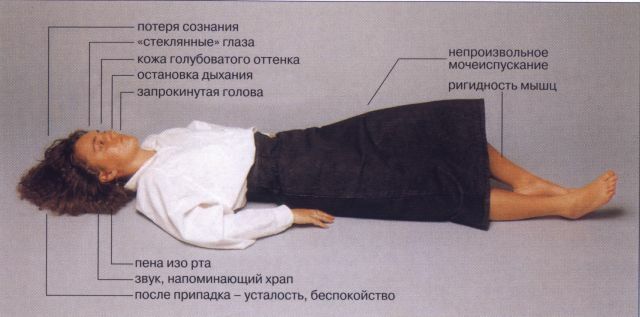
Myoclonic epilepsy is a condition characterized by a combination of epileptic seizures and chaotic jerking of the muscles.
Myoclonic epilepsy is a condition characterized by a combination of epileptic seizures and chaotic jerking of the muscles.
The name of the disease originated from the Greek.myos - "muscle" and English.clonus is a "cramp".The causes of myoclonus are considered to be degenerative changes in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum or internal organs( liver, kidneys);They are epileptic, they are pathological.
This type of epilepsy occurs in 10% of all affected by this disease, regardless of gender.
And inherited and purchased
The most common cause of the disease is a hereditary mutation in the autosomal recessive type of inheritance;cases of dominant transmission are also known.
There are other factors that can provoke myoclonus epilepsy: 
- insufficient supply of blood to the brain;
- infection, incl.intrauterine infection of the fetus;
- head trauma;
- strong nervous shock, stress;
- brain tumors;
- damage the fetal brain during pregnancy, as well as birth trauma.
In some cases, the cause can not be identified.
Another name for myoclonus is epilepsy - Yants syndrome. The main peak of the debuts of the disease falls on the pubertal period or later childhood, so the name juvenile( juvenile) myoclonic epilepsy( JME) is also common.
In children with relatives with epilepsy, the chance to inherit the juvenile form is increased, hence one more naming of myoclonic epilepsy - the family one.
No cases of direct transmission of myoclonus epilepsy from parents have been identified, but often it is detected among brothers and sisters, as well as other blood relatives. In the risk zone and suffering from absence epilepsy children.
Typically, epileptic seizures are primary, then myoclonias are attached, but sometimes the disease begins with mental changes.
Progress of the development of the disease
Conditionally the course of myoclonoepilepsy is divided into three stages:
- The epileptic-titaniform - lasts several years and is characterized by the appearance of epileptic seizures. As the
 develops, seizures become more frequent and transform from typical to tetaniform, characterized by increased sweating, painful spasms, and a sense of fear. During the seizures the patient is conscious. There are usually no neurological changes at this stage, but in some cases the patients become aggressive or withdrawn, depressed.
develops, seizures become more frequent and transform from typical to tetaniform, characterized by increased sweating, painful spasms, and a sense of fear. During the seizures the patient is conscious. There are usually no neurological changes at this stage, but in some cases the patients become aggressive or withdrawn, depressed. - The myoclonic-epileptic period of may last for many years and is expressed in a reduction in the number of seizures that are replaced by myoclonus attacks. Initially, muscle contractions are small and do not affect life;as a rule, part of the limb is affected. After a lapse of time, myoclonias spread to other parts of the face and body, the patient can not eat, write, and when walking, he throws to the side. Attacks of muscle spasms with myoclonic-epilepsy can provoke sudden movements, loud sounds, flashes of light, alcohol consumption, a strong manifestation of emotions, stress, cold or heat. Myoclonus disappears in a dream.
- The terminal period of is characterized by cachexia and serious mental changes accompanied by speech and memory disorders and bordering on dementia.
Varieties of
syndromes and seizures Myoclonic epilepsy:

- Benign myoclonic epilepsy of infants is a rare form of the disease that develops from a few months to 5 years. Identify the exact cause of its occurrence has not yet been possible, but it is known that it rarely passes into JME, almost has no serious consequences and with timely treatment quickly passes. The clinical picture consists of twitching the limbs, the head, and less often the whole body. The intensity of myoclonus is different. When falling asleep, myoclonias become worse, disappear during sleep. Psychomotor development of the child remains normal, as well as EEG.The diagnosis is made on the basis of an anamnesis.
- Severe myoclonus-epilepsy of infancy( Drave syndrome ) accounts for 5% of all early epilepsies. Before the onset of symptoms of the disease, the child develops normally. It is mainly caused genetically and, in addition to myoclonic seizures, is expressed through absences and complex focal seizures. The Drave syndrome has severe psychoneurological consequences, sometimes with a fatal outcome.
- Unferricht-Lundborg disease is the most common of the genetically conditioned myoclonus epilepsies. The peak incidence falls on later childhood;the first manifestations of the disease, as a rule - myoclonias, subsequently complicated by focal seizures and absences. The development of the disease is slow, for many years the patient's intellectual abilities do not decrease, then changes in depression, memory deterioration are noted. For Unferricht-Lundborg disease, "good" days are characteristic when the disease is not manifested, and "bad", which bind the patient to bed. The diagnosis is determined based on the clinical picture. Timely begun therapy can alleviate the symptoms of the disease and slow its development, helping patients live to their old age.
- Myoclonus epilepsy with ruptured red fibers( MERRF) .The disease causes a hereditary conditioned formation of abnormal RNA.Most often, the disease manifests itself in children and adolescents, but there are cases of adult disease. In addition to myoclonus and tonic convulsions, patients experience impaired coordination, progressive deafness, and myopathy. A characteristic phenomenon in the diagnosis is the presence in the skeletal muscles of specific "torn" fibers, as well as the high level of lactic acid in the patient's blood.

Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy - video lecture:
There are three types of attacks of myoclonus epilepsy:
- Myoclonic .Expressed in uncontrollable muscle twitchings, usually arising in the morning hours or
 , provoked by fatigue, alcohol intake, strong emotions, light and sound effects. Seizures can occur in a separate limb or muscle or spread to the entire body.
, provoked by fatigue, alcohol intake, strong emotions, light and sound effects. Seizures can occur in a separate limb or muscle or spread to the entire body. - Absenses - a sudden short-term release of consciousness, occurs in 40-50% of all patients. Due to the focus in the brain, affecting its various sites. A person falls into a stupor for a few seconds, his gaze stops, movement and speech stop. Despite the short duration of absences, they cause a serious impairment of consciousness.
- Tonic-clonic .Generalized cramps all over the body, accompanied by loss of consciousness. Possible involuntary bowel movement or urination, biting the tongue. The attack lasts a few minutes. Tonic-clonic convulsions are characteristic for more than half of the diseased and usually occur after awakening.
Diagnosis of the disease
Depending on the type of myoclonus of epilepsy, the diagnostic examination may have a different specificity. Most often, the diagnosis is made based on the age of the patient and the combination of myoclonic seizures with epileptic seizures, disorders of cerebellar activity;a blood test is also performed.
The EEG shows a disturbance in the normal alpha rhythm, which increases during an attack and exposure to bright light. CT or MRI can detect changes in the brain tissues, in particular the cerebellum and the legs of the brain.
For patients with myoclonus, epilepsy is characterized by the presence in the tissues of the internal organs of the so-called."Laforian bodies", consisting of polysaccharide compounds. In some cases, genetic testing is necessary. It is necessary to differentiate myoclonus of epilepsy from other diseases, which are characterized by a combination of the main symptoms( such as Kozhevnikov's epilepsy or encephalopathy).
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of miklonus epilepsy is aimed at alleviating the course of seizures and reducing their number, so it is predominantly symptomatic.
 As a primary treatment, it is usually prescribed sodium valproate and valproic acid - affecting the central nervous system, they reduce the number of myoclonias, and if treatment is prescribed early, the disease will progress more slowly, and the risk of complications will decrease.
As a primary treatment, it is usually prescribed sodium valproate and valproic acid - affecting the central nervous system, they reduce the number of myoclonias, and if treatment is prescribed early, the disease will progress more slowly, and the risk of complications will decrease.
Myoclonic and epileptic seizures are reduced with Chloral hydrate in the form of droppers or enemas, but due to toxicity and addictive treatment, they are treated with courses with large time intervals.
To avoid morning bouts at night, give Phenobarbital in combination with other medicines( Seductel, Benzonal).Daily Luminal is effective in controlling both epileptic seizures and with myoclonias.
Sometimes myoclonias show resistance to drug treatment;in these cases, therapy focuses on reducing epileptic seizures, as well as factors that provoke muscle contraction( stress, alcohol and drug use, elimination of concomitant diseases).
In addition to medicines, measures are taken to strengthen the body: blood and plasma transfusions, droppers with glucose, injections of B12, certain types of physiotherapy procedures. The patient should also regularly take a clinical blood test and a biopsy to monitor the indicators.

Complications and prognosis of
Often, patients with myoclonus epilepsy have a lifetime of treatment, otherwise symptoms may return.
Depending on the timeliness of the diagnosis and the appointment of therapy, seizures may permanently cease in a few years.
Given the slow course of the disease, patients usually survive to old age, but with rapidly progressing forms, it is possible for  to develop serious neurological pathologies and even death. In some cases( Drava's syndrome), myoclonus epilepsy causes irreversible changes in the psyche and a developmental lag.
to develop serious neurological pathologies and even death. In some cases( Drava's syndrome), myoclonus epilepsy causes irreversible changes in the psyche and a developmental lag.
For preventive purposes, preventive measures are needed to timely diagnose and identify genetic disorders.
Women who are at increased risk of having a baby with myoclonic epilepsy need genetic testing before and during pregnancy. It is also effective to monitor children born premature, with neurological abnormalities or low weight, taking timely measures to treat them.