 On a problem such as dysphagia( difficulty swallowing), speak in the case when the problem is swallowing not only solid food, but also liquid.
On a problem such as dysphagia( difficulty swallowing), speak in the case when the problem is swallowing not only solid food, but also liquid.
If, for some reason, it becomes difficult to swallow, anxiety can cause not only the disorder that has arisen, but also the accompanying sensations: choking, nausea with dizziness or without it. And then it immediately becomes not such a trifle as the dubious freshness of the exhaled air.
It should be remembered that swallowing is not just a process of transporting food through the esophagus. It is also a ritual of massage with a food coma intimately adjacent to the trachea and powerful vascular-neural bundles.
The act of swallowing can be upset not only by the growing tumor in the esophagus or hernia of its wall - diverticulum, but also the pressure exerted from the outside, and other reasons.
But in addition to the foundations of mechanical properties, there are also neurogenic causes of dysphagia, commonly referred to as "on a nervous basis".
Contents
- About the painful "coma in the throat"
- Classification and symptomatology
- Difficulty swallowing as a symptom of neuroses
- Features of the disorder in childhood
- Diagnostic methods
- Providing medical care
- On the consequences and prevention
On the painful "coma in the throat"
Anyoneat least once experienced a state of extreme fear, when the mouth dries up drastically, the throat is compressed and generally "stops," so it's difficult not only to swallow, but also to breathe. 
It worked a protective mechanism: the eyes saw the danger, and the brain commanded: stop, freeze!
And the throat really contracted, not admitting a threatening phenomenon inside the body - a reflex worked, which activated the musculature of the organs located on the neck.
And this is not only the respiratory throat, the esophagus also passes here. And his muscles also decreased by command from the top.
In addition to these rapidly passing moments, there is still a test of chronic stress, when "on the nerves of a piece does not climb into the throat."But it, though long, but with time passing.
The states of a coma in the throat, an "intercepted throat" can also arise on the basis of purely neurological causes, when a disease of the nervous system has long been in existence or has just started, resulting in a violation of swallowing, perceived as a feeling that it was suppressed by food or drink.
Neurological pathology leading to the development of dysphagia syndrome includes both acute conditions and diseases that cause changes in the nervous system gradually and continuously.
The first category includes the following diseases:
- stroke;
- botulism;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis.
The second includes:
- Parkinson's disease;
- Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- myasthenia gravis;
- Multiple Sclerosis.

Parkinson's disease almost always provokes difficulties in swallowing food
There are other pathologies, but their contribution to the development of dysphagia is less weighty.
It would seem that the general relationship between botulism and Parkinson's disease is between poor quality canned food and senile infirmity? And between the other reasons, too? The active principle for all these unlike states are poisons.
If, in botulism, the brain is acutely affected by a toxin that multiplies without access to the air of a microorganism, then under inadequate cerebral circulation( at any age), the under-oxidized metabolic products in the brain tissue are formed. Acting much more slowly, but as inevitably as the poison of the microbe.
The same happens in acute cerebral catastrophe - stroke, and in all the cases listed above, leading either to acute edema of the brain, or to conduction disorder in the structures of the medulla oblongata responsible for breathing and swallowing.
Classification and symptomatology
Symptomatic of dysphagia is caused not only by a provocative cause, but also depends on the degree and depth of its development - involving in the process of certain muscles of the esophagus and adjacent areas.
Therefore, dysphagia is classified, subdivided into:
- oropharyngeal;
- is esophageal;
- cryopharyngeal;
- is not associated with esophageal musculature activity.

The first( oropharyngeal) level is the area of the oropharynx, from where the swallowed piece is difficult to move into the esophagus due to whether the pathology of the musculature of this zone, the disorder of its nervous regulation, or the changes that have arisen in the okolohlot structures.
Esophageal dysphagia( pure esophagus) can have 3 levels:
- upper;
- average;
- lower.
It is due either to the mechanically difficult permeability of the esophagus, not related to the activity of its muscles, or to the disruption of the functioning of the esophagus due to one or another reason. A mechanical obstruction can be a tumor, a scar from a burn of the esophagus and similar factors.
Dysfunction can also cause both intoxication with microbial poisons, and vegetative neurosis or other causes. In the case of dysfunction of the circular musculature of the superior esophageal pulpit, discoordination is indicated at the cryopharyngeal level, or about cryopharyngeal discoordination.
The last group of reasons is the squeezing of the esophagus from the outside, as in the case of its clamping of the aortic aneurysm and other similar variants.
Depending on the severity of the situation, 4 degrees of dysphagia are described:
- first - solid food is not swallowed;
- second - in case of inability to swallow solid food, the food in a puree state( semi-liquid and soft) passes the esophagus freely;
- the third - esophagus is passed exclusively for liquids;
- the fourth - swallowing is absolutely unachievable, it is difficult to swallow even saliva.
