The old name for this very characteristic disease is "trembling paralysis".His own name was given to the disease on behalf of the English physician James Parkinson, who first drew attention to him, releasing the book "Essays on the trembling paralysis."
Parkinson died in 1824, shortly before the discovery of anesthesia. But his ideas and work were in demand in the future. The great French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot( born one year after Parkinson's death) studied the trembling paralysis a lot, and named him the predecessor's name.
For the sake of justice, it should be noted that the first information about the symptoms of the disease are found in ancient Egyptian papyri, and in Ayurveda, as well as in the texts of the Old Testament.
What is Parkinson's disease, what are its causes, how it proceeds and how it is treated? We will understand these questions.
Contents of
- 1 Parkinson's disease - what is it?
- 2 Causes of Parkinson's disease and hereditary factor
- 3 Symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease
- 4 About stages of Parkinson's disease
- 5 Treatment of Parkinson's disease, drugs
- 5.1 Forecast
Parkinson's disease - what is it?

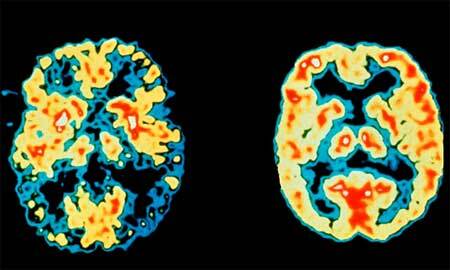
We can give two quite fair definitions of this disease. The first is morphological, more "scientific": Parkinson's disease is an impellent disorder of idiopathic etiology( unknown cause), which is based on the change in the dopaminergic neurons of the subcortical structures of the brain lying in the dense part of the black substance and other nuclei.
If nothing is clear, then a simpler language can be given a second, clinical definition: Parkinson's disease is a disease that manifests itself in a triad of symptoms: akinesia( impaired movement), muscle rigidity, and tremor.
It is important that Parkinson's disease is a particular case of a group of diseases that is manifested by parkinsonism( akinesia, tremor and rigidity).
The difference between Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism is that parkinsonism has a known cause, and Parkinson's disease occurs without them, and is inherently conditioned. Therefore, when considering the causes of the disease, basically, we will consider secondary parkinsonism.
Causes of Parkinson's Disease and Hereditary Factor
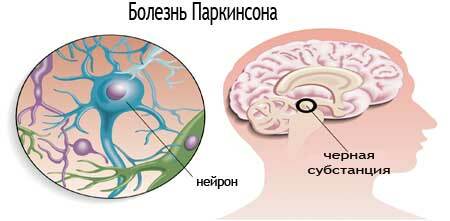 In order for parkinsonism to develop, there must be a degeneration of neurons containing melanin, and therefore coloring these structures darkly: black substance and striped body.
In order for parkinsonism to develop, there must be a degeneration of neurons containing melanin, and therefore coloring these structures darkly: black substance and striped body.
Parkinson's disease affects both the right and left structures, and in parkinsonism, one-sided lesion is possible. In this case, the symptoms appear on the opposite side of the body, thanks to the crossroads of the nerve pathways. The causes of Parkinson's disease are a number of factors provoking the development of parkinsonism:
- Encephalitis, especially lethargic and progredient forms of tick-borne encephalitis;
- Cerebral atherosclerosis, expressed in the elderly. Therefore, certain features of the disease can be found in old people with deep "sclerosis";
- Tertiary syphilis of the brain, afflicted subcortical structures;
- Defeat the mid-brain region by swelling;
- Post-traumatic injury( formation of a concussion focus in the area of subcortical structures);
- Hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke in the appropriate area. This syndrome is called Benedict's syndrome and is caused by a lesion of the red nucleus, with a tremor on the opposite side of the body;
- intoxication with carbon monoxide( carbon monoxide), manganese and its derivatives, organophosphorus compounds.
Young readers do not know, and people at the age of 40 probably will remember that their grandmothers in the 70s and 80s of the last century could take such drugs "from pressure", like "Raunatin", "Rauvazan".They contained the alkaloid rauwolfia. At long treatment( years) from these medicines parkinsonism as developed.
As already mentioned, the cause of Parkinson's disease can be hereditary - for blood relatives of the patient, the risk of getting Parkinson's disease increases by 10 times, in comparison with usual families. In fact, the identification of the cause for the treatment of Parkinson's disease does not affect, but this will be considered below.
The occurrence of the disease is, on average, one case per 1000 people, but with age its frequency increases.
Symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease
The clinical picture in this disease consists of several characteristic symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease: akinesia, rigidity and tremor. In addition, there are vegetative disorders in the form of hypersalivation, seborrhea of the face and other symptoms. Let us consider these features separately.
- AKINEZIA
Slowly but steadily decreases the patient's mobility. From his face disappears facial expressions and all manifestations of expression: anger, joy. It is very difficult to start moving. The patient resembles a vulture, which tries to fly after a full dinner from an even field. Grief makes a few awkward jumps, and the patient shifts on tiptoe, and then goes.
Even worse is the end of the movement: it can not stop suddenly. Again, additional steps are required.
Such symptoms of Parkinson's disease as propulsion, retropulation( steps back, if you push into the chest) and lateropulsy( steps sideways) are manifested. All movements become complicated, slow and incomplete. The patient does not have any unnecessary movements. He commits them only in case of emergency. Even when walking, the hands do not move, and only the legs make small steps.
The face becomes frozen and masked. On the face "live" eyes, which very rarely blink. With the help of the eye, the patient prefers to communicate, for example, by showing to the desired object. Speech is quiet, monotonous, dysarthria appears due to tremor of the tongue.
- Rigidity

