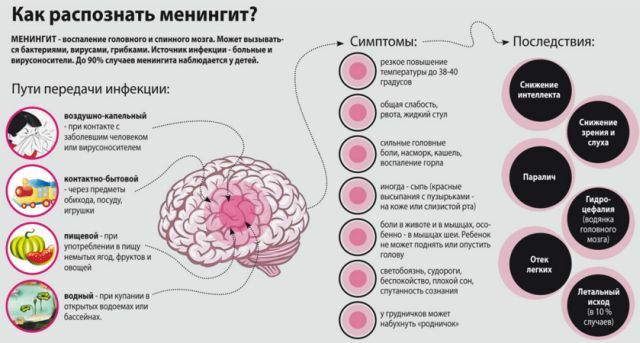
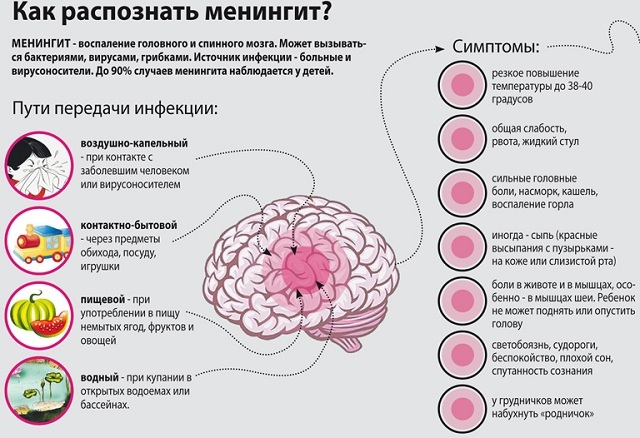
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges. To provoke the disease can drugs, viruses, fungi, bacteria, injuries, other diseases.
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges. To provoke the disease can drugs, viruses, fungi, bacteria, injuries, other diseases.
There are primary and secondary meningitis, the primary develops as an independent disease and is almost always contagious. Secondary is a complication of other diseases and in most cases is not transmitted from person to person.
In addition, depending on the pathogen, meningitis happens:
- bacterial;
- is tubercular;
- parasitic, protozoal or amoebic;
- is viral or aseptic;
- reactive;
- fungus;
- is non-infectious.
Bacterial form of the disease
Bacterial meningitis is most severe and dangerous for its complications, this kind of infection is always contagious and transmitted by airborne droplets.
The causative agent of the disease is most often:
- streptococci;
- meningococci;
- pneumococci;
- E. coli;
- Haemophilus influenzae;
- Klebsiella;
- Listeria.
The following categories of citizens are at risk:
- small children , they have an infection more often than adults;
- patients suffering from chronic alcoholism ;
- patients with immunocompromised , as well as those who underwent neurosurgical intervention or surgery on the abdominal cavity;
- persons whose professional activities are associated with pathogenic microorganisms , which are capable of causing bacterial meningitis;
- lovers travel , especially in African countries.
In addition, bacterial meningitis has a genetic predisposition, which is found in the Eskimos of America and the aborigines of Western India.
Viral form of the disease
Viral or aseptic meningitis is also a contagious disease. It can be caused by various viruses:
- enterovirus;
- adenoviruses;
- herpes simplex virus;
- causative agent of mumps and many others.
Depending on the pathogen causing the infection, viral meningitis is transmitted in different ways:
- Airborne or aerosol transmission .This mechanism of infection is possible if
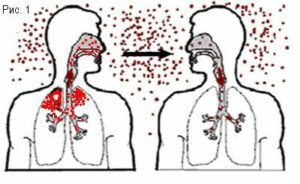 viruses are on the respiratory mucosa. During coughing and sneezing, the pathogen enters the environment and, with air flow, settles on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx of a healthy person.
viruses are on the respiratory mucosa. During coughing and sneezing, the pathogen enters the environment and, with air flow, settles on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx of a healthy person. - Contact path .If the infectious agent is on the conjunctiva of the eyes, in the mouth, on the wound surface or on the skin of the patient, it can easily get to surrounding objects, touching which a healthy person can become infected. Therefore, the probability of infection with viral meningitis increases with non-observance of personal hygiene, eating unwashed vegetables and fruits.
- Waterway .Enterovirus does not die in open water, so there may be outbreaks of infection at the height of the swimming season.
- The transmissive transmission path of the .Sometimes, viruses are spread by insects.
- Vertical pathway from mother to fetus .
Infectious meningitis can be infected by both a child and adults. But children, as well as the elderly and patients with weak immunity get sick more often, and the disease in them is more severe.
There are cases when, in contact with a patient, a healthy person can pick up a virus, but get sick, for example, with a flu that does not necessarily pass into the inflammatory process of the meninges.
Parasitic meningitis
Parasitic or amoebic meningitis is a rare but dangerous disease that usually ends in a fatal outcome.
The causative agent of infection is the Fowler Fangler, which lives:
- in freshwater reservoirs( rivers, lakes);
- in geothermal sources;
- in insufficiently chlorinated pools, and when using water heaters in them.
 The causative agent penetrates from the infected reservoir through the nose and then spreads throughout the body and reaches the brain.
The causative agent penetrates from the infected reservoir through the nose and then spreads throughout the body and reaches the brain.
Currently, there are no known factors that trigger the disease, it is established only that when the temperature of the water rises and its level decreases, the likelihood of developing amoebic meningitis increases. Therefore, it is not recommended to swim in particularly hot weather in fresh water. From person to person, the infection is not transmitted, so it is rare.
Fungal infection
Fungal meningitis can provoke:
- cryptococci;
- coccidia;
- candida.
Any person can infect a fungal infection, but the patients are especially vulnerable:
- with HIV infection and AIDS;
- taking hormonal drugs and immunosuppressants;
- receiving chemotherapy.
The causative agent from the primary focus, along with the blood, is transported to the brain, where the inflammatory process develops. Fungal meningitis is not a contagious disease, as it is not transmitted from person to person.
Non-infectious meningitis
Non-infectious meningitis, also parasitic and fungal, is not transmitted from person to person and is not contagious.
To the provocative factors are: 
- malignant neoplasms;
- head injury;
- single medicines;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- surgical operations on the brain.
Non-infectious meningitis occurs frequently. It develops in the postoperative period not only after excision of brain tumors, but also in the surgical treatment of developmental malformations and other CNS diseases.
It is proved that noninfectious meningitis occurs in all patients after removal of tumors in the head, it is an inflammatory response to surgical intervention in the central nervous system.
Summing up
It turns out that to answer the question "is it contagious meningitis?", You need to know what triggered the disease.
So the disease caused by viruses or bacteria is transmitted from person to person and is contagious.
While meningitis caused by fungi, protozoa, various herbs of the brain, oncology, surgical operations on the central nervous system, autoimmune diseases is not contagious and is not transmitted from person to person under any circumstances.
But in whatever form does meningitis occur, from this it does not become less dangerous disease.
 Therefore, it is very important to take preventive measures, which consist in observing the rules of personal hygiene, careful washing of hands, berries, vegetables and fruits, disinfection of contaminated objects, drinking only quality drinking water, bathing in specially designated water bodies, avoiding contact with sick people.
Therefore, it is very important to take preventive measures, which consist in observing the rules of personal hygiene, careful washing of hands, berries, vegetables and fruits, disinfection of contaminated objects, drinking only quality drinking water, bathing in specially designated water bodies, avoiding contact with sick people.
In addition, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, take regular vitamins and, at the slightest indisposition, visit a doctor. All this will help reduce the risk of infection and the development of a dangerous disease.