Most modern people know such a state as neurosis. Often it is caused by a lot of stress in a person's life, and manifests itself in irritability, fatigue, lethargy.
Most modern people know such a state as neurosis. Often it is caused by a lot of stress in a person's life, and manifests itself in irritability, fatigue, lethargy.
In some cases, such symptoms can occur on their own, without the presence of stressful situations. In such a situation, the symptoms are caused by existing or transferred diseases of the internal organs, the nervous and endocrine system.
Neurosis-like conditions are neuropsychiatric diseases, which are similar in manifestations to neuroses, but they do not arise from stresses or psychological factors. Experts are inclined to believe that this is an organic pathology.
content
- Varieties neurosis states
- asthenic syndrome
- Obsessive-compulsive
- syndrome hysterical syndrome
- hypochondriasis
- complex causes
- children causes
- Properties symptoms
- difference from neuroses
- K treatment specific approach
Varieties neurosis states
Among neurosis states isolated asthenic-neurotic, hypochondriacal, hysterical, obsessive-compulsive syndrome.
Asthenic syndrome
This syndrome does not occur suddenly, but progresses gradually. At first, manifestations are expressed in fatigue and a feeling of fatigue, emotional instability and increased nervousness.
Then the irritability disappears, and is replaced by inactivity and apathy. In this case, the person also appears indifferent and wrong perception of the environment, a distorted assessment of events.

Patients have difficulty carrying loud and sharp sounds, touches, bright lights, smells. Also characteristic features are night insomnia and daytime sleepiness, excessive sweating, constant attacks of headache, pain in the heart, a constant sense of tension and anxiety. The patient's condition becomes worse when changing weather and climate conditions.
This syndrome is often the beginning of many mental illnesses, but can also be observed during treatment for somatic and infectious diseases.
Obsessive-compulsive syndrome
The very name suggests that it is associated with obsessive states. The patient may be subject to obsessive thoughts, fears, inclinations, strange rituals, uncontrolled movements.
The patient understands the absurdity of their states and experiences, but can not cope with them on their own. In some cases, it is possible to get rid of obsessions with the help of self-control, but often these conditions return and medical treatment can not be avoided.
Obsessions are often a symptom of neuroses, psychopathy, schizophrenia, and severe depression.
Hysterical syndrome
With this syndrome, the patient exhibits demonstrative behavior and violent emotional manifestations. All the actions of the patient, his  mimicry, speech, gestures, go along with extremely violent emotions, crying, laughing, screaming, wringing hands, fainting, etc.
mimicry, speech, gestures, go along with extremely violent emotions, crying, laughing, screaming, wringing hands, fainting, etc.
This condition should not be confused with a real hysterical fit, as in a hysterical syndrome the patient depicts a seizure, his actions are demonstrative.
There is a possibility of developing paresis, functional paralysis, partial or complete blindness, deafness.
Hypochondriacal syndrome
With this syndrome, the patient has a persistent painful fear for his health, fear of serious diseases. Such fear does not leave the patient all depending on the time of day, or the surrounding reality.
Initially, the impetus for such fears are soreness or discomfort in the body. The patient begins to look for manifestations of various diseases, to feel specific symptoms, to visit various specialists, demanding to diagnose and cure his illness.
Complex causes of
Neuro-like syndrome often appears in childhood. The cause may be prenatal developmental disorders, which were transferred at an early age to a disease and trauma. When the disease appears at a later age, the reasons can be different.
The most common are the following:
- the presence of mental and neurological diseases ( schizophrenia, epilepsy, etc.), while the patient is regularly observed and receives treatment from a district psychiatrist;
- presence of an organic pathology of the brain ( relatively minor disorders in the structure and operation of certain parts of the brain);
- presence of chronic infections ;
- the presence of somatic diseases ( cardiovascular system, liver and gallbladder, gastrointestinal tract);
- presence of chronic allergic diseases .
