What is it?
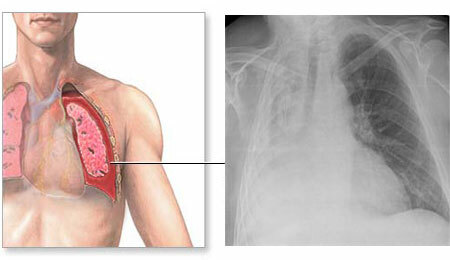
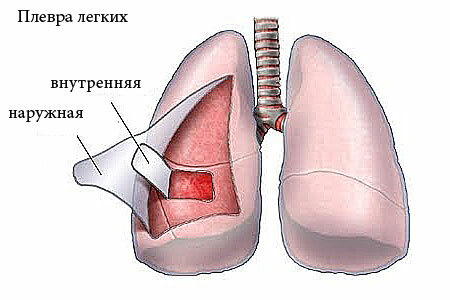
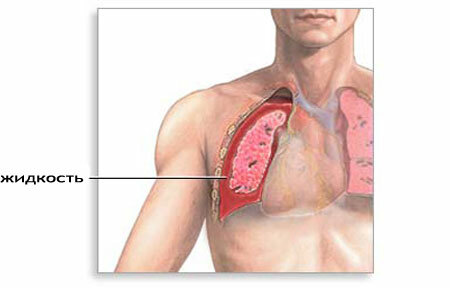
Hydrothorax is a special condition that manifests itself in the accumulation of non-inflammatory fluid, or transudate, in the pleural cavity. The pleural cavity surrounds the lungs and lies between two membranes, one of which covers the lung tissue directly and is called the visceral pleura, the second lining the thorax from the inside and is called the parietal pleura.
Normally, in the pleural cavity there are several milliliters of fluid to ensure free sliding of the lungs during breathing. With hydrothorax, the amount of fluid around the lungs can reach several liters, and can be quite moderate - 10-15 ml.
Hydrotarax of the lung is a type of manifestation of pleural effusive syndrome. The latter can also be inflammatory, i. E.when exudate accumulates( inflammatory fluid).
Classification of
 If hydrothorax is unilateral, then, depending on the side of the lesion, a left-sided or right-sided hydrothorax is distinguished.
If hydrothorax is unilateral, then, depending on the side of the lesion, a left-sided or right-sided hydrothorax is distinguished.
If fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity to the right and left, it is a two-sided hydrothorax, which can be symmetrical or asymmetric. The latter is most common.
Contents
- 1 Causes of lung hydrothorax
- 2 Signs and symptoms of hydrothorax
- 3 Treatment of lung hydrothorax
Causes of lung hydrothorax
Pleurial hydrothorax occurs due to the release of a liquid portion of blood into the pleural cavity. This "filtration" can be either with increasing hydrostatic pressure or with increasing pressure due to a change in the chemical properties of the blood, that is, colloid-osmotic pressure, at which fluid leaves the vascular bed in surrounding tissues with a low amount of protein in the blood.
At the diagnostic stage hydrothorax is any accumulation of fluid with unknown properties and from an incomprehensible source. In the future, additional research helps to establish the true mechanism of pleural effusion and determine whether it is inflammatory or non-inflammatory.
Causes and mechanism of development of hydrothorax:
- Chronic heart failure. This condition stagnates blood in a large and / or a small circle of circulation, which creates the conditions for increasing hydrostatic pressure and causes the passage of fluid into the pleural cavity. The process is usually two-sided.
- Kidney disease with the development of a nephrotic syndrome, which is characterized by a massive loss of protein in the urine. This becomes the background on which the oncotic pressure decreases, which causes the release of plasma into the pleural cavity.
- Reduction in oncotic pressure occurs in other pathological conditions - a pronounced lack of thyroid hormones in the stage of myxedema, in which the exchange of proteins is disturbed;a violation of protein absorption in the digestive tract, as well as inadequate intake of food resulting in dystrophy. As a result of violations of biochemical processes in these diseases, hypoalbuminemia develops - a decrease in the amount of protein in the blood plasma, which contributes to the fall of osmotic pressure, and the liquid part of the blood leaves the vessels into the pleural cavity.
- In ascites( abnormal fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity) and peritoneal dialysis( a special blood cleansing procedure performed in violation of kidney function, during which a large volume of fluid is injected into the abdominal cavity and then a large volume of fluid is removed), intra-abdominal pressure and fluidpores in the diaphragm by the diffusion method enters the pleural cavity.
- Cirrhosis promotes the formation of hydrothorax, both due to ascites, and due to hypoalbuminemia, characteristic of this liver disease.
- Hydrotorax with oncology of the lungs and mediastinal organs arises due to increased pressure due to impaired circulation of lymph and blood( mechanical factor).
