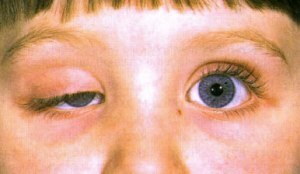
 Horner's syndrome is a syndrome caused by damage to the sympathetic nervous system of the body.
Horner's syndrome is a syndrome caused by damage to the sympathetic nervous system of the body.
Often this syndrome is called by the oculosympathetic syndrome , since it is manifested on the face - in the eye area.
It acts not only on the muscular tissues of the body, but also in some cases, on the eye itself.
It should be noted the interesting fact that the syndrome was discovered by Dr. Horner, but before him there were several physicians who described the symptomatology of this disease.
As a result, the disease was christened that way. In a number of countries, the name is added in the name - Claude Bernard Horner's syndrome.
Contents
- Causes of
- Causes of
- Classification of the disease
- Symptoms and signs of Horner's syndrome
- Diagnostic techniques
- Treatment of pathology
- Prophylaxis
- Video: Horner's syndrome
Causes of
The causes of the Horner syndrome are quite numerous, ranging from damage to the nervous system and ending with congenital malformations.
Consider them more in detail:
- Physical effect directly on the thoracic or cervical chain of the sympathetic system. This can be both squeezing and direct damage. Often the symptomatology arises from the side where the effect was made.
- When brain tissue is damaged due to lateral medullary syndrome.
- The cause of the syndrome may be a cluster headache. These are very strong headaches that are felt on the walls of the skull. The pain is so strong that it is not uncommon for suicides to get rid of such pain.
- Traumatic cause associated with severe bruise directly on the base of the neck. Surgical trauma is also possible.
- Due to various tumors. In particular, it is a tumor of Pankosta.
- Manifestation of an aneurysm. Very often, Horner's syndrome occurs after the transfer of the aortic aneurysm.
- Inflammatory processes in the middle ear zone.
- The cause may be a direct aneurysmal stratification.
- Thyroid tumor.
- The onset of this syndrome can be associated with an autoimmune disease, for example, multiple sclerosis.
- Stress of the radial nerve, due to the presence of an additional cervical rib.
- The cause may also be a blockade of nerve centers.
- In case of a cut of the sympathetic nerve of the neck.
- The cause may be a hereditary disease that can cause tumors throughout the body. This is the so-called neurofibromatosis of the first type.
 Rapid disruption of brain membranes or serous meningitis in children - treatment and prevention of disease.
Rapid disruption of brain membranes or serous meningitis in children - treatment and prevention of disease.
Especially dangerous cerebral cyst, whose treatment is feasible only surgically, has its own peculiarities of diagnosis and symptomatology.
Classification of the disease
Horner's syndrome can be both a separately developing disease and a consequence of other ailments. Based on this fact, there is the following classification:
- Idiopathic is a medical term for the independent passage of the disease from other pathogenic factors. In this case, Horner's syndrome-
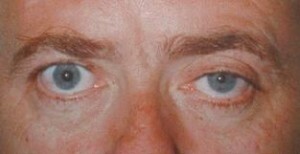 is a separate disease, and not an element of the symptomatology of another disease.
is a separate disease, and not an element of the symptomatology of another disease. - Secondary - in this case, Horner's syndrome develops as a consequence of a number of other diseases. What happens more often, it is one of the symptoms of the disease that caused the syndrome.
There is also a classification that determines the degree of damage to the neuronal chain by which the impulse is transmitted. Depending on this is allocated:
- lesion of the 1st neuron - it can be directly related to the transverse dissection of the spinal cord;
- defeat of the 2nd neuron - this species develops by squeezing the sympathetic nerve, an enlarged tumor;
- lesion of the 3rd neuron - develops when the so-called motor fibers are damaged.
Symptoms and signs of Gorner's syndrome
Bernard Horner's syndrome can be defined as a number of external signs that are expressed directly on the patient's face, and with a more delicate examination of the eyeball( in some cases more clearly).
The syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Slow adaptive ability of the pupil - the eye is able to adapt to the degree of illumination: the stronger the intensity of the illumination, the more the pupil narrows, and, conversely, for a better view in the dark. Due to Horner's syndrome, pupils are not able to adapt quickly to changes in light intensity.