Dysphagia of any etiology is manifested in the inability to swallow food( swallowed does not go beyond the pharynx and returns to the mouth).Either the swallowing is carried out, but it causes a feeling of "suppression", stopping the coma at one of the throat levels.
The extreme sensation is an acute pain in the center of the sternum, comparable to the heart.
Difficulty swallowing as a symptom of neuroses
The condition, also referred to as functional dysphagia, is a symptom of the diverse nature of neuroses. 
The risk group includes both sexes, but with a higher incidence in women and an age limit of 40 years for men, for whom a state of difficult swallowing is extremely rare.
Pediatric nerve dysphagia makes you aware of your existence in infancy and early childhood, vomiting or regurgitation, anxiety with sleep and appetite disorders.
Children who have reached the age of schoolchildren are distinguished by inexplicable irritability and aggression, closedness, replaced by deliberate, strained fun.
Symptoms of the onset of nervous dysphagia in this segment of life can be intolerance to travel in transport, causing nausea and vomiting( as from motion sickness), a slender( despite sufficient and even increased appetite) physique, a tendency to infect the body with acute infections and chronic carriage of pathogenic roto-and nasopharyngeal microflora.
In neurotic adults, difficulty swallowing arises as a response to confounding and fearful life circumstances( both domestic and industrial).Beginning with a shuffling sensation of "stopping breathing", "inability to breathe", the condition causes fear of death from suffocation, immediately flowing into a panic attack.
Features of the disorder in childhood
The basis for the emergence of a dysphagic disorder in children can serve as both congenital and acquired in the course of life pathology:
- of the nervous system;
- of the spine;
- pharynx;
- directly to the esophagus.
Concretely, the violation of swallowing can be a symptom of athetosis, cerebral palsy, Bechterew-Rossolimo syndrome, Arnold-Chiari disease, or a sign of an anomaly in the development of the esophagus, pharynx, spina bifida.
An infant with a suspected disability can be identified by the following behaviors during feeding: 
- unnatural position of the head and neck;
- is an obvious difficulty in swallowing when sucking or taking a milk formula, sucking with long stops for swallowing;
- refusal to continue sucking, despite the unnaturally small amount of accepted, far from the norm;
- coughing or stopping of breathing with red face;
- spitting out of the nostrils.
These features may occur during and after watering, with less or equal symptom severity.
In a child of an older age, dysphagia can cause frequent pneumonia or bronchitis, the development of asthma( in the absence of disease in relatives), cause reddening of the face during and after meals.
Diagnostic methods
Because the cause of dysphagia can be a variety of conditions, in addition to taking into account objective data, comprehensive diagnosis involves the following:
- X-ray of the esophagus with barium-contrast;
- EFGDS;
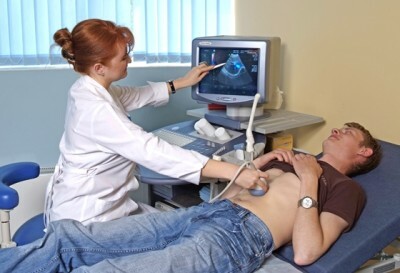
- ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
If necessary, an MRI scan of the brain is performed.
In the diagnostic process, the participation of an ENT doctor is indispensable.
Medical care
Principles of treatment are directly dependent on the cause of the swallowing disorder.
In the presence of volumetric education, leading to the disorder of the mechanics of advancement( tumor, rumen, esophageal diverticulum), 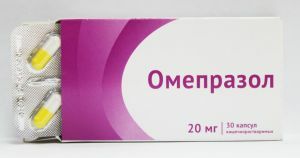 is performed their operative excision.
is performed their operative excision.
Diseases of the pharynx of infectious and inflammatory nature are treated with the use of a complex of appropriate drugs and techniques, while functional( nervous) dysphagia requires treatment from a neurologist, psychotherapist( psychoneurologist).
For dysphagia due to reflux esophagitis, treatment is medicated with Omeprazole and Domperidone.
On the consequences and prevention of
In emergency cases, emergency medical care is required, or emergency hospitalization of the patient is performed. Medicaid is reduced to measures to release the respiratory tract from ingested food and restore the patency of the esophagus when a food coma gets stuck in it,
If you ignore the reasons leading to dysphagia in everyday life, the consequences can be the most sad: the perforation of the diverticulum leading to mediastinitis, the ruptureaortic aneurysm, capable of causing death within a few minutes, a slow fading from esophageal cancer.
Hence the need to prevent pathology leading to the described condition. It is carried out through clinical observation by doctors: pediatrician, oncologist, ENT doctor, neuropathologist and other specialists.
No less important is the performance by parents of young patients and adult patients of the prescriptions of doctors on diet, regimen and compliance with the rules for taking prescribed medications.