Signs and symptoms of hydrothorax
The signs of hydrothorax depend on the amount of accumulated fluid, as well as on the extent of the lesion, and are combined with the signs of the disease that caused the accumulation of fluid.
The following specific signs are typical for the hydrothorax:
- Dyspnoea, which is different in the rate of increase and intensity, depending on the nature of the main start-up process. Initially occurs with motor activity, and then at rest. Pronounced dyspnea indicates the development of respiratory failure;
- Cyanosis is the cyanosis of the skin. In middle-severe cases, especially with heart failure, acrocyanosis is detected - cyanosis of the subungual areas, lips, nose, which is also a sign of respiratory failure. In severe course of heart failure, cyanosis becomes diffuse throughout the body;
- The lag of the patient's chest half when breathing, if the process is one-sided. In a two-sided process, it is difficult to determine the backlog visually;
- Increase in the volume of one half of the chest. With a massive accumulation of fluid, there is a smoothing or bulging of the intercostal spaces;
- Forced position of the patient on the sore side. With a significant accumulation of fluid on one side, this position helps to ensure greater opening of the healthy part of the lungs during respiration, i.e.it is compensatory in nature;
- Along with pneumothorax, hydrothorax can cause compression atelectasis - compression of the lung with loss of airiness and the ability to carry out respiratory movements, which is manifested by dyspnea and dry cough, i.e.acute incompetence of respiratory function develops;
- Pain in the chest with a formed hydrothorax is uncharacteristic. It can appear at the very beginning of the process, or during the resorption of the fluid, when the friction of the pleural sheets is observed with respect to each other;
- Associated edema of the lower extremities is often detected, in severe cases - anasarka - the hypostasis of the entire body's subcutaneous tissue, as well as the hydropericardium - the accumulation of fluid around the heart;
- When percussion( the method by which a doctor tapes your chest with your fingers) reveals an obtuse sound, the upper border of which forms a specific curved "Dmuizo line".This method allows to detect even small amounts of fluid better than X-ray diagnostics. Performing percussion in the changed position of the patient gives a displacement of the horizontal border of blunt sound relative to the body in accordance with the movement of the liquid level;
- When listening to the lungs( auscultation) above the site of fluid accumulation, either a decrease in respiratory noises or a complete absence of them is detected;
- Attenuation or absence of vocal tremor over the lungs on the sore side. The degree of severity of vocal trembling is determined by putting your hands on your chest while you are saying several phrases to the patient.
Instrumental and laboratory diagnostics:
X-ray examination reveals the presence of hydrothorax only in cases where the amount of liquid is more than 100-200 ml. On the roentgenogram, the liquid looks like a uniform darkening, the upper boundary of which is curved towards the dimming. With a vast unilateral hydrothorax, the entire affected half of the chest is darkened, and the organs are shifted to a healthy side.
Carrying out the research in a direct position is often, and in severe cases - necessarily complemented by laterography, when the patient lies on his side during the picture. At this position, the liquid in the picture looks like a dark strip with a horizontal upper level.
With the help of ultrasound of the putative site of hydrothorax, even a small amount of liquid can be detected, starting from 10-15 ml. Also this method helps to identify the best place for puncture.
To determine the nature of the accumulated fluid, make a puncture. This procedure involves the puncture of the tissues of the chest wall with a special needle to enter the pleural cavity to evacuate the fluid.
The transudate is a liquid of light yellow color, odorless, does not form sediment upon sedimentation, has a low relative density( 1006-1012) and a low protein content( of the order of 30 g / l), characterized by a small number of cells and a low activity of the LDH enzyme,the sugar content in the transudate is 3.3 mmol / l and more.
In order to distinguish the transudate from the inflammatory fluid, a Rivolt test is performed, which in this case will be negative.
Additional studies that reveal the cause of hydrothorax are ECG, Echocardiography, ultrasound of the heart, abdominal and renal organs, thyroid gland, biochemical analyzes: urea, creatinine, total protein, bilirubin, hormones TTG and T4;tests to determine the functioning of the kidneys.
Treatment of lung hydrothorax
1. The main disease is treated.
2. Puncture in hydrothorax in addition to diagnostic, is also the main treatment procedure. If there are a lot of liquids, then at a time, it is recommended to slowly evacuate no more than 1200 ml of liquid.
Otherwise, there may be a sharp drop in intrapleural pressure on the side of the hydrothorax and too rapid movement of organs to the sore side. After performing the puncture, check the radiograph.
3. The introduction of medicaments into the pleural cavity is at the discretion of the attending physician on an individual basis and depends on the cause of the hydrothorax.
Forecast
The puncture procedure greatly facilitates the well-being and facilitates the treatment of the underlying disease. Without treatment, with an increase in the amount of fluid, it is possible to develop respiratory failure, acute form.