Fracture of the skull base - trauma, which is a fracture of the bones of the , which form the base of the cerebral part of the skull.
Damage is classified as severe due to the fact that the main parts of the brain, trunk, nerves are affected and inflammatory complications can occur.
Cases of this fracture occupy up to 50% of the total list of craniocerebral injuries.
Contents
- What happens with a fracture
- Classification of skull fractures
- Symptoms and signs
- First aid
- Treatment procedures
- Conservative treatment methods
- Surgery
- Consequences and survival of
- This is important to understand
What happens when a fracture of the base of the skull is observed rupture of a solidshell of the brain , as a result, a message is formed with the environment through the mouth, nose, ear, eye socket or sinuses of the nose. These processes cause the appearance of an ear, nasal flow of spinal fluid and pneumocerephaly of a traumatic property.
Communication with the environment provokes the entry of microbes, which are the cause of infections of intracranial structures.
Fractures of the anterior fossa of the skull are characterized by the appearance of a hemorrhage in the circumorbital part of the and under the conjunctiva, nosebleeds and nasal flow of the spinal fluid. In some cases, subcutaneous emphysema may appear.
The nasal rhinorrhea is defined as the flow of spinal fluid through the nasal passages of the nose. This process occurs when the perforated plate of the bone is damaged.
Subcutaneous emphysema is caused by the penetration of air into the cellulose when the parts of the trefoil are destroyed.
This fracture is characterized by a lesion of the olfactory or optic nerve, traumas of other parts of the brain.
 Than the closed cranial cerebral trauma is fraught with consequences and complications after a head injury.
Than the closed cranial cerebral trauma is fraught with consequences and complications after a head injury.
Sensory peripheral neuropathy - methods of treatment and methods of disease prevention. What you need to know about the disease.
Classification of skull fractures
Skull fractures are open and closed. is divided into:
- Linear - damage in the form of fine lines that do not cause bone displacements and rarely require urgent measures. These types of injuries are the most harmless.
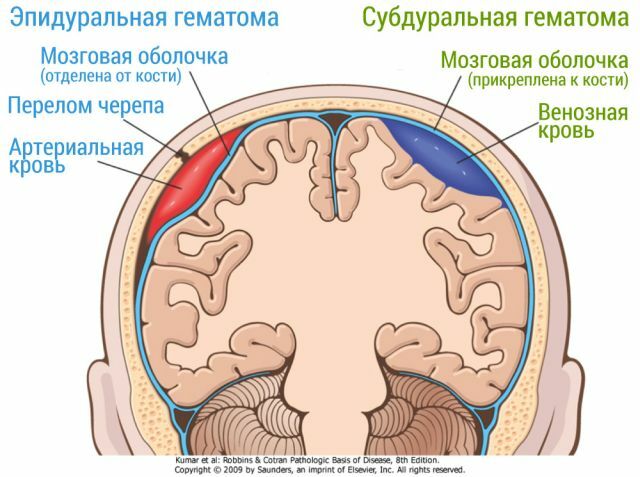
- Fragmented - lesions in the form of fragments. They can affect the hard shell of the brain, its substance and blood vessels, which can cause the formation of hematomas, as well as bruises and crushing of the brain. There may be bone mobility. Disturbances in the junction of the sinuses with the occipital injuries of the occipital bone are often incompatible with life.
- Depressed - injuries with bone insertion inside the skull box. Depressed lesions can affect the dura mater. Damage is severe if the internal structures are squeezed.
- Perforated - holes are often seen in gunshot wounds, are the most severe and deadly, because the bullet usually penetrates deep into the brain or rifle with significant destruction.
Symptoms and signs
The most vulnerable part of the skull base is the front, so here is the injury line. The assisting person should check the patient's eyes, nose and ears.
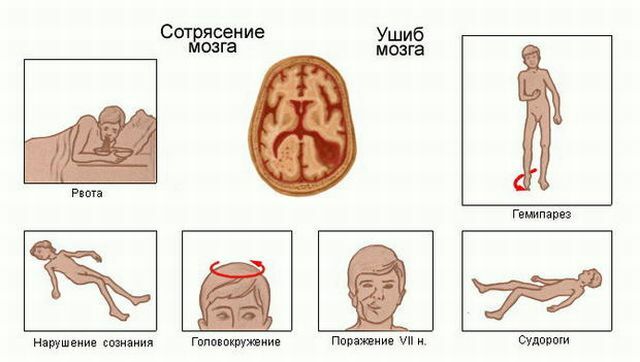
Fracture of the base of the skull usually accompanies such symptoms:
- Memory loss. Depending on the degree of shaking, a person may not remember what happened before what happened.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Dizziness.
- Darkening of consciousness or absolute loss of memory.
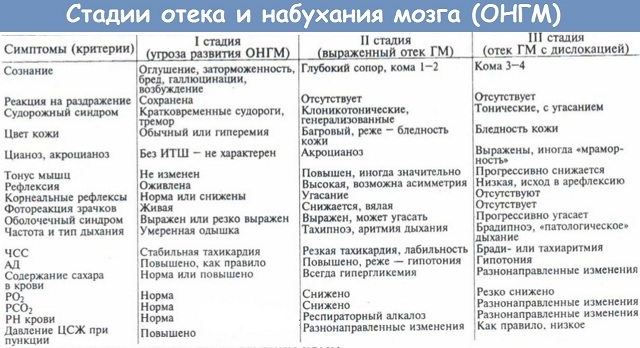
- In case of cerebral hemorrhage and compression, intracranial pressure may increase, and the pulse may slow down.
- Pupils dilated unevenly, their response to light differs.
- In some cases, manifestations of paralysis of the limbs may also appear.