If you take the hand of a patient who has had a stroke, then when you try to bend it, you will have a distinct resistance at the beginning of the movement( a symptom of a "folding knife") at the elbow. If you do the same experiment with a patient with trembling paralysis, viscous resistance similar to wax is clearly performed, despite all requests to relax.
Muscles in Parkinsonism simply never relax - this leads to the appearance of some characteristic signs of Parkinson's disease. If the muscles are liable to passive movement, then only jerks, as their tone changes stepwise. This leads to a symptom of the "cogwheel", or, as the neurologists say, the manifestation of the "denticle."
If you raise your head from a lying patient, and then release it sharply, you do not have to worry that it will fall. She will slowly descend, like the second hand on the clock, with no paralysis and muscle weakness.
- Tremor
Most patients have a tremor, but some may not. This is a tremor with a low frequency( 5-6 movements per second).Its cause is a "game" between opposing muscles - antagonists, which can not come to rest in any way.
An important feature of parkinsonism is the disappearance of tremors in conscious movement, for example, when asked to show the tip of the nose. With an essential and cerebellum tremor with intention, the tremor will only increase. Also, there is no tremor in sleep.
The type of movements is also characteristic: it is similar to "rolling paper", "bread crumb", or movement of the "coin counting" type. Especially pronounced tremor in the hands.
- Vegetative disorders
In parkinsonism, salivation changes. A large amount of sebum is allocated, the face acquires a greasy shine, often covered with sweat. There are seborrheic phenomena. In patients there is an increase in salivation.
As can be seen, such a bright clinical picture allowed Parkinson to note this disease in a special way at the turn of the XVIII-XIX centuries, and devote a whole monograph to it.
About the stages of Parkinson's disease
Many classifications, diseases, have been proposed during the time. One of the most popular created by doctors Hyun and Yar in the 60s of last century:
- In the first stage, unilateral defeat;
- The second stage - there is a bilateral symptomatology;
- The third stage is characterized by an expanded clinic;
- The fourth stage involves outside help;The fifth stage is a deep disability.
The stages of Parkinson's disease can also be classified according to the degree of predominance of symptoms( for example, there is a "jaundiced form" of trembling paralysis, that is, predominantly manifestations of akinetic-rigid syndrome).
When diagnosing this disease, it is necessary to exclude the disease in which Parkinsonism occurs. So, we are considering progressing supranuclear palsy, stryonigal degeneration, disease with Levy bodies, or Machado-Joseph disease.
Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease do not get along in the same person. In Alzheimer's, intellect, memory, and social behavior are disrupted. It is hard to care for the sick, because they are untidy, and they can leave the house without finding a way back.
In Parkinson's disease, the patient's untidiness is not due to the fact that he "does not care", but because it is difficult for him to move and he does not go anywhere, the intellect of Parkinson's does not suffer, despite the fact that it is difficult for them to express theirthoughts. Therefore, it is difficult to confuse these diseases.
Treatment of Parkinson's Disease, drugs

Therapy of trembling paralysis is a long and relatively expensive affair. The goal of the treatment is to maintain a balance between the dopamine and acetylcholine system, because in the disease there is oppression of the first of them. Therefore, either dopaminergic activity or cholinergic activity should be increased.
The disease is incurable, and the task of treating Parkinson's disease is to reduce symptoms. The following dopamine-enhancing drugs are used:
- Levodopa - used in disabling forms, reduces hypokinesia and stiffness;
- Bromocriptine( dopamine agonist);
- Selegiline( "Yumeks") - dopaminomimetic;
- Amantadine( dopaminomimetic of indirect action).
Holin blockers are shown in the early stages of Parkinson's disease, for example, to reduce tremor: profenamine, benzatropin, trihexyphenidin.
Almost all medications for Parkinson's have complex patterns of application, constant monitoring with a specialist is required, and monitoring of side effects that the drugs have in abundance.
Therefore, often used combined methods, for example, levodopa in small doses + bromocriptine.
Despite many drugs, cyclodol is still used, which removes tremors. Its side effect is euphoria and hallucinations, as well as psychosis, so it is limited in its use, although it is on the list of vital medicines, primarily because of the cheapness of production.
Severe Parkinson's disease tablets can not stop. Operative methods are applied, as well as minimally invasive neurostimulation.
Forecast
Sometimes you can hear this question: "Parkinson's disease, the last stage - how many live?"In this disease, death is observed from intercurrent diseases. Let us explain with an example.
There are diseases, the very course of which leads to death, for example, peritonitis, or hemorrhage into the brain stem. And there are diseases that lead to a deep disability, but do not lead to death. With proper care, the patient can live for years, even when switching to probe nutrition.
The following conditions are the cause of death:
- Hypostatic pneumonia with the development of acute respiratory, and then cardiovascular insufficiency;
- Appearance of pressure sores with secondary infection and sepsis;
- Habitual constipation, intestinal paresis, autointoxication, vascular collapse.
If the patient is properly cared for, then he can live years, even being confined to bed. Recall the example of Prime Minister Ariel Sharon, who suffered a severe stroke in 2006, and died without regaining consciousness after 8 years, in January 2014.
He was in a coma for 8 years, and the treatment was terminated at the request of relatives when he turned 86 years old. Therefore, the issue of maintaining the patient's life with Parkinson's disease is solved simply - it is withdrawal and support, since the disease does not lead to the immediate death of the patient.
Parkinson's disease, the symptoms and symptoms of which we have reviewed, is one of the most striking and memorable in the course of nerve diseases. She leaves a deep impression on the students, and they remember this disease well. We hope that this article will also leave a mark on your memory, and when you see a patient with signs of trembling paralysis, you will be able to determine where akinesia is, where rigidity, and how tremor is expressed.
This knowledge will not be superfluous - so you will be able to determine the defeat of relatives and friends in time, and begin timely treatment.