Metabolism or metabolism - an essential process in the body of all living beings, without which their existence would be impossible. The chemical process by which cells actively proliferate and function is divided into two very different types: plastic and energy.
Despite their differences, the two processes are closely linked, providing a harmonious distribution.
The content of the article:
- 1 The concept of metabolism
- 2 Components of metabolism
-
3 energy metabolism
- 3.1 Preparatory stage
- 3.2 glycolysis
- 3.3 aerobic respiration
-
4 plastic metabolism
- 4.1 Photosynthesis
- 4.2 chemosynthesis
- 4.3 protein biosynthesis
- 5 Comparison of photosynthesis and respiration eukaryotes
- 6 Interrelation of energy and plastic metabolism
- 7 Videos about metabolism
The concept of metabolism
Metabolism or metabolism is the totality of all biochemical reactions occurring at the cellular level. Without it the existence of any living creature. The unique feature of the living organism is the ability to extract energy from the physical the environment, and then - to use it to perform actions such as growth, development and reproduction.
Metabolism characterized by the presence of enzymatic chemical reactions that are formed continuously in the living organism. This makes it possible to extract from the environment to be synthesized energy. At the cellular level, all the biochemical processes similar to each other, which is characteristic of animals, plants or fungi.

Some bacteria and viruses are also subject to the influence of the molecular. Hundreds of coordinated multi-stage elements derived from nutrients or solar energy is converted into easily accessible molecules needed for growth and existence.
Biochemical components are divided into the following groups:
- carbohydrates;
- hormones;
- lipids;
- vitamins;
- fats;
- minerals;
- proteins.
All living things consist of complex organic compounds or proteins that support proper growth at the cellular level, while performing the storage and molecular transport. They can also be used as basic catalysts by which chemical reactions flow equally quickly at a high temperature, a relatively low concentration and neutral conditions.
Various catalyzed enzymes are combined in a more complex structural sequence, where the product of one circuit substrate becomes the next element. This feature is called metabolic pathways, which in turn are connected to each other, forming a complex biological networks.
Components of metabolism
Metabolism is the set of all biochemical reactions, aimed at the growth, reproduction, treatment and many other necessary processes.
Enzymatic reactions are directly related to the conversion of nutrients are divided into two different metabolisticheskih exchange energy (catabolism) and plastic (anabolism). In a healthy and properly functioning organism, the processes of catabolism and anabolism are strictly balanced way that allows you to evenly distribute energy.
energy metabolism
Energy and plastic metabolism though closely interrelated, have fundamental differences.
Despite this, a functional form without the other simply can not exist. Energy metabolism or catabolism occurs in the tissues of the body as long as the necessary nutrients elements not turn into carbon dioxide molecules, water or other less complex chemical connection.

The major catabolic process is digestion, whereby nutrients are ingested and digested into simpler components. Inside the cells, such processes cleave the polysaccharides starch, glycogen and cellulose to monosaccharides: glucose, ribose and fructose. This allows the required amount of energy.
In order to use anabolic synthesis of novel compounds or for the processing of old, the proteins break down into amino acids. Nucleic acids contained in the RNA and DNA are catabolized in nucleotides as part of the energy needs.
Major hormonal structures that regulate energy metabolism in the human body:
- Adrenalin. Produced by the adrenal hormone that increases the overall metabolic rate. This is a key component required to adapt to stressful situations, which speeds up the heart and opens the bronchial tubes in the lungs for a better absorption of oxygen.
- Cortisol. Similarly produced in the adrenal glands. Produced during anxiety, nervousness or prolonged discomfort. It increases blood pressure, blood sugar levels and suppresses the immune processes.
- Glucagon. Produced by the pancreatic alpha-cells, stimulates glucagon splitting of glycogen into glucose substance. It accumulates in the liver, and when the body needs more energy (physical activity, fight, stress), the hormone stimulates the liver for catabolism of the essential elements that enter the bloodstream in the form of glucose.
- Cytokines. A small protein that regulates the interaction between the cells. This type of hormone is constantly produced and destroyed in the body, where they are amino acids or re-used, or recycled for other reactions. Examples of cytokines are interleukins and lymphokines, - elements often evolved in the immune response to invasion of the organism: bacteria, tumors or trauma.
Energy metabolism is similar to combustion, since it allocated similar chemicals. Despite this, between them there is one important difference - the catabolism used capacity is not converted into thermal energy, and goes into inventory for future use.
Disintegration biochemical elements for the body of additional energy - rather complicated process.
Catabolism is characterized by several stages:
- Preparatory.
- Glycolysis (anoxic).
- Cellular respiration (aerobic).
Each stage has a particularly important role in metabolism.
Preparatory stage
The preparatory stage - the only stage of metabolism that occurs in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. The process is characterized by the disintegration of complex organic chemical compounds and more simple, which is possible due to the action of digestive enzymes.

