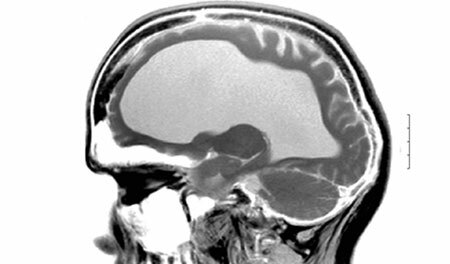
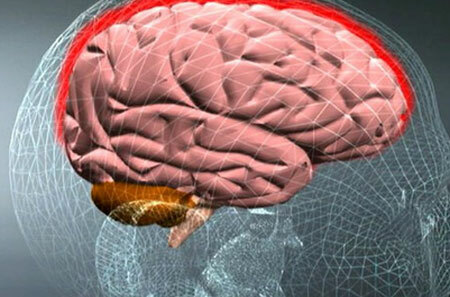
The disease called epilepsy is known to mankind for more than one century - it was first mentioned in the manuscripts of Ancient Babylon. But at the same time the exact mechanism of development of the disease, and most importantly, the methods of its treatment are still unknown. What are the symptoms of this disease, and what can parents of sick children do?

Epilepsy: causes of children
Content of material
- 1 What is epilepsy?
- 2 Causes of the disease
- 2.1 Video - Causes of epilepsy in children
- 3 Classification of epilepsy
- 4 Symptoms of epilepsy
- 5 First aid for seizures
- 6 Diagnosis of epilepsy
- 7 Treatment of epilepsy
- 8 How does epilepsy affect a child's life?
What is epilepsy?
To put it as precisely as possible, then a specific disease, which can be called epilepsy, does not exist - doctors allocate about 60 kinds of a similar syndrome. Among them there are those that flow very difficult, but there are light forms that practically do not cause human inconveniences.
According to statistics, epilepsy is most common in younger and adolescents - it affects 0.5-1% of children.
Most of us imagine this ailment as follows: the patient falls to the floor, beats convulsively, makes strange sounds, and then falls asleep from impotence. But in reality, the situation is not always the same - sometimes the symptoms are blurred, and parents do not even realize that their child is suffering from epilepsy.

What is epilepsy
Causes of the disease
As already mentioned above, scientists have not yet established the exact causes of epilepsy, so we can only talk about certain factors that affect its development.
- Genetic defects. In recent years, experts have increasingly expressed the view that genetics in the case of epilepsy plays a fundamental role. If one of the parents suffers from this disease, the risk of its development in the child is 10%.In this case, the disease is associated with the instability of neuronal membranes and the violation of neurotransmitter links. These phenomena are associated with genetically caused metabolic disorders, chromosomal defects, hereditary neurocine syndromes.
- Developmental disorders of the central nervous system. Typically, such violations occur even at the stage of perinatal development. Among the causes include severe toxicosis of pregnant women, hypoxia, intrauterine infections, birth injury to the head, abuse of mother alcohol and drugs, sepsis.
- History of infectious diseases. The earlier the baby suffered the infection, the higher the likelihood of fits in the future. Most often as a catalyst of the disease are meningitis and encephalitis, sometimes complications of influenza, pneumonia, jaundice of newborns, postvaccinal reactions. In children with cerebral palsy, the disease is diagnosed in 20-30% of cases.
- Pathologies of the brain. These include tumors, cysts and hemorrhages, as well as infectious processes that occur in the brain tissues.
- Craniocerebral trauma. Sometimes the effects of head injuries in the form of epilepsy are not immediately apparent, but after a certain time.
- Lack of some micronutrients. Recent research has shown that a deficiency of a number of trace elements can provoke the development of epilepsy. In particular, the relationship between the onset of seizures and the deficiency of zinc in the patient's body was found.
Very often epilepsy is confused with a convulsive syndrome, but you need to understand that convulsions, unlike epilepsy, are a companion of high temperature and any other conditions.
Video - Causes of epilepsy in children
Classification of epilepsy
Specialists identify several forms of the disease, each of which is characterized by mechanisms of development, symptoms and other features.
- Idiopathic. The cause of this is organic brain defects and changes in the functioning of neurons: they become more active and excitable due to lesions.
- Focal. This form often manifests itself in infancy and childhood, and the symptomatology depends on which part of the brain the pathological process is localized.
- . The temporal. The cause is a lesion of the temporal lobe of the brain caused by ancestral and head injuries, as well as some infections and diseases( brucellosis, meningitis, stroke, etc.).
- Partial. A disease that is characterized by a chronic course, and develops as a result of damage to nerve tissue and their increased activity in any part of the brain.
- Jacksonian. In this case, the convulsive syndrome affects one side of the body: it begins with the fingers, extends over the shoulder and face, and then shifts to the foot.
- The juvenile myoclonic. One of the most common forms of the disease, which is noted in patients aged 8 to 26 years, less often - in infants. The exact causes of its development are unknown, but seizures usually occur in the morning or in the evening, and after taking alcohol.

