.
Autosomal dominant type often manifests itself in a more mature age, with the course of the disease has an easy degree. The main triggers of torsion dystonia include:
- heredity;
- diseases of the central nervous system of inflammatory etiology;
- giardiasis, toxoplasmosis;
- disruption of cerebral vessels;
- cerebral dystrophy;
- intoxication;
- tumor;
- postpartum trauma;
- cerebral palsy.
In the case of a disorder in the metabolism of dopamine, dystonia may also develop. When diagnosing patients, very often dopamine rates are increased.
Clinic and symptoms of the disease
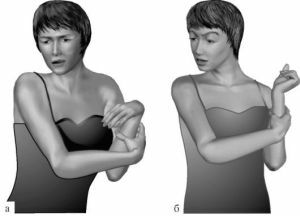 Usually, the disease manifests itself at a young age, progression is slow. The autosomal recessive form of dystonia begins to manifest earlier and stronger than in the autosomal dominant form.
Usually, the disease manifests itself at a young age, progression is slow. The autosomal recessive form of dystonia begins to manifest earlier and stronger than in the autosomal dominant form.
The very first signs are expressed in arbitrary movements of the upper or lower limbs - this gives the walk awkwardness. Involuntary movements are amplified when trying to change positions, express emotions, walking or any other movements.
The main symptoms of torsion dystonia are:
- involuntary movements of hands and feet;
- with involuntary movements there are sharp movements of the neck;
- with further development of the gait becomes swaying;
- involuntary spasms and increased muscle tone of the neck, arms and legs, head, pelvis;
- extension of the body, cramps;
- shake;
- writing spasm - contractions of the muscles of the hands during writing;
- tonic spasms;
- circular movements of the trunk around the axis;
- fixed involuntary body postures;
- hyperkinesis.
By the nature of the spread of hyperkinesis, the generalized and local form is distinguished. The most common form is local. It manifests itself in the form of involuntary contractions of the muscles of the neck, upper and lower extremities, while in each of them there can be contractions separately, which gives the patient movements pretentiousness.
Often when a local form can go to a generalized form. Develops hyperkinesis of the trunk, which with time only worsens, manifesting more pronounced.
This process leads to a curvature of the spine: the patient can unnaturally re-unravel in the zone of the waist and thoracic region. Also can mark spasms of the neck, limbs and face, speech is broken. Increased hyperkinesis can be replaced by a moderate or even normal condition.
In some cases, during movement, the patient may freeze, even in the most uncomfortable position. Sometimes there is a condition in which the patient can not service himself. But over time, the patient becomes accustomed, he adapts to such muscle disorders: they begin to control involuntary movements and even perform more complex ones: running, dancing and other.
During sleep, in prone position or simply with distraction of attention, the patient has hyperkinesis significantly reduced or stopped.

In later stages of the disease, joint deformity, rigidity of the tongue, trunk and muscles of the face, pharynx can develop - which leads to swallowing, chewing and respiratory disorders.
Diagnosis of
When seeking help from a doctor, the first thing he pays attention to: the rigidity of the muscle groups at which reflexivity, decreased sensitivity and muscle strength, and decreased intelligence can be observed.
The diagnosis is based on a clinical picture and if there were people with the same disease in the family, there is no doubt. The main methods of diagnosing torsion dystonia include:
- electromyography - reveals muscle activity disorders;
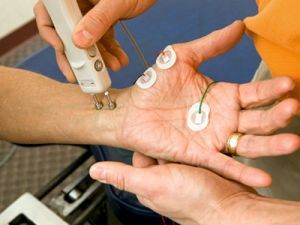
- MRI - allows you to detect damaged areas;
- X-ray examination;
- electroneuromyography - reveals abnormalities in muscle and nerve activity;
- electroencephalogram - reveals a violation of brain activity.
Timely diagnosis will allow you to quickly diagnose correctly and begin adequate treatment.
Therapy Methods
Treatment of torsion dystonia involves a conservative and surgical direction. In addition, a course of curative gymnastics and hydrotherapy are prescribed.
Conservative treatment includes drugs of different action:
- neuroleptics;
- tranquilizers;
- vitamin therapy;
- adrenoblockers;
- preparations of anticonvulsant action;
- anticholinergics, etc.
 In case the medication did not help, a surgical procedure is prescribed. The exception is if the patient has severe internal diseases, as well as blood diseases. In later stages, these diseases do not refer to contraindications.
In case the medication did not help, a surgical procedure is prescribed. The exception is if the patient has severe internal diseases, as well as blood diseases. In later stages, these diseases do not refer to contraindications.
In the late stages of development of torsion dystonia - the prognosis is not comforting, since often such patients die from intercurrent illnesses. After surgical treatment, muscular dystrophy and hyperkinesia decrease or even disappear.
With timely and adequate treatment, patients are partially restored: they can walk, perform the necessary actions and serve themselves. In 70% of cases after the operation in patients, improvement is noted.
In the event of secondary torsion dystonia, surgical treatment gives a positive result, while regress of hyperkinesia and spasms is observed.
After medical or surgical treatment, the patient should always follow the drug support. Relatives of such a patient should be under observation. Parents who have a child with a child's dystonia are advised to refuse further childbearing.