- Heterochronia - this symptom is manifested by a different color of the iris of the eye. That is, the eyes will have a different color. Very often, this symptom is seen in children with Horner's syndrome.
- Falling of the eyeball - the so-called enophthalmos.
- Miosis. Unnatural narrowing of the pupil with subsequent inability to expand.
- Ptosis .The unnatural lowering of the upper eyelid with further non-return, which results in a narrowing of the eye. Inverted ptosis is the inverse symmetry to the usual ptosis. In this case, the lower eyelid is raised.
- Anhydrosis .Reduction of sweating from the side of the affected nerve.
- Reduced production of tear fluid from the side of the lesion.
- Red color shell of the eyeball.
- The drilled face of from the side of defeat.
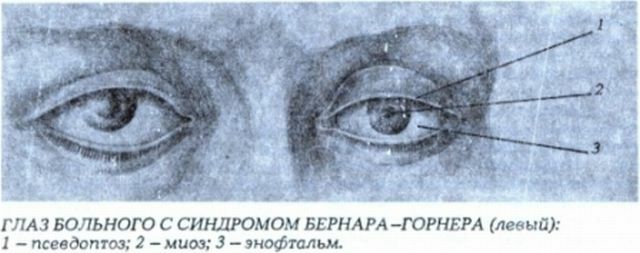
In the picture, the symptoms of the Gorner's syndrome
Diagnostic techniques
In addition to directly visual inspection of the patient, in order to identify obvious symptoms, and to draw up a detailed history, there are certain diagnostic techniques that aim to unambiguously determine this disease:
- Instillation of M-cholinoblocker solution in the eyes. With such manipulations, it is possible to uniquely identify Horner's syndrome, since the action of this solution increases the pupil of the eye. If the pupil does not respond, then there is a syndrome, or another reason.
- Definition of eye retardation time - as already noted in the symptomatology, in the presence of eye syndrome have a reduced adaptive ability to light intensity difference. As a consequence, knowing the adequate adaptation time, you can determine the time of adaptation of the patient's eye by measuring the time.
- MRI - Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to identify the formation that caused the onset of Horner's syndrome.
Treating the pathology of
 It should be noted that Horner's syndrome is a fairly innocuous disease, if it is independent, although it has a number of discomforts and cosmetic defects.
It should be noted that Horner's syndrome is a fairly innocuous disease, if it is independent, although it has a number of discomforts and cosmetic defects.
But behind the emergence of this disease can be quite specific and quite serious pathologies and problems.
Treatment of Gorner's syndrome occurs:
- By means of neurostimulation , electrodes are attached to the affected muscles or areas, and stimulation of the affected areas occurs with short electrical impulses. This leads to a better blood circulation and a further partial or complete recovery.
- Plastic surgery - surgical intervention in the affected area for the purpose of plastic correction of discomfort zones.
- Medication - a delicate selection of specialized drugs designed to stimulate the affected facial tissues. These medicines are very specific, and their selection is carried out exclusively by specialists. Therefore, self-medication does not lead to a cure for this disease. It is necessary to address exclusively to the competent person.
- Kinetotherapy is a kind of therapeutic physical activity. This technique uses a variety of massages that can stimulate affected areas through direct physical contact. Thanks to this, the areas receive proper blood circulation.
Preventive measures
The specificity of Horner's syndrome is that it does not have special courses of treatment and prevention.
It is often a symptom of a more complex and systemic disease, which already has direct methods of treatment and prevention.
The presence of the syndrome is very often determined only for the sake of exclusion or the detection of a possible more serious disease that can endanger the life of the patient.
Bernard Horner's Syndrome is an specific disease associated with complications in the work of sympathetic nerves , or their damage.
He has a number of specific symptoms, as well as methods of treatment and diagnosis of the disease. As a separate disease, he does not threaten the life of the patient, but only causes cosmetic and physical discomfort.
Treatment of this syndrome occurs by stimulating the affected tissue or eliminating the cause of its occurrence. In the treatment of this disease it is important to turn to a specialist in time to prevent really dangerous complications.
Video: Horner's Syndrome
The diagnosis of Gonrera's syndrome can only be made by looking in the mirror. What you need to know about the symptoms, treatment and prevention of the disease.



