 Polymicropathy, agiria and pahigiriya refer to congenital malformations of the brain, also called malformations of the brain.
Polymicropathy, agiria and pahigiriya refer to congenital malformations of the brain, also called malformations of the brain.
These abnormalities arise as a result of the disrupted process of brain formation or its separate structures during the prenatal period, and represent abnormal changes in the structure of the brain structures.
There is no exact data on the prevalence of congenital malformations of the brain, but the most common is considered to be polymicrogyria.
More information about each malformation:
- Polymicropathy is a rare pathology of development of the cerebral cortex, in which a significant number of small and underdeveloped convolutions form on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres. It is often combined with other genetic pathologies and anomalies in the development of the cerebral cortex. The most common pathology develops in the area of the sylvian furrow( 60% of cases), but it can occur in any part of the cerebral cortex. Pathology is diffuse, multifocal and focal. It can also be divided into one-sided( 40% of cases) and two-sided( 60% of cases), symmetrical and asymmetric.
- Agiria( lissencephalia) - an anomaly of the formation of the cerebral cortex, in which the convolutions are underdeveloped, weakly expressed,
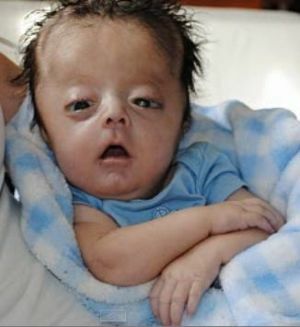 or absent, the architectonics of the cortex is broken. The appearance of the child's brain is identical to the appearance of the fetal brain in the 3-4 months of the prenatal period. Agyria is a severe form of lentencephaly. It can be both an idiopathic disease and accompany other pathologies( Miller-Dicker syndrome, Norman-Roberts syndrome, Walker-Warburg syndrome, congenital muscular dystrophy of Fukuyama).
or absent, the architectonics of the cortex is broken. The appearance of the child's brain is identical to the appearance of the fetal brain in the 3-4 months of the prenatal period. Agyria is a severe form of lentencephaly. It can be both an idiopathic disease and accompany other pathologies( Miller-Dicker syndrome, Norman-Roberts syndrome, Walker-Warburg syndrome, congenital muscular dystrophy of Fukuyama). - Pahigiria is a rare anomaly in the development of the central nervous system, in which a small number of wide and flat convolutions form in the cerebral cortex of the cerebral hemispheres. Under pahigiriya, the main convolutions are enlarged, and the secondary and tertiary are absent, the furrows are shortened and straightened, the architectonics of the cerebral cortex is broken. This pathology is considered as an "incomplete", lighter form of lissencephaly.
Aggravating factors
The main cause of the development of polymicrogyria, pahyhiria and agiria in the abnormal course of neuronal migration, caused by:
- genetic disorders;
- viral infections;
- insufficient blood supply to the child's brain during the prenatal period( 2nd trimester of pregnancy).
 Polymicropathy can be caused by cytomegalovirus infection, insufficient saturation of the placenta with oxygen, and mutations occur in the genes COL18A1( 21q22.3), PAX6( 11p13), K1AA1279( 10q22.1), TUBB2B( 6p25), EOMES( 3p21.3-p21.2), RAB3GAP1( 2q21.3), SRPX2( Xq21.33-q23).
Polymicropathy can be caused by cytomegalovirus infection, insufficient saturation of the placenta with oxygen, and mutations occur in the genes COL18A1( 21q22.3), PAX6( 11p13), K1AA1279( 10q22.1), TUBB2B( 6p25), EOMES( 3p21.3-p21.2), RAB3GAP1( 2q21.3), SRPX2( Xq21.33-q23).
Agiria can occur due to viral infections that enter the uterus or fetus during the first trimester, inadequate blood supply to the fetal brain during the first months of pregnancy. Genetic factors include mutations in the RELN gene( 7q22), X chromosome genes, and 17 chromosomes.
Pahigiria causes mutations in the genes LIS1( 17p13.3) and DCX( Xq22.3-q23).
Symptomatic of
Symptoms for the polymicrogyria are as follows:
- severe developmental delay;
- hypoplasia of the brain;
- disorders in facial muscles, as well as muscles responsible for swallowing, chewing, movement of the tongue;
- mental disabilities of varying severity;
- quadriparesis and hemiparesis of limbs;
- movement disorders;
- breathing complications;
- convulsions;
- epilepsy;
- pseudobulbar syndrome;
- arthrogryposis;
- Cerebral Palsy.
Pahigiriya manifests itself at the age of 2 years. Its main features are:
- delay in physical, motor development;

- epilepsy;
- hypotension( decreased muscle tone);
- mental retardation;
- infantile spasms;
- microcephaly;
- low muscle control;
- difficulty in swallowing, eating problems.
Agiria manifests itself to 3-5 months of the child's life, less often to 8-9 months, the main symptom of pathology is expressed in the rapid retardation of the child in physical and mental development.