Epilepsy classification
Symptoms of epilepsy
Symptoms of the disease are quite complex and multifaceted phenomenon, so it is very difficult to determine it. The most striking and characteristic symptom of the disease is the classic seizure, which is divided into several stages and usually occurs spontaneously, regardless of any external factors.
| Phase | Manifestations of |
|---|---|
| Harbinger | Harbinger can develop long( a few hours or days) before an epileptic attack. The patient feels a headache, discomfort, fatigue, a decrease in working capacity, his mood constantly changes. The |
| temperature can rise | Aura immediately precedes an attack, and can be characterized by various symptoms: visual and auditory hallucinations( usually anxious and frightening), a sense of unpleasant odors, etc. |
| Tonic | The child suddenly loses consciousness, his muscles become very tight. After this, there is a sharp fall to the floor, sometimes the patient bites his tongue. This is accompanied by a characteristic sound, arising from the squeezing of the chest, there is no breath, the skin covers turn pale, after which they acquire a bluish color. There is spontaneous bowel movement and urination, pupils do not respond to light. The phase lasts no more than one minute - otherwise the likelihood of a lethal outcome is high due to respiratory arrest |
| Clonical | The patient begins seizures, the respiratory function is restored, the foam of the child comes out with blood. The duration of the phase is about 2-3 minutes |
| Comatose | Deep coma with no response to external stimuli |
| Sleep | The last phase of the seizure is characterized by deep sleep, and after awakening the patient does not remember what happened to him. In addition, he has a disruption in coordination and spatial orientation, speech disorders |

