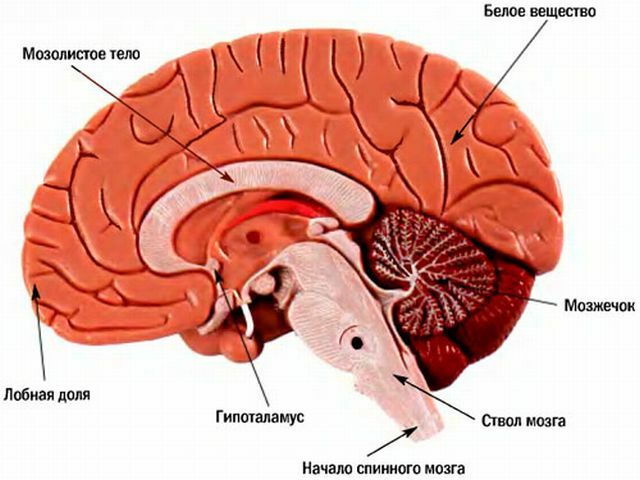
When diagnosed with an ischemic stroke, the left-hand side: the consequences and how many live on these issues, and experts do not give a clear answer. Pathology manifests itself suddenly, blood ceases to flow to the brain as a result of acute disorders of blood flow. Cerebral and neurological focal symptoms is observed within a few minutes, at least - hours. It continues throughout the day, with the untimely appeal to a medical facility the patient may die.

Causes
Ischemic stroke It may be hemorrhagic (artery rupture) of the left brain hemisphere. Predisposing factors differ. Conventionally, they are divided into 2 categories:
- endogenous;
- exogenous.
Left-sided stroke develops when several predisposing factors affects the patient's body. Exogenous causes include:
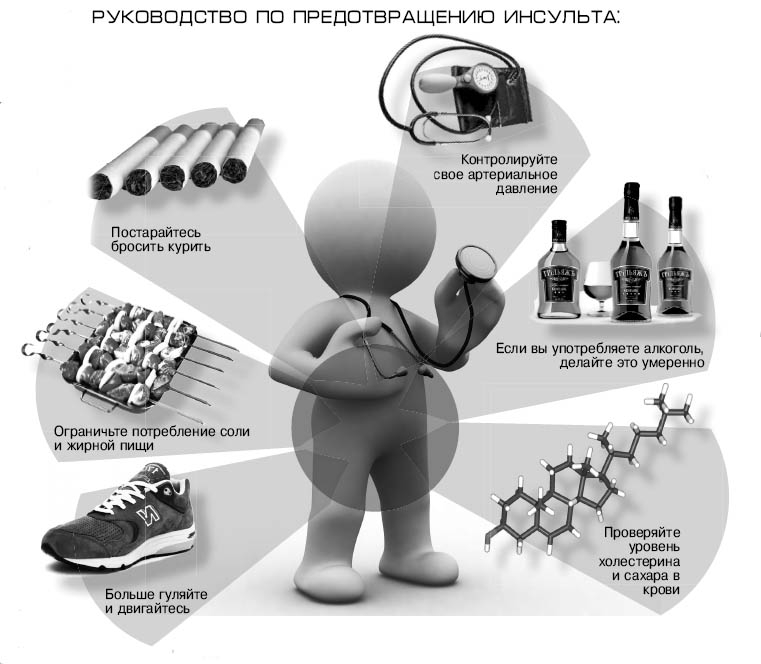
- obesity;
- physical inactivity;
- wrong diet;
- abuse of medicines;
- physical stress.
Excess weight and lack of physical activity lead to a thinning of the blood vessels in the body metabolic processes also violated. Poor diet, overeating, consumption of animal fats increases the risk of formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels and thrombosis. Uncontrolled medication use thins the blood, resulting in intracranial bleeding can occur.
endogenous:
- autoimmune disease;
- heart disease and blood vessels;
- age-related changes of the body.

Diseases that have emerged against the background of failure immunity, can reduce the rate of assimilation of mineral for the body micro and macro. Pathologies of the cardiovascular and circulatory systems, lead to fragility of vessels, thrombosis and aneurysm. The natural aging process violates a number of compensatory functions.
clinical picture
Ischemic stroke, the left hemisphere is manifested in the form of characteristic symptoms that reflect the clinical picture of the disease. They are most pronounced during the Pre-stroke conditions:
- prolonged migraine accompanied by sound and photophobia;
- chest pain;
- Blood pressure drops;
- retching;
- nausea;
- dizziness and stiffness.
Stroke occurs in a few minutes. Acute disorders of blood circulation in the brain are accompanied by:
- convulsions;
- paresis of the upper and lower extremities;
- skewed smile (one corner of the mouth is lowered down);
- incoherent speech, or complete lack thereof;
- short-term amnesia;
- partial or complete paralysis of the left side of the body.

