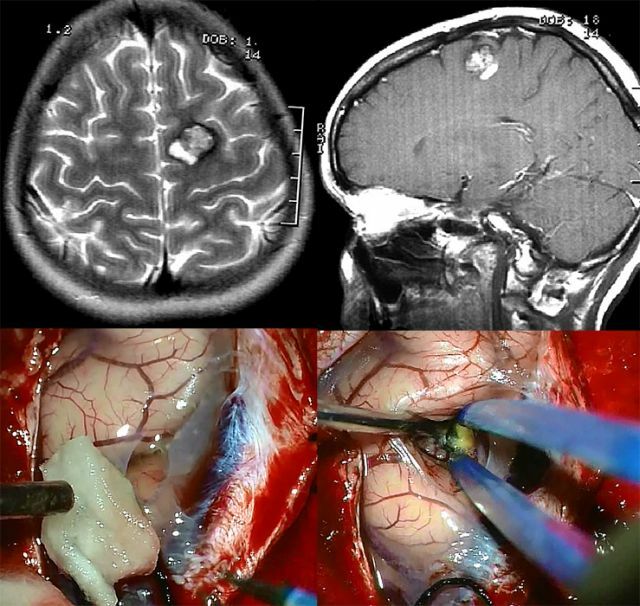
 The human brain consists of a special tissue called ependyma. It is she who lays the cavities in the brain. This tissue, under the influence of various factors, has the property of expanding in the form of tumors. These tumors are called ependymomas.
The human brain consists of a special tissue called ependyma. It is she who lays the cavities in the brain. This tissue, under the influence of various factors, has the property of expanding in the form of tumors. These tumors are called ependymomas.
This pathology can occur in any person, and this disease has no age limitations. Most of the formations are benign in nature, that is, those that do not give metastasis.
A few cases of malignant ependyma are very insidious and dangerous for the patient's life.
Some types of tumors can expand into other brain areas, getting into them with cerebrospinal fluid. Malignant species are characterized by very caustic metastasis, often even beyond the limits of the neuro-systemic structures. If there is a relapse, a new tumor occurs in the old place or next to it.
Content
- localization and classification of malignancy
- reasons for the development of tumor
- symptoms and manifestations
- If struck by a spinal cord area
- tumor struck brain
- tumor process golovnomozgovyh ventricles
- diagnosis and treatment
- Problems reduction step
- prognosis and survival
- How to reduce the risks?
Localization and classification of malignancy
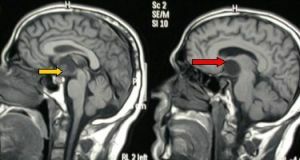
There is a disease due to the mutation of ependyma cells with which the spinal canal and the ventricles of the brain are lined. Consequently, the new formation occurs precisely in these zones.
According to statistics: 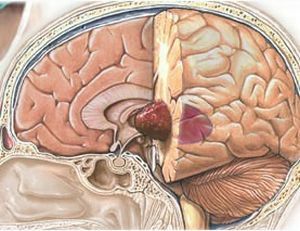
- In 60% of all cases ependymoma is diagnosed in the region of the 4th ventricle of the brain in the posterior cranial pit. From this place, formation can often sprout into the trunk of the spinal cord, into the upper cervical region or into the cerebellum. This type of pathology is called in the medicine infrastructorial .
- Approximately 30% of such neoplasms can form in the lateral ventricles of the large or third ventricle of the midbrain. This form is called supradentorial .
- In 10% of cases, the tumor arises precisely in the spinal canal. And this type of disease is called intraspinal .
The properties and structure of the tissue in the neoplasm( epindimoma) are very diverse. The tumor can have:
- Low degree of malignancy .This indicates a low rate of cell division. Consequently, education itself is growing very slowly.
- High degree of malignancy .In this case, the rate of division of pathological cells is higher. The structure of the tumor is quite different. The tumor grows aggressively and swiftly.
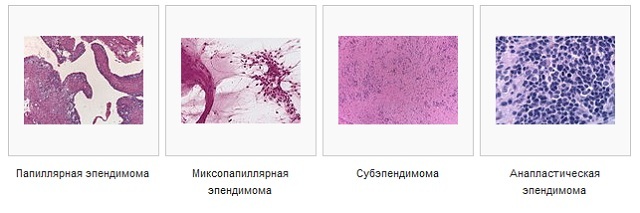
Classification by ependyme, according to WHO( World Health Organization):
- Subepindimoma ( 1st degree of malignancy).Expand and divide very slowly.
- Mixopapillary epindimoma( I-st degree of malignancy).The tumor grows slowly with a low level of malignancy, often formed in the spinal canal.
- Tumor of the 2nd degree of malignancy .Tumors grow slowly, but tend to grow aggressively. Cancer cells have several varieties.
- Anaplastic ependymoma III degree of malignancy. A pathology characterized by a high level of aggressiveness.
Reasons for the development of the tumor process
A reliable reason for the development of the pathology in question has not been fully established to date. Histology shows only the presence in the tumors of a very active virus of the SV40 form. However, this fact requires further scientific research in order to determine the etiology of this disease.
