Resetting is an easy degree of impairment of consciousness( stunning of an easy stage).This state is accompanied by a "blurring" of consciousness and a poor perception of reality. Patients with this diagnosis are slightly inhibited, have illogical thinking and for a long time give answers to the questions posed to them.
Resetting is an easy degree of impairment of consciousness( stunning of an easy stage).This state is accompanied by a "blurring" of consciousness and a poor perception of reality. Patients with this diagnosis are slightly inhibited, have illogical thinking and for a long time give answers to the questions posed to them.
Motor coordination is very slow or nonexistent. Patients can sit in a certain position for several hours at a time. The patient's view is not always purposeful and is directed to one point.
When recruiting a person explains his thoughts with great difficulty and is able to respond only to a loud voice. Stunned very often has a periodic character and alternates with enlightenment, in which a person adequately perceives reality.
Although this type of impairment is characterized by mild disorder, it can still progress to the stage of coma.
Degrees of inhibition of consciousness from mild to severe:
- stunnedness( overcrowding) - degree of impairment of consciousness, in which limited verbal contact is maintained and human self-activity decreases;
- sop - accompanied by a shutdown of consciousness, with the safety of protective reactions, the opening of the eyes to pain, the shortest short-term verbal contact;
- drowsiness( somnolence) - characterized by a long and deep sleep, which can be awakened by using vigorous stimulation;
- coma - total loss of consciousness.
Possible causes of
reassembly The appearance of mild to moderate stun is due to the following reasons:
- resulting head injury;
- strokes;
- presence of diabetes mellitus or other diseases of the metabolic spectrum;
- oxygen starvation;
- alcohol intoxication;
- result of toxic effects of drugs;
- overdose with hypnotics;
- presence of brain tumor or cancer metastases;
- manifestation of convulsive syndrome;
- manifestations of allergic reactions;
- dehydration and loss of electrolytes;
- body overheating;
- influence of electric current;
- overdose with narcotic drugs;
- disturbed blood supply to the brain;
- infections of the nervous system and inflammatory processes in the brain.
Consciousness consciousness can also be manifested for physiological reasons: severe body fatigue and chronic lack of sleep. Unlike other forms of mental distress, there are no hallucinations when stunned.
Characteristic manifestations of
The overall clinical picture is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Sluggish response to exogenous stimuli;
- lowering the level of linguistic abilities( the patient does not understand the essence of the questions posed and is not responding correctly to them);
- lack of logical thinking;
- sluggishness and poor orientation in space;
- detachment( alienation from everything that happens around);
- memory impairment;
- periodic spatial disorientation;
- not recognizing relatives and acquaintances;
- loss of ability to remember information;
- absence of any contact and aspiration of a sight in one point;
- is a periodic manifestation of increased mood;
- increase in the threshold of sensitivity;
- suppression of mental processes.
 The external facial expression of the patient is impoverished, the face is constantly pale and sleepy. Patients do not always remember recent events and have absolutely no emotions.
The external facial expression of the patient is impoverished, the face is constantly pale and sleepy. Patients do not always remember recent events and have absolutely no emotions.
Easy obnubilation occurs in children up to three years old. Her symptoms are expressed in the child's inhibition, his indifference to toys. It also notes complete disregard for parental messages. Patients are very sluggish and quickly exhausted.
Complex of diagnostic procedures and analyzes
For the diagnosis, the following examinations are performed and the following tests are taken:
- Collection of anamnesis of the patient .
- Neurological examination .The doctor assesses the patient's level of consciousness on the Glasgow coma scale. Also, a search for signs of neurological disorders is carried out. Usually they are manifested by weakness in the limbs, unilateral expansion of the pupil, lack of stem reflexes.
- ECG( electrocardiography) .With the help of this study, the heart rate is studied;
- Radiography of the skull .It is carried out if there is a suspicion of a craniocerebral injury.
- Radiography of the chest .
- Laboratory tests of urine and blood .Patients should submit a general blood test, an analysis of the capacity of glucose in urine and blood, an analysis of the presence of electrolytes, phosphates, calcium and creatinine in the blood. An analysis is also being conducted to determine the biochemical parameters of liver function.

- EEG( electroencephalography) .Helps distinguish psychic reactivity from coma.
- MRI and CT of the brain .These studies can determine the presence of stroke, encephalitis and the consequences of the craniocerebral trauma( a displacement of the brain structures, a brain contusion, epidural and subdural hematoma).
- Screening of toxic elements .This research is carried out in specialized toxicological laboratories. Thus, signs of intoxication with alcohol, drugs and heavy metal salts are revealed.
- US of extracranial arteries .It is in the study of the patency of arteries supplying blood to the brain. A special sensor is used.
Provision of medical care to
Even in the presence of the easiest degree of inoculation, the patient needs inpatient treatment. Provision of first aid consists of the following manipulations:
- resumption of normal blood circulation and blood pressure;
- stop vomiting and seizures;
- in case of intoxication, toxins are eliminated from the body;
- introduction of special medicines to increase activity;
- recovery of normal body temperature.
Drug therapy consists in prescribing drugs that normalize metabolic processes in the brain. These are drugs from the group of nootropics: pyriditol, Piracetam, Aminalon, Pantogam.
The most effective and popular drug of this group is Piracetam. Treatment with this medication should begin with a dose of 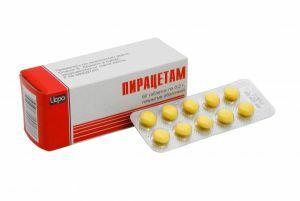 three to four grams( IV or IM), gradually increasing it to five or six grams. To achieve a pronounced anticonvulsant and antihypoxic effect, Piracetam is combined with Pantogam.
three to four grams( IV or IM), gradually increasing it to five or six grams. To achieve a pronounced anticonvulsant and antihypoxic effect, Piracetam is combined with Pantogam.
If unconsciousness is accompanied by a decrease in blood glucose, the patient is injected with a solution of glucose and vitamin B1.If breathing is disturbed, artificial ventilation is performed.
If the cause of impaired consciousness is cerebral edema, then the appointment of diuretics.
If necessary, the following measures are taken:
- defibrillation or indirect cardiac massage( with cardiac arrest);
- use of antipsychotics( in the case of psychomotor agitation);
- application of hormone therapy( use of steroid hormones).
In some cases, patients are hospitalized in a psychiatric hospital, but this issue is decided on the basis of the nature and  of the severity of the underlying somatic ailment.
of the severity of the underlying somatic ailment.
Untimely or incorrect treatment leads to a disruption of the supply of soft tissues in the buttocks and shoulder blades, resulting in the formation of pressure sores.
Also increases the likelihood of development of coma and death of obnubilation, which was caused by a violation of blood flow or the presence of a brain tumor.