Modern doctors knowingly recommend to pay attention to their health and apply for qualified medical help in a timely manner.
Modern doctors knowingly recommend to pay attention to their health and apply for qualified medical help in a timely manner.
Some diseases, such as ARVI, meningitis, hypertension, are fraught with the development of a number of complications, one of which may be sensorineural hearing loss. The disease is dangerous because it is difficult to treat and can lead to the fact that the world of sounds will disappear forever from the life of the patient.
Very often, not the ENT doctor, but the neurologist, is engaged in the treatment of this disease, especially in cases when the hearing loss is caused by a violation of the cerebral circulation.
Contents of
Contents of
-
- development mechanism
- development mechanism All causes complex
- Progress stages of the disease
- Character of the violation progress
- Symptoms of the pathology
- Diagnosis
- Treatment of the disease
- Complications and prediction
- Both hearing and nerves are intact. ..
Several interesting facts
About 6% of peopleall over the globe suffer from hearing impairment as a result of neurosensory hearing loss.
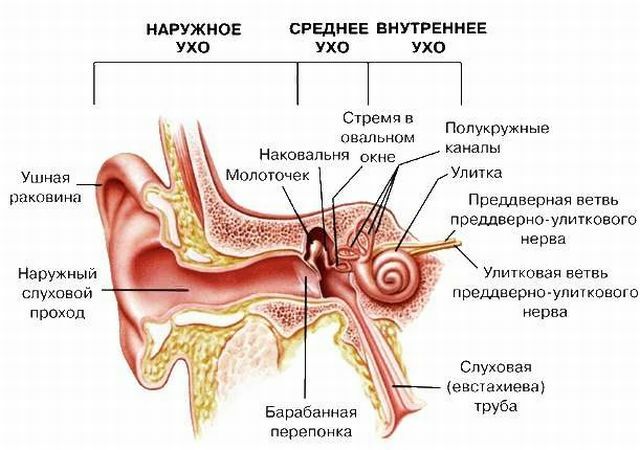
Sensorineural hearing loss( neuritis of the auditory nerve) or cochlear neuritis is a non-infectious disease that occurs with equal frequency in both the elderly and young patients.
In the course of its development, the inner ear is exposed to structural changes, namely the auditory nerve, the pre-vertebral cochlear nerve, the parts of the auditory analyzer in the cerebral cortex.
As a result of the disease, not only does hearing decrease, but also in 90% of cases there may be noise in the ears. The disease is usually one-sided.

Mechanism of development of
The mechanism of development of cochlear neuritis is not certain. If the cause of neuritis of the auditory nerve is associated with vascular pathology, the disease develops as follows.
As a result of circulatory failure, the cells of the auditory nerve are deficient in nutrients and oxygen, resulting in death. Progression of the nerve trunk is affected, its atrophy develops, which leads to a significant decrease in the quality of perception of sounds or complete deafness.
As a result of meningitis or other viral infection, the inflammatory process affects the connective fibers surrounding the auditory nerve. In the future, necrosis of its cells occurs, connective tissue grows. Consequence - the emergence of sensorineural hearing loss.
In some types of head trauma, for example, as a result of a stroke, the temporal nerve trunk is damaged in the temporal region, its cells die. After that, he can not fully perform his functions, develops cochlear neuritis.
Sometimes, as a result of head injuries, swelling or swelling compresses the nerve fibers, and this condition leads to a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses, resulting in hearing impairment.
The whole complex of causes
Causes of the disease can be divided into 2 groups: congenital and acquired.
Congenital causes are mainly associated with genetic abnormalities, such as intrauterine malformation of the inner ear, Usher syndrome, Alport syndrome, Waardenburg, as well as birth trauma, fetal hypoxia. The acquired causes of development of deafness are more diverse.
So, the development of cochlear neuritis may be due to:
- infections of the viral and bacterial nature of : SARS, influenza, meningitis, syphilis;
- vascular pathology , including hypertension, cerebral circulation disorder: cerebral atherosclerosis, vertebro-basilar insufficiency;
- by the toxic effects of on certain medicines, household and industrial substances;
- head injuries, brain tumors ;
- with acoustic injuries of , related to professional activity, namely constant work in noisy rooms.
Stages of progress of the disease
Depending on the spread of the disease, the neuritis of the auditory nerve can be divided into a one-sided one, in which one auditory analyzer is affected, and two-sided, in which the pathological process has affected both ears.