Hierarchical model of the collapse of the preparatory phase:
- exchange of proteins on amino acid compounds;
- conversion of fats to glycerol and fatty nitric acid;
- starch decomposition compounds on glucose.
At the dissimilation process described, there is a slight degree of thermal energy in the human body. Further reactions are cell-molecular.
glycolysis
Glycolysis - a metabolic process of energy exchange that occurs during anaerobic respiration of living organisms within the cytoplasm. Characterized by a sequence of ten enzyme catalysed biochemical reactions, in which glucose is cleaved into two molecules of pyruvate.
The process of glycolysis involves the consumption of energy for further conversion of one glucose into two molecules of the three carbon molecule of phosphate sugar - glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
Many metabolic pathways are totally dependent on glycolysis:
- glycogen synthesis;
- citric acid cycle.
- fatty acid synthesis;
- the pentose phosphate pathway;
- the synthesis of cholesterol.
Exchange with the help of anaerobic respiration is universal for all types of organisms. Since its use is possible even in bacteria, it has found its application in the food industry. Lactic acid, ethyl alcohol and many other products produced glycolysis.
aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration or cell splitting - is a set of metabolic processes that occur in cells for biochemical conversion of energy from adenosine triphosphate nutrients in foods life. Exchange reaction in this case is impossible without oxygen.
The processes involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that break large molecules into smaller, releasing additional energy.
Cell splitting is considered an exothermic redox reaction. Step phase oxidation in the aerobic respiration is the most important in energy metabolism, as produced by the cell reaction provides necessary amount adenozintrifosfatnoy acid.
plastic metabolism
Energy and plastic metabolism use different methods of dealing with energy. Thus, when plastic processes (also called anabolism and biosynthesis) simple molecules used to create more complex chemical compounds or final products.

They will uchuvstvovat in maintaining growth, treatment, reproduction or adaptation to environmental changes. At the cellular level, for forming polymers anabolic processes use more simple monomers that results in the creation of complex molecular structures. For example, amino acids may be synthesized in the proteinaceous elements.
Hormones that regulate plastic metabolism in the human body:
- Estrogen. It is present in both men and women. Mainly produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands. Plays an important role in strengthening the bone, regulates some female sexual characteristics, and (the growth of breast and thighs) establishes the menstrual cycle.
- Testosterone. The primary male sex hormone that is also present in women. It is produced from cholesterol in the cells of the ovaries and testes. Characterized by regulation of male sexual characteristics (hair on the face, rough voice), strengthens bones, helps build and maintain muscle mass. Testosterone levels can influence mood and the distribution of fat cells.
- Insulin. It is produced in the pancreas by beta cells, which contributes to adjustment of the level of leukocyte. Without this hormone, the body can not use glucose - the main source of energy. Disorders of insulin can lead to the development of diabetes.
- A growth hormone. It is produced in the pituitary gland tissues. It stimulates and regulates the growth and early adolescence. At the end of maturation plays an important role in the natural restoration of bone mass.
In addition to the special effects on humans, plastic metabolism also affects many other organisms. The main processes of anabolism include photosynthesis, biosynthesis and chemosynthesis - the important elements of the entire existence of the Earth's biosphere.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis - the process particularly important for the existence of all living organisms on Earth. Characterized by converting light energy into biochemical, which leads to further release a complex molecular structures required for activity.
The main product of photosynthesis - oxygen which is converted from the molecules of water and carbon dioxide, resulting in the formation of glucose, which is output together with oxygen. Plastic process is possible only under the direct influence of light, worked out by solar energy.

Although photosynthesis is carried out in each species differently, the process always starts with the absorption of light energy protein reaction centers that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Such proteins are within the chloroplast, that is most prevalent in leaf cells, whereas bacteria are introduced into the plasma membrane.
Some of the energy in the light-dependent reactions used to remove substances such as water, oxygen gas, and others. Hydrogen is released as a result of water splitting is used to create two additional compounds, which serve as a short-term energy storage, allowing you to transfer it for future biochemical processes.
chemosynthesis
chemosynthesis process occurs in the majority of microorganisms which are capable of simultaneous conversion of biological compounds in organic inorganic type.
These include the following types of bacteria:
- sulfur bacteria;
- hydrogen;
- iron bacteria;
- nitrifying or aerobic.
Preparation chemosynthesis energy occurs due to the oxidation reaction of inorganic compounds: potassium permanganate, iron, sulfur, ammonia, and others. Oxidation proceeds without the presence of oxygen molecules. The most significant element is the carbon dioxide, by which organic compounds are synthesized important.
protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis - molecular complex process by which the incoming cells into the body break up into separate parts, and then are synthesized protein structures. Conversion occurs in two steps: transcription and translation.

