 Every person in his life periodically encounters these or other diseases. This, always an unpleasant situation, is accompanied by anxiety, confusion and even fright.
Every person in his life periodically encounters these or other diseases. This, always an unpleasant situation, is accompanied by anxiety, confusion and even fright.
Special concerns are caused by medical definitions, the meaning of which is unknown.
One of these narrowly specialized concepts is the term "hemiplegia".
Contents
- Definition
- The definition of
- The pathogenesis of the disorder
- What causes the violation
- Clinical manifestations
- The topical diagnosis
- The variants of the development of the violation
- The complex of therapeutic measures
- The definition of
The definition of the concept
Hemiplegia is a neurological syndrome manifested by the complete absence of voluntary movements in the upper and lower limbs on one side.
Pathology arises as a result of total defeat of the pyramidal pathway, in particular its cortico-spinal part, responsible for the motor skills of skeletal musculature.
In clinical practice, hemiplegia is often considered a synonym for hemiparesis, or hemiparality. However, the classical neurological
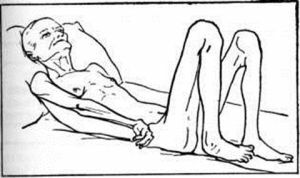 schools define hemiplegia as a kind of stage of defeat of the pyramidal tract, the immediate outcome depends on the features of the flow.
schools define hemiplegia as a kind of stage of defeat of the pyramidal tract, the immediate outcome depends on the features of the flow. This can be, indeed, hemiparality( absence of movements in the extremities due to irreversible changes) or hemiparesis( restriction of the ability to perform arbitrary movements and reduce their volume due to partial damage to the corticospinal pathway).
Pathogenesis of the disorder
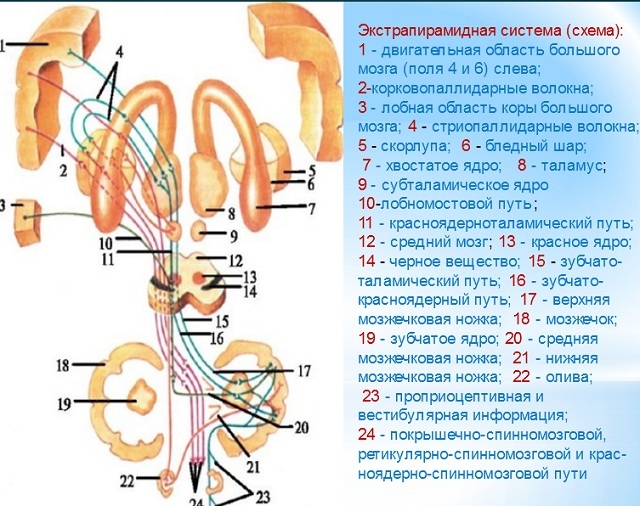
The pyramidal tract itself originates from the V layer of the cerebral cortex and is most vividly represented in the region of the precentral gyri.
The central neuron of the tract descends through the cerebral structures to the level of the medulla oblongata, where it makes a transition to the opposite side, then follows the lateral columns of the spinal cord to its anterior horns and meets peripheral motoneuron.
For most muscles, the cross of the corticospinal pathway is incomplete, that is, part of the path goes to the peripheral motor neurons of its side. Such a mechanism is a kind of protection of the musculature from the consequences of one-sided defeat of the pyramidal path.
In this case, the function of the damaged pyramidal tract on one side will take on the opposite cortical-spinal path.
However, there are muscles particularly vulnerable in this regard. For them, the pyramid path commits a complete crossroads. These are the muscles of the lower part of the facial muscles, the muscles of the tongue and the muscles of the upper and lower extremities.
Therefore, in the unilateral pathology of cerebral structures, these muscles suffer. In case of unilateral damage to the central neuron of the cortico-spinal tract before the cross, the symptom of hemiplegia is formed on the opposite side, after the cross - on the side of the lesion.
What provokes the violation
Factors that can lead to hemiplegia are quite diverse:
- cerebral and spinal strokes , at which the blood supply of the brain region with the motor path passing through it ceases;
- head and spinal cord injuries ;
- infectious diseases of the central nervous system ;
- extensive diffuse foci of ischemia discirculatory;
- of the neoplasm of the brain ;
- functional disorders , in particular hysterical neurosis, in this case the pyramidal path is preserved, and hemiplegia( hemiparesis) is a manifestation of pathological psychoemotional reactions of a person.