Doctors allocate 4 stages of development of sensorineural hearing loss:
- 1( light) degree of , for this stage the threshold of perception of sounds for the patient varies from 26 to 40 dB, that is, a person hears
 ordinary speech no further than at a distance of 4-6 meters fromyourself;
ordinary speech no further than at a distance of 4-6 meters fromyourself; - 2( moderate) degree is characterized by a perception boundary of sounds from 41 to 55 decibels, that is, a person perceives conversations of other people only at a distance of 1-4 meters from himself;
- 3( moderately heavy) corresponds to the threshold of perception from 56-70dB, while a person hears spoken speech only at a distance of 0.25-1 meter;
- at 4( severe) the auditory margin is in the range of 71-90 db, this is almost complete deafness.
Depending on the cause of the disease, central neurosensory hearing loss is identified, in which hearing loss is associated with impaired brain structures, and peripheral, in which the auditory nerve itself is affected.
The nature of the
disorder The nature of the course of the disease is:
- acute sensorineural hearing loss, in which the disease lasts from a week to a month, with the timely access to a doctor, the probability of complete cure is up to 90%;
- subacute form occurs in a situation where the disease lasts from 1 to several months, the chances of a full recovery are already 30-70%;
- chronic bradyacoustic therapy lends itself poorly, the chances of recovery are minimal, it is diagnosed when the disease lasts more than 3 months.
Symptoms of pathology
 Patients complain of a deterioration in the perception of sounds in one ear, and in both at once. There may be noise in the ears, which manifests itself in the form of a ringing, a squeak, a buzz. Very often the patient can not determine where the sound comes from.
Patients complain of a deterioration in the perception of sounds in one ear, and in both at once. There may be noise in the ears, which manifests itself in the form of a ringing, a squeak, a buzz. Very often the patient can not determine where the sound comes from.
If a sudden illness occurs within a few hours, the patient stops hearing normally, sometimes the first symptoms appear during the morning awakening.
In some cases, hearing loss occurs within 2-3 days.
With a progressive and stable form of the auditory nerve neuritis, the main symptoms begin to be associated with headache, dizziness, imbalance, uncertainty during walking.
Diagnosis of
Initially, the doctor conducts an examination of the hearing condition to determine the audibility of whispered and loud speech, and if there are impaired perception, the patient is sent for additional studies. 
The final diagnosis is made after audiometric examination, analysis of auditory samples. They are conducted in order to reveal the degree and nature of the damage to the inner ear.
To determine the cause of the disease, dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and brain may be required. In addition, the doctor can appoint an MRI or CT of the brain in order to exclude the presence of a tumor, bone pathologies, vascular disorders.
Treatment of the disease
Therapy of the disease should be carried out by several doctors: an otolaryngologist, neurologist, therapist. If the cause of the disease is damage to the auditory structures of the cerebral cortex, a disorder of cerebral circulation, then such a patient will be to a greater extent a patient of a neurologist than an otolaryngologist.
The aim of the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss is to prevent the transition of the disease into a chronic form, exclude the risk of hearing loss, and in the process of running - the prevention of deafness and at least a partial restoration of the work of the hearing organ.
 A neurologist usually prescribes sedatives: Elenium, Seduxen, Valerian, they reduce the excitation of the CNS and auditory nerve.
A neurologist usually prescribes sedatives: Elenium, Seduxen, Valerian, they reduce the excitation of the CNS and auditory nerve.
In the future, the specialist prescribes nootropics to his patient, means that can prevent the death of the cells of the auditory analyzer as a result of hypoxia and improve cognitive functions. These include Piracetam, Aminalon, Nootropil.
In the course are drugs that have a beneficial effect on cerebral circulation: Vinpocetine, Cinnarizin. In parallel, vitamins B1, B6, B12, A, E can be prescribed.
Symptomatic treatment is performed, Betazhistin may be discharged with dizziness, and if there is inflammation, tumors, edema due to trauma, glucocorticosteroids and diuretics.
In addition to medical methods of treatment, phonophoresis, electrostimulation proved to be a good idea.
Complications and prognosis of
The only complication of cochlear neuritis is complete or partial deafness, which is very difficult to treat. Side effects of  may cause long-term use of certain drugs used to treat hearing loss.
may cause long-term use of certain drugs used to treat hearing loss.
The earlier the treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis for the patient. If the abnormalities occurred suddenly and are not very pronounced - the prognosis is favorable, after 4 months after the therapy the symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
The risk of a partial loss of hearing or deafness is more likely in elderly patients. The chronic form of the disease inevitably leads to persistent deterioration of hearing and even deafness.
And hearing and nerves are intact. ..
The best prevention of hearing loss is timely and competent treatment of the initial stage of the neuritis of the auditory nerve.
If the patient has chronic diseases, endocrine disorders, neurological problems, it is necessary to follow the doctor's recommendations so that their complication is not neurosensory deafness.
It is advisable to refrain from smoking, drinking alcohol, avoiding stress, staying as little as possible in rooms with high noise, fully eating, and treating catarrhal diseases in a timely manner. Do not use ototoxic drugs or use them in case of emergency.