The syndrome, called Far's disease, was first described in the 1930s. Under this name, a group of pathological changes in parts of the brain caused by deposits of calcium salts on the walls of arteries and capillaries was combined.
The syndrome, called Far's disease, was first described in the 1930s. Under this name, a group of pathological changes in parts of the brain caused by deposits of calcium salts on the walls of arteries and capillaries was combined.
As a neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system, Fara syndrome leads to a slow decay of the main functions of the brain.
Calcinates can be found in the brain everywhere, but most often they are noted among the complex of subcortical neuron nodes( basal nuclei).The basal ganglia include the structures of the brain responsible for the correct functioning of the system of unconscious movements.
Calcification in the cerebellum and in some other parts of the brain is possible.
The disease manifests itself with various disorders of the nervous system, delayed or aggressive reaction to external stimuli,  disorders in coordination of movements. Isolate juvenile( children, adolescents) and senile form of the disease, characteristic for persons older than forty years.
disorders in coordination of movements. Isolate juvenile( children, adolescents) and senile form of the disease, characteristic for persons older than forty years.
Often, the disease occurs without any obvious symptoms and may appear during a primary examination. Ethological factors are not finally established, but it is believed that the pathogenetic mechanism is triggered by a violation of calcium phosphorus metabolism.
The complexity of determining the syndrome of Farah is also that the morphological picture does not correspond to the symptoms of the disease. That is, strongly pronounced calcification is often accompanied by mild symptoms.
Causes of the disease
Given the rarity of the illness, the reasons for which the syndrome develops, have not been precisely clarified to date. It is established that the main 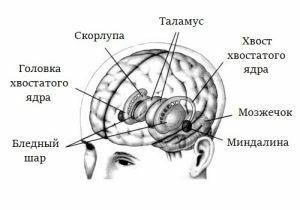 effect on the development of the syndrome of the headlight has pathological changes in the thyroid or other endocrine glands that are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
effect on the development of the syndrome of the headlight has pathological changes in the thyroid or other endocrine glands that are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
In case of malfunctions in their work, changes in the processes of calcium and phosphorus exchange are triggered. Another cause of neurodegenerative disease may be a violation of the acid-base balance of the body, in which the content of acids decreases and, conversely, the amount of alkaline compounds increases very much.
Very contradictory, but has the right to exist, a hypothesis about the genetic nature of the disease. Calcification of the basal ganglia can cause birth trauma. Occasionally, the disease is diagnosed in children with Down's syndrome, in people who underwent head irradiation, and also as a consequence of poisoning with poisons and lead.
The disease can occur at any age in all people, but more often men suffer. In the risk group are people with signs of cerebral calcinosis, patients with hypoparathyroidism, as well as elderly people who have a small vascular calcification.
Pro basal core professionally:
Clinic and symptoms
Determining the presence of the disease The headlight is complicated by an unclear clinical picture. The disease is often asymptomatic. Even if a person has developed the syndrome, then often he does not feel it. Pathological accumulation of calcium in the brain area is manifested by the following symptoms:
- impaired motor function;
- impairment of mental activity, down to dementia;
- spastic paralysis;
- headache;
- abnormalities in the movement of the eyeball;
- dysarthria;
- convulsive syndrome.
When developing the Farah syndrome with signs of parkinsonism, its symptoms can be:
- tremor;

- constant muscle stays in a stressed state;
- shuffling gait;
- fixed face resembling a mask;
- involuntary finger compression, simulating the rolling of pills.
These symptoms are characteristic of the late stage of the disease. In addition to neurological and psychiatric symptoms of the disease, signs of anomaly of the skull, glaucoma, pigment retinitis, pathology of the endocrine system( hypoparathyroidism) are possible, albeit much less often.
The forms of the disorder are their symptoms
Common to any neurodegenerative disease is the slowly progressing death of nerve cells, but it can manifest itself in  in different forms and varieties.
in different forms and varieties.
The most common manifestation of parakinsonism, increased muscle rigidity. Violation of parathyroid function, primary or after surgery, changes the production of parathyroid hormone, which in turn increases the level of phosphorus in the blood and reduces the level of calcium.
Such disorders can occur as tremor, dystonia, dyskinesia, involuntary convulsions of the face, limbs or trunk.
The most common are violations of the basic functions of the brain, which are manifested by a weakening of memory, an excessively strong reaction to various events in human life.
The association of the disease with a violation of normal calcium metabolism, leads to neurological manifestations, accompanied by muscle spasms. The disease also manifests itself in psychiatric disorders, changes in approach, and strong pain sensations.
Often, Far's syndrome is diagnosed on the background of such diseases as toxoplasmosis, parasite infestation of pork chain, echinococcosis. Less commonly, the disease is expressed by tuberous sclerosis of Burneville.