In ischemic stroke patient is unable to raise the left arm up. Impaired coordination of movements. When ischemia occurs sagging skin on the left side of the face.
Features of treatment
Treating pathologies provoked thrombus occlusion of the vessel in the brain, based on the use of a number of drugs. Drug therapy for stroke include:
- thrombolytics, and anticoagulants;
- nootropics;
- vitamins.
Thrombolytics thin the blood, accelerate the dissolution of blood clots and the transport of oxygen to the brain. Nootropics strengthen neural connections and normalize blood circulation in the affected hemisphere of the brain. Vitamins after stroke promotes central nervous system.
How to recover
Recovery from stroke It occurs in several stages. Rehabilitation is needed - there is a restoration of all vital functions lost after the stroke during this period. To speed up the recovery of patients need to go to a specialized center. Rehabilitation consists of three periods:
- early (up to 6 months);
- late (6 to 12 months);
- residual (from 12 months).

Each stage of the restoration should be accompanied by medical physical culture. Special exercises help develop a paralyzed limb. Speech and psycho-emotional state are restored under the supervision of specialists - speech therapist and psychotherapist.
Effects
If the recovery was partly, the consequences may be different after the left-hand stroke. These include:
- violations of the speech center, including muteness;
- short term memory loss;
- inability to self-service;
- reduced motility of fingers;
- partial or complete paralysis;
- psycho-emotional disorders.
Complications after acute circulatory disorders in the brain can lead to disability. In rare cases, a stroke results in the development of brain edema. The pathology progresses rapidly, the patient dies. Relapse occurs when non-compliance with medical prescriptions.
Violations of speech functions
Violations of the speech apparatus are restored partly or fully during the rehabilitation period. Immediately after hitting it the patient becomes slow, meaningless and incoherent. He is not able to build proposals for meaning in the phrases there is no emotional load. If after a stroke paralyzed the left side, the speech disorder is most often observed in right-handers.

Reduced training functions
The patient has difficulty with reading and memorizing information, not only in ischemic type of stroke. The second type - a hemorrhagic stroke: the left side of the brain in such a shock too impressed. The patient can not write without mastering new skills. Rehabilitation does not guarantee full recovery of the old skills - the man, who suffered a stroke, it is difficult for even play songs.
Paralysis of the right side of the body
When left-sided ischemic stroke muscles of the right side of the face and the body lose their tone, nerve impulses does not reach them. The patient had a partial or complete paralysis of the limbs, which increases the risk of disability. On the face there is "false" smile, in which the right-hand corner of the lips constantly lowered.
violation of articulation
After acute disorders of blood flow observed various violations of articulation - the patient is not able to gesticulate when talking, mouth is coordinated properly. Against this background, the patient can not correctly pronounce certain vowels and consonants are sizzling.
Memory loss
After a stroke on the left side effects are reflected in the patient's memory. The main types of violations:
- a complete loss of memory;
- partial memory loss.

Complete amnesia requires a long recovery period. After impact, the patient does not remember past lives, he does not know his own name, does not recognize relatives and people from his entourage. In partial amnesia in the patient's individual memory float pictures from the past, he knows some people. Long period of rehabilitation allows you to fully restore memory properties.
Pathology arises against brain cell death. Patient is unable to remember simple things - how to comb your hair, brush your teeth and get dressed. In most cases, this kind of gaps arise unexpectedly.
Reduction of visual functions
left hand paralysis after a stroke is accompanied by disorders of the organs of vision:
- the image becomes blurry;
- field of vision is narrowed;
- We have to look a long time to concentrate on one subject;
- total vision deteriorates;
- there are jumps in intraocular pressure.
In stroke risk for glaucoma and cataracts increases. The disease can lead to complete loss of vision.
Mental disorders
brain stroke able to shake the psycho-emotional state of the patient. After impact, the patient may receive:
- aggression;
- apathy.

Aggressive state is accompanied by an abrupt change of mood: the patient becomes violent, roughly expresses displeasure. Apathy - the opposite of aggression state in this case, a zest for life is lost, the patient becomes quiet, sluggish, does not show any initiative. Psychic reactions are reduced.
The disorder occurs against previously experienced fear. Stressful situations involving a threat to health after a stroke, causes a person to withdraw into themselves.
Lack of control of natural processes
Ischemic stroke, the left side of the brain affects the cortex, so the background of this part of the lost reflexes. The main manifestations of complications are:
- in difficulty in swallowing;
- the inability to independently control the bowel movement process and the bladder;
- in the appearance of shortness of breath on each inhalation and exhalation.

