Sinusitis is a collective name for inflammatory processes that occur in the paranasal sinuses. The diagnosed sinusitis requires clarification: it is necessary to know the localization of the process, as well as its severity. Sinusitis is almost never a primary disease, but more often - complications of the course of various infections of the ENT region.
Thus, sinusitis is a group of diseases, each of which has a specific clinical picture and features of treatment.
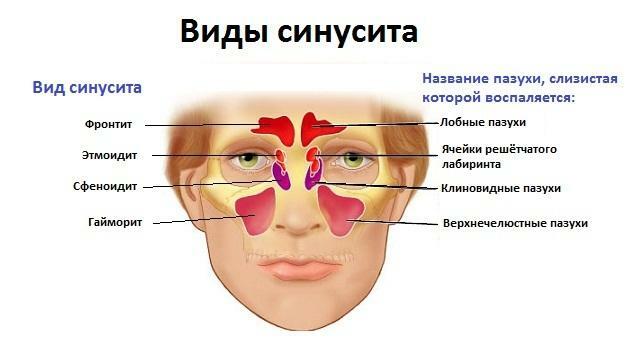
Symptoms of sinusitis in adults
Content of material
- 1 Assimilable sinuses and their role in human life
- 2 Sinusitis: current classification
- 3 Symptoms of sinusitis in adult
- 3.1 General symptoms group for sinusitis
- 3.2 Group of local symptoms for sinusitis
- 3.3 Additional methods for diagnosis of sinusitis
- 3.4 Video - Sinusitis: how to recognize and how to treat
Complementary sinuses and their role in human life
The skull box contains cavities that arenyayut some important, their roles. For example, the cranial cavity is designed by nature to store and protect the brain, the nasal cavity is the most important part of the airway. The accessory sinuses are closed cavities of various shapes, symmetrically located, communicating with the nasal cavity and, in their functionality, related to the airway pathways. The medical name of the paranasal sinuses is, hence the name of the inflammation of these structures is sinusitis.
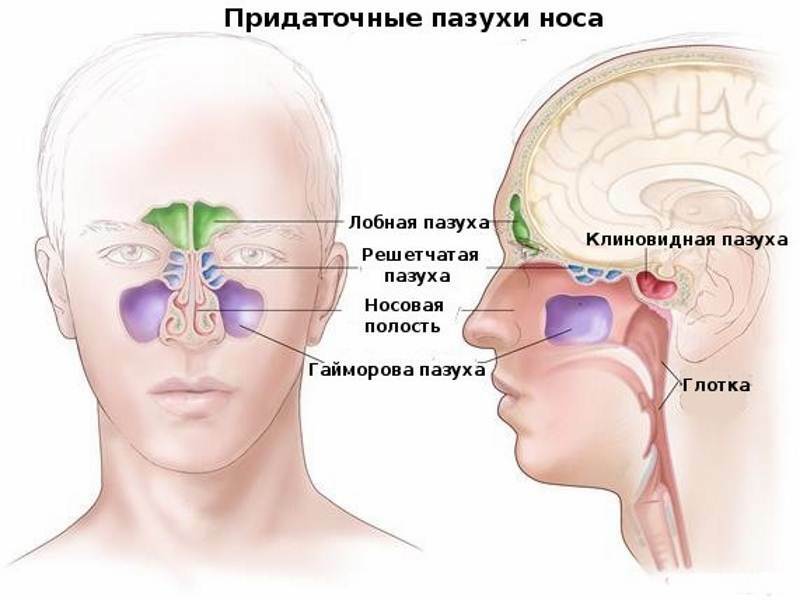
There are three groups of paired sinuses and one centrally located unpaired, namely:
- Maxillary, or maxillary sinus, located in the bone base of the upper jaw. It is involved in pathological processes most often.
- The frontal, or frontal sinus - is located in the thickness of the frontal bone, according to the frequency of occurrence of sinusitis takes the second place.
- The trellis labyrinth, which is sometimes incorrectly called the treacle, is in the trellis. Unlike previous sinuses, it is a group of cavities - cells separated from each other by thin bone bridges, like honeycombs. Of all the sinuses, the trellis labyrinth is organized most difficultly.
- The sphenoid sinus is the only unpaired, but centrally and symmetrically located cavity. In relation to facial structures is located in the cavity of the skull deeper.
Nasal congestion of the nose
All paranasal sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity( or, as doctors say, open into the nasal cavity) through rather narrow apertures or canals. From the inside, the sinuses are lined with the same cells as the surface of the nasal passages. Two types of cells form the basis of the structure of these integumentary tissues:
- Goblet cells - were named in accordance with their shape, perfectly distinguishable under a microscope. The main task of this type of cells is the production of mucus, which envelops the surface of the sinuses and moisturizes them. Humidification is necessary both for the normal operation of all cellular enzymes and for cleaning air passing through the sinuses: dust particles, settling on the moist surface of the airways, can not penetrate into the lungs and are subsequently removed.
- Cells of ciliated epithelium, containing on their surfaces numerous thin outgrowths - cilia. Cilia are in constant motion, pushing the mucous contents of the paranasal sinus outward, thereby contributing to their purification and prevention of infection of these formations. Normal work of the ciliated epithelium is the key to the prevention of sinusitis!
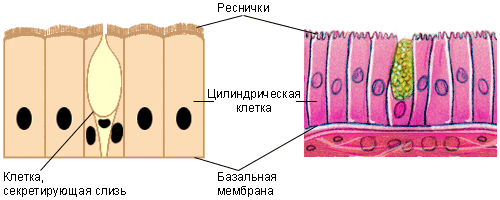
Ciliary epithelium
The final role of paranasal sinuses in human life remains a subject of discussion today. Scientists make their conclusions about the usefulness and function of an organ on the basis of the "duties" performed by it in the body. Among the proven useful properties of sinuses to date, we can distinguish the following:
- Warming and moisturizing the passing air is perhaps the main task of the paranasal sinuses. The air inhaled by a person can have different humidity. Dry air will absorb condensate, evaporating from the surface of the tissues. If there were no sinuses and other airways, this dry air would get into the alveoli in an unchanged state and in the shortest possible time would dry them up. Gas exchange would not be possible. However, with normally functioning sinuses, air during inspiration has time to be saturated with water vapor to almost 100%( !).This is due to the slow, turbulent movement of air in the paranasal sinuses.
- Hollow bones have less weight, but a relatively larger volume than bones that do not have cavities. This phenomenon is very widely used by nature in the animal world, and the most striking example is the bones of birds, whose "relief" allows them to fly. The light and convex facial skeleton in humans provides reliable fixation points for the facial musculature, incl.- mimic muscles, through which inter-specific communications are carried out.
- Complementary sinuses are original resonators that form the strength, timbre and height of the voice. Every person who once had a runny nose could see how much his vocal data is changing at the same time. It is the anatomical features of the structure of the facial skull and affect the characteristics of the voice.
- The protective role of the paranasal sinuses consists in buffering the strokes applied to the face and preventing the deep-seated elements of the nervous system from being damaged. Since most sinuses are located superficially, the injuries cause their outer walls to break first. The inner walls, which are partly part of the skull, usually remain intact.
- Upon inhalation of cold air, it would have to significantly cool the bone structures and thereby negatively affect the formation located in the cranial cavity - eyeballs, teeth, etc. However, the presence of an air "interlayer" in the form of paranasal sinuses protects these organs from a sharp temperature drop.