Diagnostic criteria and methods
Diagnosis is confirmed on the basis of neuroimaging methods, but only after the absence of malformations and calcium metabolism disorders is established.
When diagnosing a physician, they first of all rely on generalized data, taken from observations of the patient and his complaints.
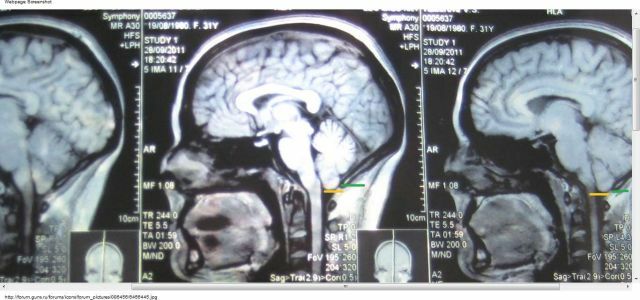
The main tool in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease can be called computer and magnetic resonance imaging. Most of the images show specific lesions that it was difficult to identify with the radiographs of the skull. Confirmation of the diagnosis is the determination of the qualitative content of parathyroid hormone and thyrocalcitonin in the blood plasma.
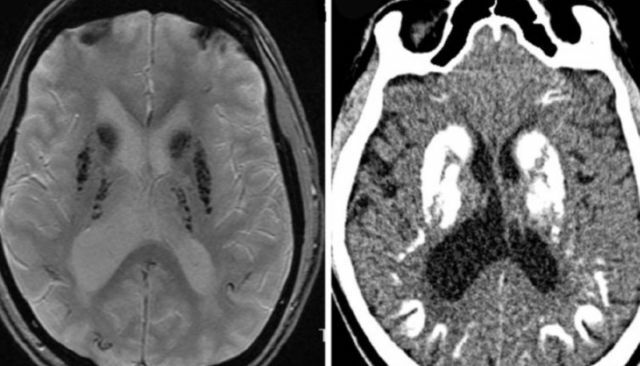
On a photo MRI with brain degeneration with a disease of the headlight
Treatment of
disease It should be noted that it is impossible to remove calcifications in the brain. Therefore, treatment of Farah's disease is symptomatic.
The therapeutic methods used do not affect the degree of calcification and are used to relieve symptoms. If there are special cells in the bone tissue that absorb calcifications, then they are not in the brain.
Principles of therapy include:
- measures that improve the metabolic processes of calcium and phosphorus;
- , when symptoms of parkinsonism develop, treatment with appropriate drugs;
- use of stimulants of brain activity.
Among the most commonly used drugs should be allocated analogues polypeptide hormone. The principle of their action is to enhance the absorption of calcium in the body with active digestion by the body. In addition, they have analgesic effect.
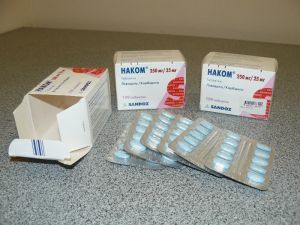 Teriparatide is used to stimulate the development of cells that build up new bone tissue. When accompanied by the symptoms characteristic of Parkinson's disease, Levodopa, Nakom, Medonor, Memantine are recommended. The initial dose is selected in accordance with the patient's response and indications.
Teriparatide is used to stimulate the development of cells that build up new bone tissue. When accompanied by the symptoms characteristic of Parkinson's disease, Levodopa, Nakom, Medonor, Memantine are recommended. The initial dose is selected in accordance with the patient's response and indications.
The specific drug, which is necessary for the treatment of the disease in each case, is appointed by the doctor. The very process of therapy is carried out under close medical supervision and is accompanied by ECG monitoring.
If necessary, adjust the dose of antihypertensive drug. Tablets Akatinol with active ingredient memantine, block calcium channels, there is a normalization of the membrane space.
At the same time, behavioral reactions become normal, cerebral palsy increases and physical activity increases. The drug Levodopa eliminates tremors, dysphagia, hypokinesia, rigidity. In cases of severe illness, accompanied by a worsening of intellectual functions, nootropic drugs are used.
Forecasts are ambiguous
Given that the disease is rare enough and to date has not been adequately studied, the predictions for Far's disease are very  ambiguous.
ambiguous.
The increase in calcium deposits is very slow, over a period of dozens of years. In addition, in the early stages of the disease is practically not diagnosed, and the size of the lesions can be in contradiction with external signs.
The problem is the lack of sufficient information and the impossibility of determining the specific treatment. With the accumulation of informative material and the development of methods for early diagnosis, it will be possible to avoid the irreversible consequences of the disease.