The anomaly can also exhibit the following symptoms:
- microcephaly( proportionally small head size);
- lag in growth, in speech and motor development;
- general sluggish state of the child;
- large distance between the eyes, disproportionately small eyes, thin upper lip, high forehead, short nose, low ears;
- epilepsy, convulsive syndrome;
- mental retardation;
- increased muscle tone, due to the lack of inhibitory control of the central nervous system over the neurons of the anterior horns of the spinal cord;
- increased distance between the lungs, the kidneys;
- rapidly developing dementia;
- lack of control over pelvic organs( enuresis, stool incontinence);
- muscular dystrophy.
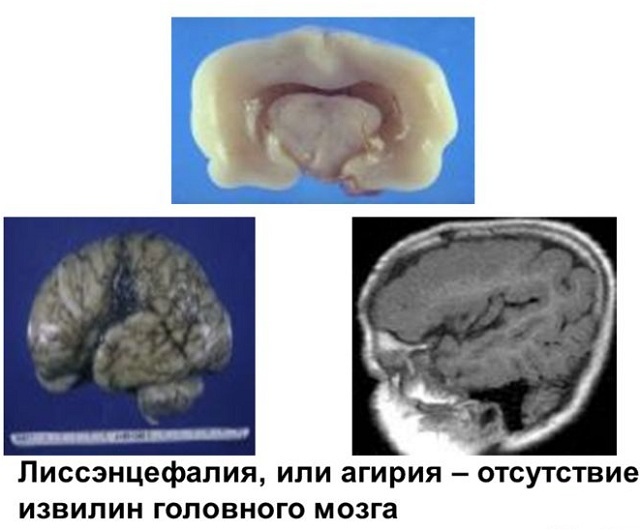
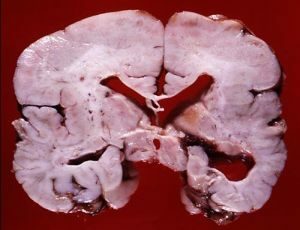
Brain photos in the section and MRI of a child diagnosed with agiria
Diagnosis of
To diagnose malformations of the brain, the following tests are used:
- computed tomography ( defines abnormalities in gray and white matter of the brain);
- genetic analysis ;
- magnetic resonance imaging ( helps to determine the type of disease);
- electroencephalography ( helps to determine the nature of electrical brain activity).
In polymicrogia, the cerebral cortex is abnormally thin, the subarachnoid spaces and the ventricles of the brain are enlarged. Defeats 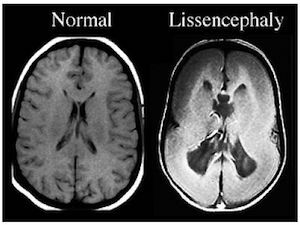 can be located on one or two sides, can be local or extensive. The bark may look abnormally thick due to the large number of small convolutions that merge and form thick, deep masses.
can be located on one or two sides, can be local or extensive. The bark may look abnormally thick due to the large number of small convolutions that merge and form thick, deep masses.
Pahigiriya is determined by the results of MRI, which shows thickening of the cerebral cortex, small convolutions, and an underdeveloped sylvian furrow.
In the prenatal period, malformations of the brain can be determined using ultrasound of the fetus. If suspicions of anomalies in development are sent to additional studies( MRI, genetic analysis of candidate genes).
Medicine is practically powerless.
Effective methods of treating brain malformations are absent in modern medicine. Therapy is aimed at alleviating the symptoms, and maintaining the functioning of the body at an acceptable level.
With polymicrogyria and pahigiria, such methods of alleviating the condition of patients are recommended:
- physiotherapy, including water procedures;
- speech therapy methods;
- wearing orthoses;
- occupational therapy( for motor function disorders);
- reception of anticonvulsants;
- surgical methods.
 With adherence, classical methods of therapy are considered ineffective: taking nootropic medications, massage, physiotherapy.
With adherence, classical methods of therapy are considered ineffective: taking nootropic medications, massage, physiotherapy.
The greatest effectiveness shows treatment with anticonvulsant drugs and muscle relaxants of central action, which can reduce the tone in skeletal muscles.
Often, epilepsy, accompanying the pathology of the development of the brain, is resistant to therapy, and then it is recommended to use a combination of two drugs.
Studies are under way to treat these abnormalities through stem cell transplantation, transplantation of growth factors.
Prognosis and life expectancy of
Patients with polymicrogyria with mild pathology can survive to adulthood. In severe cases, death occurs at an early and young age due to pneumonia or seizures.
There is no single forecast for patients with pahigiria. It can vary in each case and depends on the severity of the pathology of the brain, and the intensity of the symptoms. But usually children with pahigirie live no longer than 20 years.
Underdevelopment of the brain in children with agiria is irreversible and the forecast is unfavorable. Most patients do not survive until the age of 5 years. All patients have complete disability.
Due to depressed swallowing reflexes, it often requires probe feeding. Lethal outcome can occur because of diseases that occur against the background of the main pathology: intestinal paresis, cardiovascular failure, respiratory failure, respiratory muscle atrophy, hypostatic pneumonia.