What is sinusitis
? Sinusitis: the modern classification of
In the International Classification of Diseases of the Tenth Revision( ICD-10), there are fourteen points for sinusitis. Each item is a separate type of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses with its diagnostic criteria and methods of treatment, each point being an independent diagnosis that the doctor has the right to place. The table below summarizes the current understanding of the classification of sinusitis.
| On the severity of the process | Acute( code J01) | Chronic( code J32) |
|---|---|---|
| Localization | Sphenoidal. Ethmoidal. Frontal. Maxillary. Unspecified. Another | Sphenoidal. Ethmoidal. Frontal. Maxillary. Unspecified. Another |

Classification of sinusitis
The word "other" in the classification implies that not one but several paranasal sinuses are involved in the pathological process. If all sinuses are affected, this condition is called "pansinusitis".The process, which covers all the paranasal sinuses on the one hand, is called hemisinusitis.
The word "unspecified" says, respectively, that there is a suspicion of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, but there is not enough information to determine which of these is the site of inflammation.
For adequate treatment of sinusitis, it is necessary to clarify the severity of the process and its localization!
Symptoms of sinusitis in an adult
Since sinusitis is a collective concept, there are no signs of "sinusitis in general", the pathological process will have its own features depending on the localization. Nevertheless, there are a number of common symptoms that are a reflection of what is happening in the body of inflammation.
All symptoms with sinusitis can be divided into two large groups: general and local. Common symptoms are a reflection of the inflammatory process, local - local changes in one or another sinus.