If a person is not capable to swallow the food introduced into the stomach via a nasogastric tube. Long hollow flexible tube is inserted into the esophagus through the nose. Enteral nutrition is carried out as long as one does not acquire the ability to independently swallow.
After suffering a stroke patient can walk for some time for yourself. The patient, in the absence of violations on the part of the speech apparatus, can indicate their desire to empty the bowel or bladder and ask the boat. If it is broken, experts recommend the use of diapers and diapers for the bedridden patients.
social degradation
Social activity of the patient after ischemic stroke left hand is on the decline. For the first time there is degradation - the state, accompanied by setbacks, the loss of stability and reduce emotional balance. The main manifestations of complications:
- irritability;
- isolation;
- tightness.
Social degradation manifests itself in the patient's unwillingness to communicate with loved ones.
The weakening of mental abilities
After a stroke the left blood, oxygenated, ceases to act in the affected area. This leads to the death of the cells of the cerebral cortex. By a slight weakening of mental abilities include the inability of a man to make simple mathematical calculations (addition, subtraction of one-digit numbers). Stroke in women passes heavier brains recover longer.
If the vessel looked at the site and is responsible for thinking, the risk of post-stroke dementia increases. State is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- sharp memory impairment;
- neuralgia;
- inability to independently count;
- speech disorders;
- the inability to analyze the situation;
- violation of adequate thinking;
- apathy;
- gradual mental deterioration.

Individually, these symptoms do not consider post-stroke dementia. Complex neurological signs categorized as mental deterioration.
Violations of fine motor skills
Fingers and hands are set in motion after the brain sends nerve impulses and gives a "team" to action. The process involves visual, and motor nervous system. Left-handed stroke is able to loosen the motor function of the lower limbs:
- decreased locomotor activity joints;
- muscle loses its tone;
- against the backdrop of swelling and / or pain is observed loss of coordination;
- partial or complete lack of sensitivity.

Reduction process can prevent a number of factors:
- injury to tissue close to the joints;
- incorrect diagnostic activities;
- formation of trophic ulcers on the upper limbs;
- the delays (between stroke and rehabilitation of more than 12 months);
- unstable psycho-emotional state.
Fine motor skills are reduced by massage therapy.
Coma
Signs of severe brain damage is considered to be a coma. The patient is unconscious, he does not respond to external stimuli, it kept alive with the help of machines. Identify several basic types of coma after a stroke:
- precoma;
- first degree;
- pronounced degree (semisopor);
- deep coma;
- fourth degree.
Precoma accompanied by a slight confusion and disorientation, emotional excitement is replaced by sleepiness. During stupor (first degree coma) the patient responds poorly to a stimulus from the outside. Increased muscle tone, cutaneous reflexes are weakened. Babinski symptom saved.

When stupor (marked type) to establish contact with the patient is impossible. Extremities sometimes move chaotically breath infrequent. Sphincters relax, the urine and the feces stand out involuntarily. Pupils contracted, the light reacts poorly. Muscles tense at first, then completely relax. Impaired swallowing reflex.
The patient, who is in a deep coma, does not react to light, pain and other stimuli. Decreased muscle tone, tendon twitch slightly. Temperature and pulse fall, breath broken. The last, fourth phase, characterized by a complete lack of reaction. The lungs are not able to function independently, the patient's life support machine.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy after a stroke left hemisphere of the brain is most commonly diagnosed in patients older than 50 years. Neurodevelopmental nature arise for several reasons:
- withering away portion of the cerebral cortex;
- growth of scar tissue;
- metabolic changes in the body.

The clinical picture of epileptic seizures:
- psycho-emotional disorders (insomnia, headache, loss of appetite, fatigue appear 1-2 days before the seizure);
- convulsions;
- foam mouth;
- fainting;
- tongue retraction;
- wheezing.
Epilepsy after stroke is able to provoke a number of complications, detrimental affect weakened body. The risk of coma and pathology of the cardiovascular system is increased, the patient no longer function normally internal organs and bloodstream.
paralysis
Symptoms of complications vary depending on what part of the body paralyzed. If a stroke occurred on the left, then it paralyzes the right side, and vice versa. Common symptoms that characterize a complication:
- severe headache;
- dizziness;
- numbness of one limb;
- vomiting and nausea;
- hearing and visual impairment;
- lack of coordination;
- fainting;
- acceleration of the heart rate.

Complications with right hemisphere stroke:
- left-sided paralysis of the face and extremities (hemiplegia);
- left-sided full body paralysis (gemisteziya);
- loss of vision (hemianopsia).
Complications with the defeat of the left side of the brain:
- partial or complete loss of speech (aphasia motor);
- reflex twitch limbs (synkinesis);
- mental confusion;
- complete paralysis of the right side;
- amyotrophy.
Paralyzed patients can suffer bouts of unprovoked aggression.
Lethal outcome: many live
The chances to survive after the ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, with proper treatment and first aid timely high. With extensive ischemic stroke left cerebral hemisphere 2/3 patients remain disabled. Paralysis of the left side of the body tolerated harder: the left side is reduced more. Further outlook for life depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and comply with medical prescriptions during the rehabilitation period.