Signs of epilepsy in humans
In addition to classic seizures, the disease can be characterized by the following manifestations.
- A cataleptic fit. A similar condition develops during emotional stress or stress, sometimes even during a fit of laughter. The child descends to the floor, but not abruptly, but by weakening the muscles, that is, it simply settles. Consciousness and memory persist.
- A hysterical fit. Such seizures have two characteristic features: they develop due to some psychoemotional stress and necessarily in the presence of strangers. The fall in this case is cautious, without striking the surface, consciousness is disturbed, but not critical, and never completely disappears. The child begins to roll on the floor, beat him with his feet, makes loud cries, cries and groans.
- Narcoleptic fit. Is manifested by a strong and irresistible desire to sleep. Sleep is short and not strong, but the patient can suddenly fall asleep in the strangest poses and inappropriate places for this. The state of health after awakening is vigorous, the child feels rested, reflexes are present, all mental and physiological processes are normal.
Epileptic seizures need not necessarily follow the above schemes, since they are highly variable. Seizures can be accompanied by loss of consciousness or without it, spread not only to the whole body, but also to one part of it - the upper or lower limb. In addition, epilepsy can be characterized by non-convulsive symptoms: for example, a patient can sit or stand, and suddenly his eye focuses at one point, hands drop, he stops responding to hailstones or other irritants, and then does not remember what happened to him.
First aid for seizures
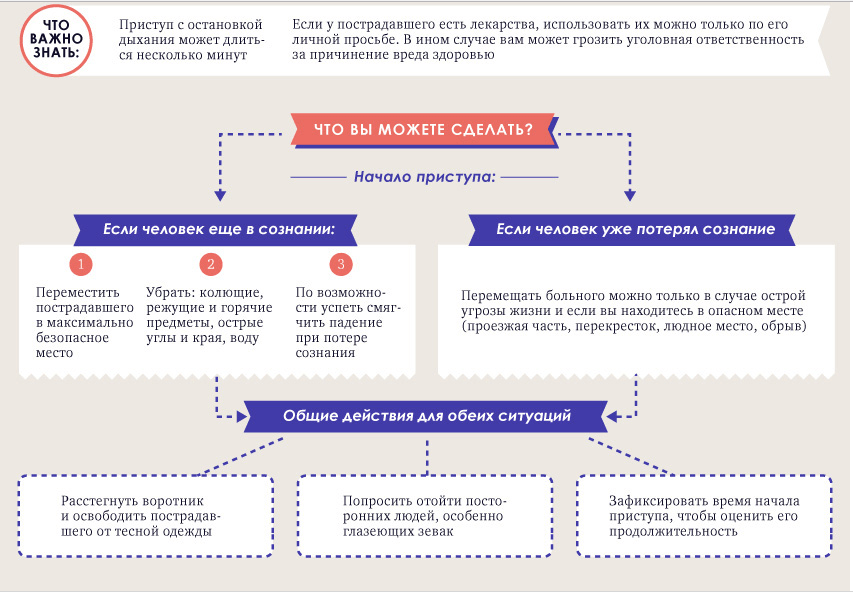
Actions for epilepsy
Parents need to know that the main danger of epilepsy usually does not lie in the convulsions themselves, but that they can get serious injuries, including heads, during the fall. That is why it is necessary to recognize the approach of the seizure as soon as possible and take all possible measures so that the patient can not harm himself.
- At the first signs of a child's seizure, it is necessary to lay it gently on any flat surface so that during convulsions it does not hit the head with sharp objects or edges.
- The head of the patient should be securely fixed, it is best to keep hands.
- If possible, the child needs to be deployed on its side so that it does not get choked with foam, vomit or saliva.
- If the mouth is open, put a folded handkerchief or some soft object between the teeth so that it does not block the airways. Forcibly unclench your teeth with a spoon or knife, hold your tongue, and conduct reanimation during cramps is strictly prohibited!
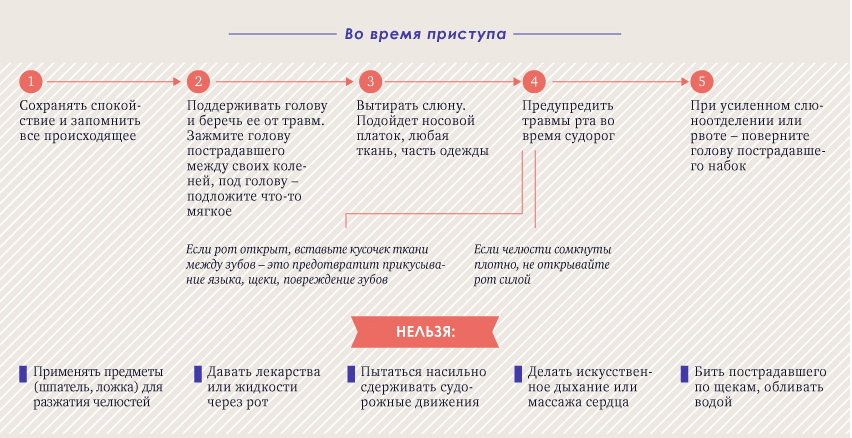
What to do during an attack of epilepsy
Usually, the attack ends after 2-3 minutes, after which you need to take the following actions:
- to check the respiratory activity of the child - if it does not breathe, do artificial respiration by mouth-to-mouth;
- stay close to the patient until his consciousness completely recovers - it may take some time, depending on the form of the disease;
- does not feed or give birth to a baby until it feels normal, and all symptoms of a seizure are left behind;
- if after a fit the fever has risen, it should be brought down by age-appropriate drug.
The doctor should be called in cases where the seizures occurred for the first time or the attack was repeated a second time in a short time, if it lasted more than five minutes, and if there were any injuries that were caused during the seizure.
All children whose epileptic seizure occurred for the first time are subject to hospitalization and a detailed examination. The diagnosis will facilitate the video recording of the incident, so the second parent or another person is recommended to remove the attack on the video.
Diagnosis of epilepsy
Preparation for an encephalogram
Despite the fact that epilepsy is quite common today, it is not easy to establish an accurate diagnosis. The fact that convulsive activity in infancy is high enough, therefore, babies can be marked with conditions accompanied by convulsions that are not epileptic. The most informative kind of research is encephalography, which allows you to accurately determine not only the violations and pathologies of the brain, but also to establish their localization and size. The main advantage of EEG is the ability to differentiate true epilepsy from similar conditions. To exclude hemorrhages, tumors and cysts of the brain, patients are prescribed MRT, and other studies and analyzes are used to clarify the diagnosis. After this, the doctor finds out what type of disease the disease is, resulting in the appointment of further treatment.
Treatment of epilepsy
Algorithm for treating a child with epileptic seizures
Therapeutic measures for epilepsy in children are no different from those used in the treatment of adults. Specific drugs and other drugs depend on the form of epilepsy and other aspects - for example, one or two single seizures do not mean that the child needs special treatment. On the other hand, if the form of the disease is serious enough, then it must be treated, otherwise it will progress. In addition, treatment is not always intravital - sometimes it stops after the patient's condition improves.
The main goal of epilepsy therapy is to prevent seizures in the future. Treatment is always selected for each child individually, including the selection of drugs and doses( there are no general therapeutic regimens).
Another aspect of the fight against epilepsy is that it will not be possible to get rid of this disease quickly - it is a rather long process, and the change of preparations( if necessary) is carried out gradually to avoid possible complications. It should be noted that in about 30% of cases, medication leads to a significant reduction in the frequency of seizures and complete recovery of the child.
How does epilepsy affect a child's life?

In most cases, epilepsy is not a factor that can worsen a child's quality of life
In most cases, epilepsy is not a factor that can worsen a child's quality of life, but for this, parents should have a clear control of the baby's condition. The patient should regularly and clearly take the schedule prescribed by the doctor preparations. No less important role is played by the help of a psychologist - the child should be able to control his emotions and not have complexes about his state of health.
Once the diagnosis of epilepsy was considered a serious violation of health and almost a sentence for the patient, but today the times have changed dramatically. With the right attitude toward your own health or your child's health, the vast majority of people with this ailment lead a full and active lifestyle.