Perhaps one of the most unpleasant and suddenly arising problems( and for young girls - and terrible) is the neuritis of the facial nerve. As a rule, after waking up on a sunny morning a person comes to a mirror, and understands that one half of his face does not obey.
The mouth can not whistle, the lips do not fold into the tube. When drinking water pours out from one corner of the mouth, the eye on the same side is not squeezed. .. At the same time, there is no pain or precursors of deterioration of well-being. You can imagine what a "shock" for a young girl who was going to go on a date in the evening. ..
For consolation one can say that neuritis of the facial nerve is the only disease not accompanied by pain and deterioration of well-being, in which turnout to a doctor for obvious reasons inThe first day after the detection of paralysis of the facial musculature is almost 100%.
Even with acute toothache patients can postpone the visit to the doctor for a few days, but not with neuritis of the facial nerve.
A bit of anatomy
A lot of nerves come out on the person's face, and to some extent they are all facial. But only one pair of nerves( as is known, a person possesses bilateral, or mirror symmetry) is called the facial nerve, nervus facialis. This nerve is also called the VII pair of cranial nerves.
This nerve never hurts, because it is not sensitive, it is purely motor. His task is the innervation of the whole musculature of the face, that is, he creates facial expressions and expression of human emotions."Brovki house, frowning forehead, ironic eye squint - this is the work of the facial nerve.
Blinking the eyes, pulling the lips with a tube, smiling, inflating the cheeks is also a function of the facial nerve.
This nerve helps with drinking, finally, it is indispensable for kissing.
Contents
- 1 Neuritis of the facial nerve - what is it?
- 2 Symptoms of neuritis of the facial nerve
- 2.1 Diagnosis of neuritis
- 3 Treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve
- 4 Prognosis and consequences of neuritis
Neuritis of the facial nerve - what is it?

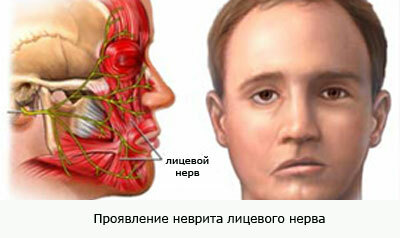
Neuritis of the facial nerve photo
As is known, medical terminology suffix "- it" assigns inflammatory diseases. Neuritis is a condition in which not only the insulating, outer membrane of the nerve fiber( myelin) suffers, but also the axial cylinder itself, through which electrical impulses pass. In this case, there are degenerative changes in the nerve fiber, which, in some cases, may be irreversible.
Then the control of the nerve over the muscles will be permanently lost, and there will be persistent residual( residual) signs in the form of paralysis and paresis( partial paralysis) of facial muscles.
On the other hand, the term "neuralgia" means pain along the nerves. There is neuralgia on the face, but in its appearance the trigeminal nerve, or V pair of cranial nerves is to blame. By mistake it is sometimes called "neuralgia of the facial nerve", although this is a completely incorrect statement.
Classification of
Neuritis of the facial nerve can be acute, subacute and chronic( downstream), and it can be one-sided( in 99% of all cases) and bilateral. Unilateral neuritis in typical localization occurs on average in 1-2 cases per 10000 population annually.
The defeat of the nerve immediately from both sides and complete paralysis of facial muscles turns the face of a person into a petrified mask. This case is very rare: a person has a much higher chance of breaking two hands at once, in two places each, than getting a bilateral paresis of the facial nerve.
Much more often there is neuritis on the one hand, and then, after a few days, the defeat on the opposite side joins.
This occurs when there is a significant drop in immunity( for example, with the transition of HIV infection to AIDS) or inappropriate treatment.
Reasons for the
Neuritis of the facial nerve: the causes of its appearance can be considered very diverse. But the leading mechanism is edema of the nerve in the narrow canal of the temporal bone, where it passes. After all, if the nerve is surrounded by fiber, then the inflammation spreads outward, and it does not suffer so much.
And in the case of a nerve in the narrow bony canals, with the development of inflammation and swelling, the nerve is subjected to a pronounced compression, which is so strong that the nerves stop passing electrical impulses - the commands to the muscles.
That's why the process develops at night: each of us knows that in the morning a person has a "sleepy" face. This means that in the waking state the head is high above the ground, and to apply blood to the head, the heart needs to be exerted with great strength.
At night, during sleep, it is much easier to accumulate water in the face and head area due to the horizontal position of the body. That's why all inflammatory swelling on the face is intensifying at night. The same applies to the structures of the cranial cavity.
For example, for the same reason, persistent head "bursting" pain in the morning is characteristic for a significant increase in intracranial pressure.
The main cause of neuritis of the facial nerve leading to swelling and impairment of its function is herpes damage, thereby, which is very similar to a chickenpox rash with chickenpox( because the pathogens are almost identical) and which appears after hypothermia, like "cold on the lips".In addition to herpes simplex virus, pathogens can be other neurotropic viruses, for example, the influenza virus.
In more rare cases, the cause may be industrial intoxication( lead, mercury, manganese, thallium).But, unfortunately, most often - this intoxication with ethyl alcohol and chronic alcoholism.
Symptoms of neuritis of the facial nerve

As a rule, at first a person suffers from a cold or trivial hypothermia, with the development of rhinitis and "snot".In the event that the herpes rashes on the lips appear frequently, the risk of nerve damage increases significantly. In addition, it can be just hypothermia, for example, when driving in a car with an open window.