Most of all manifestations of hemiplegia are acquired due to some organic damage to the brain and spinal cord.
However, there are also innate options, in which the baby is already born with a violation. This is a consequence of incorrect insertion of central motoneurons in the process of embryogenesis or other disorders of cerebral and spinal functions during the intrauterine development.
As a rule, this is not one, but several causes, manifested in hemiplegia or delay in the formation of cerebral structures.
The most common pathogenesis are discirculatory disorders of intracerebral, uterine and fetoplacental blood circulation, leading to dysgenesis and malformations of the brain of the newborn.
Clinical manifestations of
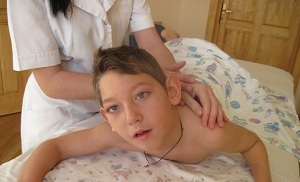 Given that hemiplegia is manifested by the absence of arbitrary movements in limbs on the side of the side, clinically it is right-sided, left-sided or double, which is most often observed in cerebral palsy.
Given that hemiplegia is manifested by the absence of arbitrary movements in limbs on the side of the side, clinically it is right-sided, left-sided or double, which is most often observed in cerebral palsy.
Depending on where the lesion of the motor tract has occurred( its central or peripheral neuron has suffered), hemiplegia may be central or spastic and peripheral or lethargic.
Spastic hemiplegia always has a number of common features. First, tendon reflexes( carporadial, bicipital and tricipital for the upper limb and knee and Achilles for the lower) increase in the affected limbs.
This is due to the lack of dominant influence of the affected pyramid path on conditioned reflex arcs.
Increases muscle tone, which in its essence is also an unconditioned reflex. In this case, hypertension in the upper limb is manifested in the flexor muscles, and in the lower extremity - in the extensors.
In addition, the so-called pathological reflexes begin to appear on the paralyzed limbs-these are the innate unconditioned reactions of the body, which are gradually suppressed by the active function of the cortico-spinal tract.
To pathological reflexes include:
- flexor stop signs Rossalimo, Zhukovsky, Bechterew;
- extensible stop signs of Babinsky, Oppenheim, Gordon and Schaeffer;
- symptoms of oral automatism ;
- pathological signs from the upper extremity of ( Rossolimo, Jacobson-Lask, Bekhterev, Zhukovsky).
Peripheral plegia is characterized by a decrease in muscle tone, muscle atrophy and extinction of reflexes.
These changes occur as a result of peripheral motor neurone damage, because of which the reflex arc does not close.
Topical diagnosis
Topical diagnosis is based on the presence of a complete crosshair of the pyramidal path at the level of the medulla oblongata for the muscles of the upper and lower extremities.
- With the central right-sided hemiplegia, the lesion focus should be sought in the left hemisphere of the brain, in the left parts of the cerebral trunk or in the right lateral column of the spinal cord above the cervical thickening( in these parts the first neuron of the pyramidal path passes).
- The same can be said for the left-sided hemiplegia, in the presence of which pathology should be assumed in the right parts of the brain or to the left in the lateral column of the spinal cord to the level of the segments giving the innervation of the upper limb.
- If the pathological process of affected half of the diameter of the spinal cord at the level of the cervical thickening of the ( segments C5-Th1), hemiplegia will be represented by a spastic lesion for the lower limb and a sluggish plection for the upper( due to peripheral alpha motoneurons).
- In the lesion, localized in the spinal cord , below the cervical thickening of , there will be no violation, since the hands will be intact.
Variants of development of a violation
Depending on the location of the lesion, hemiplegia can be:
- contralateral if it appears on the side opposite to the lesion( in case of cerebral pathology);
- homolateral if the lesion is on the same side as the affected limbs( with spinal processes);
- double , when the upper and lower limbs are involved immediately from both sides. Double hemiplegia is the most severe form of infantile cerebral palsy.
An alternate form of contralateral hemiplegia is the alternating variant. It is said, if on the opposite side of the affected limbs, there is another neurologic symptomatology, which can be explained by the same lesion, which led to the development of the disorder.