Clinical signs and symptoms of sinusitis
General symptoms group with sinusitis
- Temperature rise .Depending on the severity and prevalence of the process, the temperature may rise to 39-400C( acute sinusitis, pansinusitis, hemisinusitis) or be subfebrile( 37.2-37.50C), such as exacerbation of chronic sinusitis or limited involvement of accessory sinuses. The temperature may not rise at all if a person has decreased immunoreactivity or if chronic sinusitis occurs.
- The manifestations of intoxication : weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbance, loss of appetite, impaired concentration, decreased efficiency.
These symptoms are completely nonspecific and occur in any inflammatory process, so their presence does not make it possible to diagnose sinusitis. More important for this reason are local, local manifestations of the disease.

Clinical picture of sinusitis depending on the severity of the disease
Group of local symptoms with sinusitis
- Runny nose is one of the most important and common signs of sinusitis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses is accompanied by an increase in the amount of detachable from them. Nasal discharge, depending on the nature of the lesion, is transparent( viral sinusitis) or colored yellow, green( bacterial sinusitis), have a whitish, brown character( fungal sinusitis).Since the paranasal sinuses communicate with the nose through the narrow apertures, in the case of edema of the last discharge may not be observed!
- Nasal congestion of - occurs for the same reason as the common cold: the constant secretion of mucus leads to nasal congestion. If the process is one-sided, then one half of the nose can be laid down. This changes the voice, its timbre and color. Headache or analgesia .As the inflammation increases in the sinuses, they swell, the outflow of secret from them is hampered, the inflammation intensifies. In the early stages of the patient's illness, unpleasant, burgeoning, hard-to-localize sensations are disturbed. If the process progresses and outflow from the sinuses becomes difficult, a headache arises that has its characteristics depending on the primary localization of the inflammation:
- sinusitis : the pain is concentrated in the middle part of the face and "in the depth" of the head;
- fronts : the patient is concerned about pain in the forehead;
- etmoiditis : pain irradiates into eyeballs;
- sphenoiditis : pain is located in the depth of the head, and in chronic course - in the occiput, in the parietal region, in the area of the eye socket projection.

Diagnosis and recommended clinical trials
In the diagnosis and treatment of chronic headache, one of the first diseases requiring exclusion is sinusitis!
Other symptoms that can occur with sinusitis are caused by damage to the structures of the nasal cavity. These include:
- Photophobia.
- Visual impairment( especially with sphenoiditis).
- Impaired smell.
- Edema of the face, eyelid( especially with the front).
- Fistula formation and destruction of the nasal septum.
In case of violation of the evacuation of the contents of the sinus and its suppuration( which can occur in the case of pronounced edema of the sinuses) it is possible to develop suppuration with the destruction of bone structures and the formation of severe complications - cerebral abscess, acute otitis media, meningitis, sepsis. In this regard, timely diagnosis of sinusitis is very important.

Principles of sinusitis treatment
Additional diagnostic methods for sinusitis
- The presence of inflammatory contents in the paranasal sinuses can be "seen" with the help of radiography: the horizontal level of the liquid and the shading of the sinus cavity become noticeable.
- When examining the nasal passages, the ENT doctor can see the discharge of mucous or purulent contents from the sinus communication sites with airway pathways.
- In the general analysis of blood in an acute period, leukocytosis, an increase in the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation, an inflammatory shift of the leukocyte formula are observed.
Sinusitis should be suspected in the presence of headache or a feeling of raspiraniya in the head, which are accompanied by discharge from the nose, signs of intoxication and specific changes on the radiograph.
The treatment of sinusitis is performed by otolaryngologists, with three main areas: treatment of the underlying disease, conservative therapy, surgical treatment. Depending on localization, severity, severity of the process and the presence of complications, one or another method of therapy is chosen.