After this morning, a person feels some discomfort, and approaches the mirror. As a result, it turns out that:
- There was an asymmetry of the face: the usual folds of the skin( nasolabial, folds on the forehead) on one side were smoothed out, like after Botox injection;
on the side of the lesion lost the tone of the ocular muscle of the eye( orbicularis oculi), causing the eye slit to increase, and the eyes became "different".The eye on the healthy side seems smaller; - On the patient side the lower lip is bulged;
- Since the circular muscle of the mouth, unlike the circular muscles of the eyes, is common, the mouth becomes distorted when you try to smile, grin - the mouth pulls to a healthy side;
- The eyebrow does not lift or the cheek on the side of the paresis inflates;
- You can not blink your eyes too, and through the narrow, distorted eye-slit you can see a "sunken" eye without a pupil. This "oblique" look was called lagophthalmus, or "hare's eye".This condition, especially at night, can lead to the drying out of the eyeball and the appearance of keratoconjunctivitis, with red eyes, a feeling of rezi or a feeling of "sand" in the eye. Therefore, you need to use an artificial tear;
is also impossible to whistle; - To top it all off, the mouth does not fit on the side of the mug, so when you drink, liquid pours on clothes;
- Due to the weakness and decrease in the tonus of the buccinator( buccal muscle), the cheek "sail", the food sticks between the cheek and the branch of the lower jaw. To top it all off, it's easy to bite that cheek, because it is constantly between your teeth.
Diagnosis of neuritis
Probably, the above picture did not leave anyone indifferent. It is on it and the diagnosis of paresis of the facial nerve is exposed. Naturally, this clinical picture should be isolated( that is, not accompanied by other neurological symptoms, for example, dizziness, falling, paralysis of the arm and leg, or meningeal symptoms).
A very important sign is the doctor's finding of herpetic bubble rashes in the external auditory canal( if you move the earlobe downwards and backwards) or behind the ear.
An additional fact pointing to the nature of the disease is the mention of a history of hypothermia.
Treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve is treated by a neurologist. But, given the complexity and even the inability to get to a neurologist in Russian free health care without the therapist's "sanction", as well as the lack of an opportunity to take a turn to him within the next two weeks, one must act on his own.
The best option is to go urgently to a well-known private center for a good doctor-neurologist. Do not feel sorry for a thousand rubles for a paid reception.
Treatment of this disease is complex, and consists of several stages:
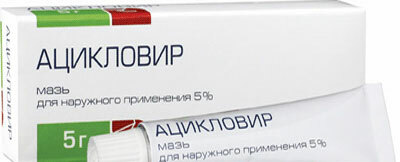
- The most important for paresis of the facial nerve is the urgent start of antiviral therapy( drugs acyclovir, famciclovir, ganciclovir, zovirax) are used in tablets according to the scheme. In addition, you can lubricate the area of the external ear canal with antiviral cream - this is the most important event to be done as quickly as possible: on the first day after the onset of symptoms, even in the first hours, possibly before a visit to the doctor.
This is perhaps one of the few self-medication cases that is forgivable, given the potential for the development of residual events. After 3 to 4 days after the onset of neuritis, the effect of antiviral therapy will be much lower, if not zero.
- To reduce edema, patients should be prescribed diuretics. It will be enough for such drugs as "Veroshpiron" or "Torasemide".Rough and old drugs, like "Lasix"( furosemide) are not used;
- It is necessary to make fixing bandages on the face from narrow strips of the patch, "pulling" the paralyzed muscles and not letting them hang;
- To reduce inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used, for example, "Xefokam", "Movalis" for several days;
- The patient should receive B vitamins, for example, as part of Milgamma Compositum, Kombilipen;
- Sometimes in the early days, hormones are also prescribed for the removal of possible edema( prednisolone);
- Alpha-lipoic acid( Berlition) has a good effect, administered intravenously or intramuscularly;
- Gymnastics with neuritis of the facial nerve is of great importance. It is clear that it is carried out for the muscles of the healthy side of the face. They need to strain and relax, you need to practice 10 to 15 minutes twice a day. Imitate mimic reactions, pronounce letters.
spend medical massage of a healthy half of face and cervical collar zone, then with transition to the sick side, but in a very gentle and delicate technique; - Already from the very beginning of the disease the patient should visit the physio-cabinet. Particularly shown UHF sessions, courses acupuncture, exposure to the magnetic field.
Prognosis and consequences of neuritis
Complete recovery after neuritis of the facial nerve, while observing the regimen and fulfilling the prescriptions occurs in 60-70% of cases. Every fifth patient can develop muscle contracture, and then, on the contrary, the face will be stretched to the sore side. Most often this condition occurs if the patient completely ignores the treatment and visits to the doctor.
There are signs that suggest a possible adverse outcome, in which improvement may not occur. It:
- Complete paralysis from the first day;
- Presence of concomitant diabetes,
- Appearance of dry eye with paralysis;
- No improvement after 21 days after the onset of the disease.
Neuritis of the facial nerve, the symptoms and treatment of which have been described above, is a disease reflecting the medical literacy of the population. Only the timely beginning of treatment, and its usefulness can lead to a cure. Therefore, do not waste time waiting for spontaneous improvement and wander in the queues of polyclinics.
To act quickly: on the first day of the onset of symptoms, all possible measures for recovery should be taken.