The risk group includes:
- patients with a genetic predisposition to the disease;
- workers, whose scope of activities is related to harmful substances;
- patients who received a high dose of radiological radiation;
- infected with a highly co-genic virus.
Symptoms and manifestations
The clinical picture of the disease manifests itself in different ways, this is explained by the tumor localization zone.
If the spinal cord region is affected
If ependymoma is localized in the spinal cord, the patient feels:
- a sensitivity disorder in relation to tactile touches, pain, warmth and cold, unpleasant sensations can be felt both in one side of the spine and in both;
- with increasing neoplasm develops paresis or paralysis;
- radicular syndrome is absent;
- in view of the violation of functionality and sensitivity, the patient may show clumsiness, changes in motor skills, gait and so on.
The tumor affected the brain
If the location of ependymoma is the brain, then the patient begins to worry about the following symptoms:
- headaches of a paroxysmal nature, especially often associated with physical exertion, change in temperature or
 conditions, change in posture, sometimes arising and without reason;
conditions, change in posture, sometimes arising and without reason; - vomiting, most often unreasonable with accompanying a headache or without it;
- the patient begins to change the position in which his headaches become less intense;
- Bruns syndrome - with sharp turns of the neck or a change in the position of the body, dizziness occurs;
- can sometimes be seen convulsive muscle contraction, a bit like a banal twitching;
- in advanced phases of the development of pathology symptomatology is supplemented by mental disorders in the form of stun, psychoemotional inhibition, lethargy and so on.
Tumor process in the cerebrospinal ventricles
When the ependymoma is localized in the lateral ventricles( cerebrospinal), the course of the disease can proceed for a long time latently. The first signs can only be known about themselves in the later stages.
In this case, the patient also develops concomitant diseases, such as intracranial hypertension and the like.
Symptom is manifested as:
- impairment of consciousness, psyche or memory;
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- spatial disorientation;
- lethargy or lethargy.
Diagnosis and treatment of
Diagnosis of the tumor in question is based on a thorough examination of the patient, which includes:
- assessment of reflex function;
- skin sensitivity;
- some types of neurological tests;
- may require a visual assessment;
- electroneuromyography;
- ultrasound;
- MRI and other related brain studies.
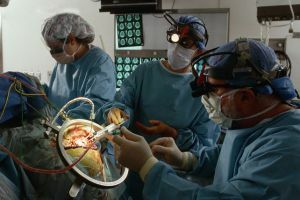 Treatment of ependymoma can be complex, surgical and / or radial. The use of a specific method of therapy depends on the severity and stage of development of the tumor process at the time of diagnosis.
Treatment of ependymoma can be complex, surgical and / or radial. The use of a specific method of therapy depends on the severity and stage of development of the tumor process at the time of diagnosis.
Chemotherapy is considered ineffective in this case, it is used exclusively in extreme cases when it is not a question of treatment but a prolongation of life to a patient with a relapse.
The standard of therapy is considered to be surgical intervention. It involves trepanation of the skull, when the skull is opened to gain access to the affected area. After that the neoplasm is excised. In fact, this method is also not considered ideal.
It does not give one hundred percent guarantee that the new formations will not appear in the same place. For this reason, surgical intervention is combined with radiotherapy. Due to this, it is possible to reduce the size of education.
Radiation therapy can be used both before and after surgery. In cases where surgery can not be applied, then radiation therapy is considered the only way of treatment.
Rehabilitation problems
Surgical intervention on the brain is in itself considered a serious test for the patient, after all, not all patients manage to survive. Even more difficult is the passage of the rehabilitation period, especially if the patient is a child.
Problems that patients may encounter after surgery:
- for children - growth retardation possible;
- incapacity for work;
- depressive states, fast fatigue;
- development of hydrocephalus;
- auditory and speech disorders;
- possible cramps;
- changing the perception of the environment.
If similar signs are revealed, the patient is recommended special treatment, regular visits to doctors for the detection of metastases or other pathologies.
Forecasts and Survival
Statistics show that mortality in the first days after surgery of patients who have ependymoma of the brain removed is approximately 8%, while the overall prognosis for survival is very negative.
If you take into account the five-year survival rate, then its percentage increases to 60 and then, subject to the surgical treatment.
The prediction is affected primarily by the degree of resection. A successful resection improves the prognosis, its percentage is about 80%.
In case of unsuccessful or incomplete removal of cancer cells, the tumor will form again.
How to reduce risks?
Unfortunately, preventive measures preventing the development of this disease at the moment, no. But to reduce the likelihood of the formation of any tumor can be generally accepted principles of a healthy, full-fledged way of life:
- to abandon the harmful habits;
- revise the diet, start eating properly;
- to minimize the impact of harmful environmental influences;
- to undergo medical examinations in a timely manner;
- regularly work on improving the immune system.

All patients, who have been treated for this pathology, without exception, are obliged to visit oncological centers on a regular basis with the purpose of timely detection of new formations or recurrence of current ones.