These conditions appear as a result of abnormalities in the hypothalamic-limbic structures of the brain( caused by the aforementioned diseases), and as a result, the neurodynamics of the cerebral cortex develops.
Childhood causes
In children, the neurosis-like syndrome begins to manifest itself in the age range from 2 to 7 years. 
The appearance of the syndrome in childhood can arise for various reasons. These include:
- pathology of intrauterine development, a negative effect during pregnancy( alcohol, drugs, tobacco smoking);
- diseases of the nervous system of various origins( infectious, traumatic);
- somatic disorders( chronic infectious inflammation, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system);
- hereditary pathologies of various parts of the brain.
Symptoms of
Suspected neurosis-like condition in children is possible in the presence of such symptoms:
- hyperactivity, attention deficit, increased emotional excitability;
- nightmares, fears, phobias;
- attacks of aggression, tearfulness;
- of reduced tone, weakness;
- tics, stuttering, enuresis;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased sweating, or dry skin.
In adults, the syndrome has the following symptoms:
- rapid mood changes, increased anxiety and irritability, predominance of negative emotions;
- appearance of complexities with control behavior, aggression, hot temper;
- vomiting and nausea during stress;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- increased fatigue;
- drowsiness, insomnia, nightmares;
- lack of appetite;
- sharp increase and decrease in heart rate and blood pressure;
- suspiciousness, anxiety, unreasonable fears;
- sweating and tearfulness;
- enuresis.
Difference from neuroses
 Neurosis-like conditions and neuroses have the same manifestations and symptoms. The difference between them lies in the nature of appearance.
Neurosis-like conditions and neuroses have the same manifestations and symptoms. The difference between them lies in the nature of appearance.
Neuroses appear as a result of prolonged stressful situations, which deplete the nervous system, cause anxiety, vegetative disorders. Neuro-like conditions do not have psychological causes. They belong to organic diseases. Previously, they were called "organoids."
The cause of such disorders is a mild cerebral pathology caused by intrauterine growth pathologies, or resulting from a number of diseases.
Special approach to treatment
One of the main signs that help to distinguish a neurosis-like state from a neurosis is the absence of psychotraumatic situations, as well as the ineffectiveness of psychotherapy.
It is necessary to search for the organic cause of the disease. For correct diagnosis, the neuropathologist will appoint a comprehensive examination, including an electroencephalogram and magnetic resonance imaging, a consultation of a gastroenterologist, cardiologist and endocrinologist.
The treatment of these conditions requires a comprehensive approach. A neurologist makes a program of treatment based on the causes of the disease, the symptoms and the severity of the manifestation of the disease.
The focus is on eliminating the causes of the disease( infectious, somatic, organic), and then treating the consequences( brain and nervous system disorders).
The treatment program can consist of such items:
- Medication therapy .It is aimed at combating the organic, infectious, somatic causes of the disease, the normalization in the work of the hypothalamus and the brain. Also helps in the removal of aggression, excitability. The doctor may prescribe
 antidepressants.
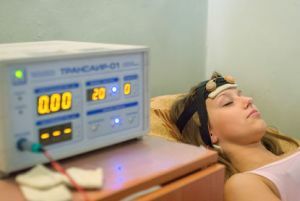
antidepressants. - Physiotherapy .Neuropathologists are directed to electrophoresis procedures using calcium, bromine, dimedrol, aminazine, magnesium sulfate. Electrosleep can also be assigned.
- Psychotherapeutic assistance .Although the disease is not of a psychological nature, however, the disease can cause stress.
- Acupuncture and reflexology .
- Therapeutic gymnastics .
- Sanatorium treatment for .
The main recommendation for the prevention of neurosis-like conditions is a careful attitude to one's health, and timely treatment of existing diseases.
It is also recommended to observe the regime of the day, have enough sleep, avoid physical and mental stress, have adequate nutrition, get rid of bad habits, play sports.