The first stage is characterized by copying the transcription of genetic information from DNA to mRNA. Since bimolecular complementarity or correspondence between molecules and enzymes in reading from all the code leads to degeneracy, the data shall be used only with one genetic portion.
As a result, amorphous-crystal substance is completely reproduce the short piece of DNA with a difference in component equivalence to uracil thymine. Broadcast is different from the transfer of the transcription of the synthesized code data already under construction on the protein polypeptide, whose structure is indicated from existing properties in the copied section.
The entire process takes place on a non-membrane organelles ribosomes, which are located in the cytoplasmic contents of the cells.
information transfer step is characterized by several stages:
- Activation of amino acid compound with an aminoacyl adenylate using adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and enzymatic molecules.
- Isolation of adenosine triphosphate, in which the amino acid binds with RNA tolerated.
- The molecular complex formed and patterned in the step of transcription is combined with non-membrane ribosome.
- Necessary amino compound are replaced in the peptide structure, which is characterized by the simultaneous release tRNA chain.
In the first step of protein synthesis can be activated immediately 20 different proteinogenic amino acids. All of them are esterified tRNA specific for them. This process occurs in the cytoplasm using the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Energy consumption is provided by the release of adenosine triphosphate.
In the last step the synthesis of the protein polypeptide chain ends termination signals (three special stop codon) in the structure of mRNA that leads to its separation from the ribosome.
The release of the polypeptide molecules is initiated tRNA specific protein factor that is attached to the ribosome and hydrolytically cleaves the ester linkage between the polypeptide and the chain. All incoming biochemicals are distributed on a living body so as to bring him as much as possible benefit.
Comparison of photosynthesis and respiration eukaryotes
Energy and plastic metabolism characterized by separate stages which are completely different functional effects. So, the main difference between photosynthesis and respiration is that the first only occurs in plants and some bacteria, while breathing - in all living organisms.
Other differences between respiration and photosynthesis eucaryotes are presented in the following table:
| Characteristic | Photosynthesis | Breath |
| Consumed reaction substance | Carbon dioxide; in some cases it is possible the use of water | Oxygen or organic elements; shine |
| place flow | plant chloroplasts | Mitochondria and hyaloplasm (by incomplete oxidation type) |
| Interaction with solar energy | The presence of light is required; the conversion of solar energy into a biochemical property | It can occur both in the light, and without it; conversion of translational energy into the process of energy-rich ATP molecules |
| important stage | The reducing pentose phosphate cycle | Glycolysis, cellular respiration |
The important difference lies in the functional length of each process. If photosynthesis takes place during the day just because it depends on the light, the breath - is a continuous function, without which virtually any living organism simply can not exist.
Photosynthesis converts radiant, or light energy into chemical or organic elements, including oxygen. Breathing also releases the biological potential energy for some other body functions.
Interrelation of energy and plastic metabolism
Energy and plastic metabolism even occur almost simultaneously, their speeds are controlled independently. Thus anabolism cellular structure provides the necessary organic components (carbohydrates, acids) and enzymatic protein structures for the possibility of energy metabolism.
While the catabolism of supplying the cell with energy. Various ways to allow the cell to control the catabolic and anabolic reactions independently. Moreover, some opposing metabolic pathways occur in different parts of the same cells. For example, the liver fatty acid cleaved to acetyl-CoA in mitochondria, and in the synthesis of acetyl-CoA - the cytoplasm.
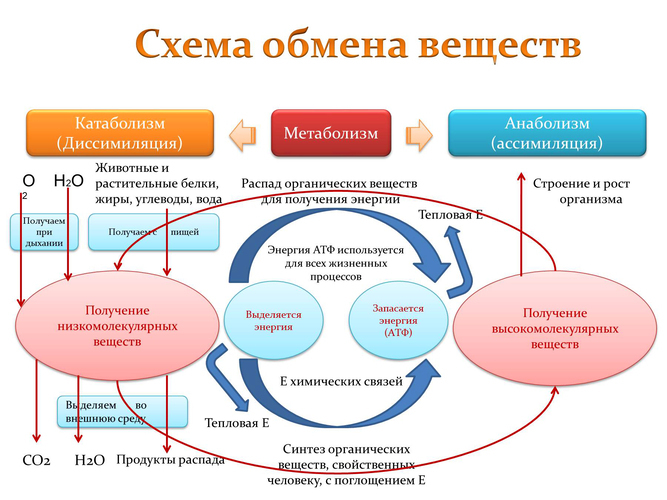
And catabolism and anabolism are important general sequence of reactions, known as the citric acid cycle, or Krebs, which is part of a larger series of enzymatic reactions - oxidative phosphorylation.
Here glucose is cleaved to release energy and is stored in the form of ATP (catabolism), while the other molecules are used as precursors for the anabolic reactions which produce proteins, fats and carbohydrates (anabolism).
Cells regulate the rate of catabolic pathways via allosteric enzyme whose activity increases or decreases in response to the presence or absence of the final product cycle. For example, during the Krebs reaction citrate synthase activity slows down due to accumulation of succinyl-CoA - the product formed later.
Metabolism or metabolism - this is the most important process of life of all living beings. Its harmonious distribution through two stages: the energy and plastic supports the basic functions of the body, without which existence would be impossible.
Videos about metabolism
How to restore the body's metabolism:



