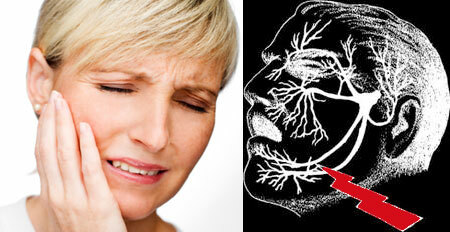
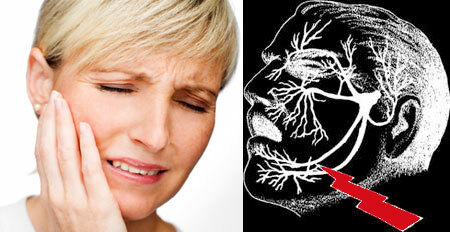
The tee nerve refers to the 5 pair of cranial nerves and has branches - the ocular, located in the region of the upper jaw and located in the region of the lower jaw. With the development of the inflammatory process in the area of this nerve, one speaks of neuralgia.
What is it?
Neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve is a disease of chronic course, in which the branches of the nerve are affected, as a result of which the patient suffers constant paroxysmal pains in the area of their innervation. With this pathology, pain occurs more often in one half of the face.
Common causes of neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve are:
- Subcooling the body;
- Foci of chronic infection in the body( carious teeth, sinusitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, frontalitis);
- Tumor formation in the brain;
- Aneurysm of cerebral blood vessels;
- Nerve transmission by the bones of the skull;
- Osteochondrosis in the cervical region;
- Head injuries;
- Herpetic infection;
- Poliomyelitis;
- Postoperative surgical interventions in the oral cavity.
People at risk are:
- Older than 45 years;
- Subject to constant stress;
- Sufferers of avitaminosis;
- Allergies;
- Persons with helminthiosis;
- Suffering disorders of the organs of the endocrine system( diabetes, hypo and hyperthyroidism).
Contents
- 1 Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
- 2 Diagnosis of neuralgia
- 3 Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
- 3.1 Forecast
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia

The main clinical symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is pain localized usually in one half of the face. The attack occurs suddenly, with the slightest irritation of the affected nerve. The patient complains of the pain of a shooting character, which is often equated with current hits.
The pain does not last long, usually not more than a few minutes. After this, there comes a period of remission, which can last up to several weeks or months, but as the disease progresses, pain occurs more often, and the intervals between them become shorter.
With neuralgia of the 1st branch of the trigeminal nerve, the pain is localized in the region of the wing of the nose, eye, eyebrows, temple, crown.
Another attack of pain provokes simple actions of the patient:
- Smile, laughter, yawning;
- Hygienic procedures and a simple touch to the face, etc.;
- Eating and mastication;
- Stay in the cold or draft.
In addition to the pain syndrome, before the effective treatment, the symptoms of neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve are the following conditions:
- Lacrimation on the part of the lesion;
- Ample transparent discharge from the nose;Reddening of lower eyelids and mucous membranes of the eyes;
- Twitching of the facial muscles - the affected half is convulsively contracted;
- Disorders of the patient's psyche - so any actions( laughter, eating, yawning, etc.) can provoke another bout of pain, the patient becomes irritable, withdrawn, refuses to eat, and is afraid to fall asleep. In addition, in severe cases, thoughts of suicide are possible;
- Disturbance of the sensitivity of a half of the face - the patient complains of numbness of the face in the area of the lesion, a feeling of crawling under the skin;
- Atrophy of the muscles of the affected half of the face - develops as a result of impaired blood flow and lymph flow. Under the influence of such changes, eyelashes, eyebrows, teeth appear on the affected half of the face, wrinkles appear, the corner of the lips rises and the eyelid descends, and the chewing capacity deteriorates.
Diagnosis of neuralgia
Diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia begins with a visit to a neurologist. The doctor examines the patient during remission and after exposure to painful points, which can be affected by an attack of pain, collects an anamnesis of life and illness, appoints additional studies:
- Electroencephalography;
- Computed tomography, MRI;
- Electroencephalography;
- Biochemistry of blood;
- Puncture of the spinal cord if necessary - with suspected meningitis;
- Consultation of the otolaryngologist, dentist, neurosurgeon.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
 Therapy of the disease is carried out in a complex manner, the main steps in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia are as follows:
Therapy of the disease is carried out in a complex manner, the main steps in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia are as follows:
- Preventing factors that can trigger the development of neuralgia;
- Normalization of the CNS - prevention of stress, reduction of hyperexcitability;
- Physiotherapy - electrophoresis, acupuncture, massage.
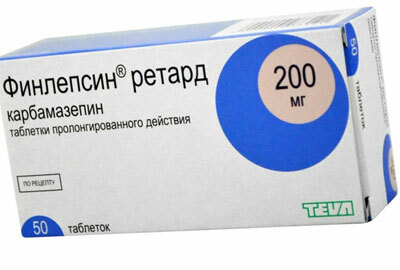
To stop an attack of trigeminal neuralgia and prevent pain in the future, the patient is prescribed Finlepsin. This medicine belongs to the group of anticonvulsants and helps to reduce the excitability of nerve fibers and inhibit the production of neurotransmitters.
This medication can be taken strictly according to the doctor's indications and in an individually indicated dosage, since the tablets have a number of serious contraindications.
In addition to finlepsin, the patient is prescribed:
- B vitamins - beneficial effect on the CNS;
- Sedatives - Valerian;
- Glycine or Glycesed - amino acids that participate in the transmission of nerve impulses;
- Antihistamines;
- Muscle relaxants;
- Antidepressants.
During a stable remission, physiotherapy and spa treatment are shown.
Operative treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
In case conservative methods of treatment are not effective, the patient is prescribed a surgical procedure. The main indications are brain tumors, the presence of narrowed sections in the nerve exit channel from the skull, pinching of the nervous branches, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
In modern surgery, an operation to eliminate trigeminal neuralgia is performed by a laser. This intervention is minimally invasive and well tolerated by the patient.
Forecast
When seeking medical help on time and correctly prescribed treatment, the prognosis of the disease is generally favorable. The implementation of simple preventive recommendations allows you to achieve a stable remission or completely get rid of the problem.
Self-medication is strictly forbidden, as this can lead to the progression of the disease and aggravation of the clinical picture of neuralgia.