The term "botulism" comes from the Latin word, in the translation meaning "sausage".Such an interesting comparison of the infectious disease with the alimentary product arose because in 1822 the sausage products were thought to be the cause of infection.
This was explained by the fact that they allegedly contain a dangerous fatty acid. But only in 1897 a true causal relationship was established, revealing why the disease develops with the use of sausages. This sensational discovery was made by Ermengen, who isolated bacterial toxin.
Contents of
- 1 Botulism, what is it?
- 2 Pathogen of botulism
- 3 First signs of botulism, incubation period
- 4 Symptoms of botulism
- 5 Diagnosis of botulism
- 6 Treatment of botulism
- 6.1 Complications of disease
- 7 Botulism prevention
Botulism, what is it?

Botulism is an acute infection in which pathological processes in the body are associated with exotoxin of botulinum clostridia. Typical clinical manifestations are paralyzes of skeletal and smooth muscles.
The latter is localized in internal organs. Her paralysis can lead to the development of acute pulmonary insufficiency, with the involvement of respiratory muscles in the pathological process.
The cause of botulism is the neurotoxin produced by clostridia. It causes damage to the nervous system, which leads to paralysis. Currently, 8 serological types of this toxin are known, and in the antigenic relationship they are completely different.
This means that the formation of antibodies to one kind of toxins does not protect from others at all. Currently, botulinum toxin is recognized as the most powerful biological poison. Its toxicity is compared with sarin, which it exceeds by 20-100 thousand times.
Pathogen of botulism
Under adverse conditions, causative agents of botulism form spores that allow to remain viable for a long time. These "protective" forms are widespread in soil, water, rotting plants and animal corpses. However, they do not become the cause of the disease.
The most common route when botulism is poisoned is the consumption of unsuitable preserves, especially prepared at home, for food. This is due to the incredible resistance to environmental factors:
- boiling they last for 5 hours;
- salt concentration up to 18% does not kill them;
- in an acidic medium( pH more than 4.7) they remain viable;
- do not die even under severe freezing( up to -190 ° C);
- direct ultraviolet rays are indifferent to them.
However, the clinical symptoms of botulism can only cause toxin, which is released by vegetative forms( spores do not form it).The danger arises when spores germinate and the propagation of the pathogen occurs under suitable conditions.
The latter include:
- lack of oxygen;
- sufficient temperature regime;
- a certain level of acidity of the medium;
- presence of other microbes, etc.
To develop the disease, all these factors must necessarily be present - only their combined effect leads to the formation of botulinum toxin. For this reason, botulism is not a common pathology.
In most cases there is botulinum toxin in conservation, which is the source of infection. When eating fresh food poisoning is impossible, even if it contains controversy. They are not toxin-producing.
Sources and ways of entering a bacterial toxin into the body can be different. On this basis four main forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Nutritional, developing when a toxin enters the food in which it is already contained.
- Wound - toxin is formed in the anoxic conditions of a wound infected with clostridia.
- Infant, which can develop only in children up to 12 months of age due to absorption of toxin into the bloodstream resulting from spore germination.
- Botulism of children older than 12 months and adults( in the literature there are isolated reports of this variant), which is also associated with the formation of toxins in the intestine.
Food botulism is the most common form. Infection often occurs when using products such as:
- canned food, especially cooked at home;
- smoked products;
- dried products;
- fish products;
- canned mushrooms.
The main condition when a disease can occur is eating only foods that were stored without access to oxygen( or with insignificant intake) and that were not thermally treated( at the proper temperature for a certain time).
So, at home it is not possible to kill the spores, becauseit is not possible to create a high pressure and a temperature of 120 ° C.At the same time, there are no signs of botulism in conservation: the dishes do not have an unpleasant odor; they appear to be normal in appearance, so it is impossible to calculate the organoleptically the contaminated products.
First signs of botulism, incubation period
The first clinical signs of botulism appear after the incubation period, which lasts from 6 hours to 10 days. Its average duration is from 18 to 36 hours.
The onset of the disease can be either acute or gradual. The severity of the symptoms is also different. In some cases, they can be mild, but in others they can be very pronounced. In most cases, patients are engaged in self-diagnosis, referring to various specialists - depending on what hurts. However, this approach only leads to a prolonged time.
Common signs of botulism that distinguish it from other diseases are:
- absence of a rise in body temperature( for fevers, there is almost always a fever in acute infections);
- symmetrical development of neurological symptoms;
- absence of oppression and loss of consciousness except in cases of acute insufficiency of the respiratory system;
- no disturbance of sensitivity.
The first suspicious signs of botulism are:
- dry mouth;
- difficulties when considering closely spaced objects;
- difficulties when reading a common font, which was previously easily perceived;
- the net appears before your eyes;
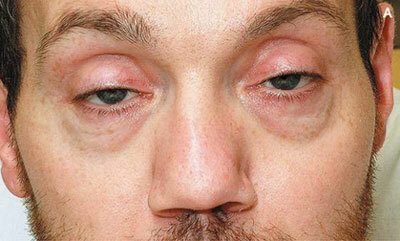
- double the objects under consideration( see photo).
In some patients this progression of clinical symptoms ceases, and the person recovers. As a rule, he does not apply for medical care and these cases remain unaccounted for. With a more severe course, the initial symptomatology is aggravated and new signs of the disease appear. These include:
- changes in voice - it becomes rasping and hoarse;
- speech becomes obscure and smeared with characteristic French pronans;
- feels a lump in the throat;
- perephivanie;
- inadequate salivary formation, which additionally increases the manifestations of dysphagia;
- pronounced weakness of muscles( a person does not want to do anything because of muscle weakness);
- constipation associated with paresis of intestinal musculature;
- difficulty urinating, etc.