Examples of alternating syndromes are:
- Weber Syndrome .In the legs of the brain, the pyramidal tract runs in the immediate vicinity of the nucleus of the gas-motor nerve. With the pathological process localized in this area, the symptomatology of the third cranial nerve( ptosis, divergent strabismus, mydriasis, diplopia, limitation of the mobility of the eyeball up, down and inside, the pathology of accommodation) will appear on the side of the lesion on the side of the lesion, and on the opposite side the central hemiplegia.
- Syndrome of Miyyara-Gubler .If hemiplegia is found on one side and peripheral paresis of the facial nerve on the opposite side, it is worthwhile to look for a lesion in the variola bridge, since there the cortico-spinal path goes alongside the nucleus of the VII nerve.
- Fauville Syndrome occurs if peripheral paresis of the abducent nerve is added to the clinical picture of Miyar-Goebler syndrome. In this case, the lesion focus must also be assumed in the bridge, but think about a more extensive process than with an alternating syndrome involving only the nucleus of the facial nerve.
- Jackson Syndrome .In the medulla oblongata is the nucleus of the hyoid nerve, which provides the movements of the muscles of the tongue. With the joint destruction of it with the pyramidal tract, this alternating syndrome arises, manifested by peripheral paresis of the muscles of the tongue from the pathology side and contralateral hemiplegia.
Complex of therapeutic measures
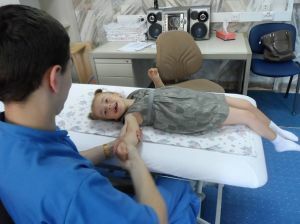 Complex treatment of hemiplegia means several mandatory programs - inpatient, outpatient and home. A separate point of recovery is allocated to rehabilitation centers.
Complex treatment of hemiplegia means several mandatory programs - inpatient, outpatient and home. A separate point of recovery is allocated to rehabilitation centers.
Early rehabilitation is considered justified, which begins in the acute period of the main disease in the hospital, and then continues at home.
Hemiplegia is only a syndrome of the disease. Therefore, to begin with, we must work on the underlying root cause of the development of the disorder.
Most often, medications for cerebral and spinal processes prescribe drugs to improve the trophism of nervous tissue and conduct a nerve impulse, restore the pathways, and remove spasticity.
To this therapy include:
- neurotrophic drugs;
- neuroprotectors;
- vasoactive agents;
- antioxidants;
- B vitamins;
- cholinesterase inhibitors;
- muscle relaxants.
Direct action on the affected limbs is provided by mechanical methods of rehabilitation:
- massage;
- kinesitherapy;
- medical gymnastics.
These methods involve the physiological position of the limbs, periodic turns in the bed, regular passive movements in all joints, mechanical improvement of blood circulation and lymph drainage will help.
All this is aimed at preventing the formation of contractures, pressure sores, muscle atrophies and the attachment of secondary infections.
The standers in this regard have been shown to be reliable in performance - special devices that allow the patient to take a vertical position. Their use is justified even in the acute period of the underlying disease.
A significant contribution to the overall therapy is made and physiotherapy: 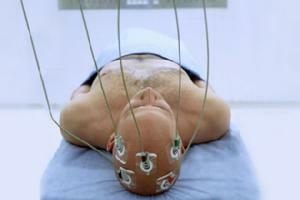
- muscle electrical stimulation;
- influence of magnetic field;
- barotherapy;
- laser therapy.
There are non-traditional methods of treatment for hemiplegia( acupuncture, manual therapy, treatment with medicinal herbs).
Compulsory and social rehabilitation of patients. A person who has lost the ability to fully use his hand and foot, needs a separate socially-domestic and environmental adaptation, especially if the affected limb is dominant.
This includes teaching patients how to use objects in everyday life, adapting the room itself to the needs of a person with, prosthetic-orthopedic care. In the future, retraining is provided for persons of working age.
In addition, with a comprehensive approach to recovery, resort to psychotherapeutic correction.
The prognosis directly depends on the severity of the disease, which formed the basis for the development of hemiplegia. More often than not, total damage to the pathway is not completely restored.
However, with the timely begun competent treatment complex hemiplegia can be translated into the category of hemiparesis.