- If the vessels are broken, the person starts bleeding from the nose, mouth and ears.
- In case of dysmotility, cerebrospinal fluid may leak.
The main sign of skull damage is bruising around the eyes. But this manifestation occurs after the time of trauma. Hemorrhages appear behind the ears. In this injury, there is a risk of breathing problems. Therefore, should monitor the vital functions of the affected to the person who provides assistance. With severe bleeding, a person may have a shock.
First aid
For fractures of the vault and the base of the skull, a person is placed on a stretcher on his back. The head wound is bandaged with an antiseptic dressing.
In the absence of consciousness, the patient is placed on his back in a semi-recess , for which a roller is placed under one side of the body. The head rotates to the side so that when vomiting the mass does not reach the respiratory system.
Shattering clothing is unfastened, glasses or dentures are removed.
In case of breathing problems, should be used for artificial respiration. Then cardiac drugs are injected.
Do not inject narcotic analgesics, as this can exacerbate breathing disorders. In acute respiratory disturbance, the mouth of the patient is released from the vomit, the lower jaw is pushed forward and an artificial respiration is made by the AND device through the mask.
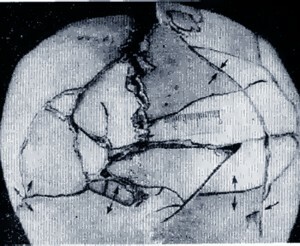
In the photo, a fractured skull fracture
The vein is injected with 20 ml of glucose, the lasix is 40 mg .If there is severe bleeding and low blood pressure, the lasix is not applied, in such cases, gelatin is overflowed intravenously.
With motor excitement, 1 ml of suprastin is injected into the muscle. Subdermally, the cordiamine is also administered.
When the patient is hospitalized, ice is applied to his head.
If there is no serious violation of breathing, then give dimedrol, furosemide. When open wounds are prescribed antimicrobial agents( penicillin), a wound dressing is performed.
Treatment procedures
In the treatment of fracture of the base of the skull, great importance is attached to the prevention of purulent complications.
For this antibiotics are applied, treatment of the middle ear and nasopharynx is carried out by instillation of antibiotics in them. The patient is examined by a neurologist, otolaryngologist, oculist.
Conservative treatment methods
Conservative treatment methods are used for relatively light injuries of the skull, middle ear, and paranasal sinuses, when one can hope for the withdrawal of cerebrospinal fluid without surgery.
Treatment begins with bed rest, raising the head above the body line. This is conducive to reducing the outflow of the spinal fluid.
The treatment complex also includes excretion of excess fluid, repeated lumbar punctures 24 hours later, with a withdrawal of 30 ml of CSF, as well as subarachnoid insufflation with 30 ml of air or oxygen.
Among decongestants, preference is given to diacarp;it reduces the production of liquor. In his absence, lasix or other diuretics are used.
If purulent complications do occur, then the introduction of antibacterial agents is combined with endolumbic. For endolumbal administration, kanamycin, levomycetin, monomycin are used. The best option for selecting a medicine is to study the flora of the spinal fluid or a smear from the nasal mucosa.
Surgery
Operative treatment of fractures is performed with multi-lobed lesions of the anterior parts of the skull, the walls of the paranasal sinuses, the base of the anterior fossa, the impressed lesions that extend to the walls of the parabasal sinuses, the parts of the temple bone.
Surgical methods of are also used for compression of the brain under the influence of increasing pneumo-cephaly, with nasal liquorrhea not subject to drug treatment and recurrences of complications of a purulent property.
Consequences and Survival of
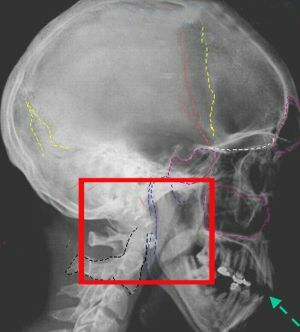
In the photo, a dangerous fracture of the skull base
The quality of life of patients depends on the severity and nature of the injury, the concomitant disorder and possible infection of the pia mater.
If fractures without displacement of , which do not need surgery, are observed, in the absence of purulent processes, the consequences of fracture of the base of the skull will not be catastrophic and the patient will be able to fully recover.
If presents infectious complications, there may be encephalopathy, uncontrolled pressure build-up, headaches with epileptic seizures.
With less blood loss, cephalomatomas, intracerebral hematomas and encephalopathy may occur during the recovery period.
The benefit of the outcome for fracture of the base of the skull in such conditions is observed with timely and competent treatment.
Fracture of the base of the skull is often the cause of severe bleeding, they can be so plentiful that survival in the first hours after injury can be minimal, at best a comatose state occurs, the prognosis is also very negative. With severe bleeding immediately and within the first 24 hours after the lesion, there is a high risk of death, but if the patient survives, then for the most part he can remain a deeply disabled person for life.
Therefore, it is important that immediately contact the and follow all the prescribing doctor's instructions.
This is important to understand
Skull base fracture is severe lesion, having received which a person can die in the first hours or days. In case the patient is alive, he can often become disabled.
Therefore, it is necessary to comply with all safety rules that will protect against damage.
The possibility of complications and unfortunate consequences can be reduced if appropriate measures are taken in time, diagnose correctly and start treatment very quickly.
It is also important to follow the appointment of a treating specialist.such actions give the chance to hope for risk reduction and a positive outcome.
 Than the closed cranial cerebral trauma is fraught with consequences and complications after a head injury.
Than the closed cranial cerebral trauma is fraught with consequences and complications after a head injury.
Sensory peripheral neuropathy - methods of treatment and methods of disease prevention. What you need to know about the disease.

In the photo, a fractured skull fracture

In the photo, a dangerous fracture of the skull base