Symptoms of botulism

Neurological symptoms of botulism are dominant. In some cases, there may be an increase in body temperature. This is due to the presence in the food of other bacteria, which can additionally provoke a gastrointestinal syndrome. It manifests itself:
- with nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- abdominal pain.
However, these signs are not specific to botulism. They can either be present or absent, so they are not included in the diagnosis. These symptoms may appear before neurological disorders or even against their background.
The lesions of the nervous system are characterized by a number of symptoms:
- symmetry of disorders;
- descending weakness, which in severe cases goes into paralysis;
- involvement of the muscles of the trunk and neck, arms and legs.
Severe intoxication leads to a severe course of ophthalmic manifestations and bulbar palsy. During this period, the risk of aspiration of food, saliva and water increases, which leads to the development of an aspiration syndrome, manifested by purulent tracheobronchitis and pneumonia.
A patient with botulism has a characteristic appearance:
- adynamicity;
- maskedness of the face, which is devoid of facial expressions;
- bilateral ovulation of the eyelids( sometimes it can be one-sided);
- dilates the pupils that practically do not respond to light;
- floating view;
- strabismus;
- dryness of the oral mucosa;
- lack of mobility and gait;
- respiration is rapid and weak;
- pallor of the skin, associated with a drop in pressure;
- bloating due to intestinal paresis.
In the general clinical analysis of blood, the deviations from the norm are minimal. However, monocytosis is a characteristic hematologic trait. The increase in the number of leukocytes and neutrophils, as well as the acceleration of ESR, are suspicious of purulent inflammation.
Diagnosis of botulism
The final diagnosis is based on clinical data and the results of the epidemiological investigation. The presence of neurological disorders can lead to diagnostic errors, when botulism is taken for the disease of the nervous system. At the same time, the doctor takes into account the signs that exclude poisoning by botulinum toxin. These include:
- the presence of tension of the occipital muscles;
- sharp pain in the head;
- pathological signs in the cerebrospinal fluid;
- paralysis of central origin;
- sensitive violations;
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness;
- mental disorders.
In difficult cases, laboratory diagnostics may be required. It involves the detection of botulinum toxin in the blood, vomit, and food that may have caused poisoning. PCR diagnosis for this disease is currently under development.
Botulism treatment
Botulism treatment is carried out without delay, becausethere may be a need for respiratory resuscitation. The main therapeutic directions for this bacterial poisoning are:
1) Gastric lavage of , if no more than 72 hours have elapsed since the time of ingestion of contaminated food. At the first stage, it is carried out by boiling water, and on the second stage - with the addition of soda neutralizing the toxin.
Gastric lavage should not be performed if there is a paresis of pharyngeal and laryngeal muscles,the contents of the stomach can get into the respiratory tract.
2) Introduction of antitoxic anti-butulinic serum. It is not necessary to procrastinate, tk. Serum can neutralize only the toxin that circulates in the blood until it has contacted the nerve endings.
Before the introduction of an anatoxin, a skin test is required,there may be cases of allergic intolerance. If the sample turns out to be positive, then the serum can be administered only according to vital indications.
3) The use of equine immunoglobulin is a promising therapeutic area. It can be used for preventive purposes, development in this direction continues.
4) Symptomatic therapy - desensitization, vitamins, detoxification, artificial pulmonary ventilation, antibiotics, etc. The choice of this or that method( remedy) depends on the specific clinical symptoms.
Complications of the disease
Direct complications of botulism are:
- aspiration pneumonia;
- sites of lung recession( atelectasis);
- tracheobronchitis of purulent character;
- sialodenitis, purulent form( inflammation of the salivary glands).
Attachment of a secondary bacterial infection, which significantly increases the course of the disease, is observed with the use of invasive methods of treatment. Thus, the risk of purulent processes increases with intubation of trachea, tracheostomy, artificial pulmonary ventilation and catheterization of the bladder.
Drug therapy may be complicated by the development of serum sickness. It develops in children approximately on the 8th-10th day after the administration of anti-botulinum serum. Its main mechanism is immune. Symptoms of serum sickness usually appear when clinical neurological symptoms regress.
Botulism prevention
Botulism prevention is based on strict adherence to the rules for the manufacture and storage of canned food, as well as meat and fish semi-finished products.
It should be remembered that it is especially dangerous to eat household canned food in which the controversy can not perish. Therefore, to avoid infection, before eating, homemade canned food is recommended to boil for 15 minutes.
This will completely neutralize botulinum toxins. Persons using unknown products should be under medical supervision for 12 days to identify the very first signs of the disease.
When preparing canned food at home, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- should not make canned canned foods from greens, meats, mushrooms and fish;
- vegetables that do not contain natural acid( green peas, cucumbers), require its artificial introduction( so add vinegar or citric acid);
- can not preserve spoiled vegetables and fruits that have been lying for a long time;
- procure only clean processed raw materials;
- carefully handle the cans and covers, observing the temperature regime;
- optimum storage temperature from 3 to 6 ° C;
- in time to cull bombarded canned food.
The introduction of a vaccine( specific prophylaxis) is indicated only to those who can contact botulinum toxin. To create a lasting immunity, a triple vaccination is necessary.