This disease, like many in neurology( Parkinson, Binswanger, Van Bogart, Creutzfeldt-Jakob, Wernicke), bears the name of its "pioneer".Of course, in this case it is not so much about the pioneer as the first physician who systematized and pointed out the remaining medical community to one of the types of dementia. It's about the German psychiatrist and neurologist, Alois Alzheimer.
Since 1907, he was the first to describe special cases of senile dementia, which later became known as "Alzheimer's disease."In the XX century, especially at the end, this disease became widely known, especially in intellectual circles.
And often, in the form of self-irony, a man said to himself: "Yes, while it manages to escape from Alzheimer's."It came down to the fact that the name of the disease began to be written with a small letter. But today we will return this disease to our real name, and out of respect for Alois Alzheimer, we will refer to the illness discovered by him as it should, with a capital letter.
Contents of
- 1 Alzheimer's disease - what is it?
- 1.1 About risk factors
- 2 Symptoms and signs of Alzheimer's disease, photo
- 3 Stages of Alzheimer's disease
- 4 How many live with Alzheimer's disease
- 5 Treatment of Alzheimer's disease - drugs and techniques
Alzheimer's disease - what is it?

Alzheimer's disease is one of the types of dementia, or acquired dementia. To immediately put an end to the possible questions, we say that there are three degrees of congenital dementia, which is called oligophrenia( lack of intelligence).
The names of these stages are well known to everyone, as they are often used in everyday life as "soft" curses: debility, imbecility and idiocy.
Idiotic is the heaviest form in which a patient needs a thorough care all his life, is not able to control natural items, and often can not eat without help.
The debility of is the easiest stage in which a person can graduate from a special school, acquire social and labor skills, get a job and even support a family if it is well adapted to the conditions of a stable social environment.
Alzheimer's disease( BA) is one of the most common forms of acquired dementia. And if oligophrenia is a consequence of underdevelopment of the functions of the central nervous system, the essence of Alzheimer's disease lies in their disintegration.
In everyday life you can find such terms as senile dementia, senile dementia, senile dementia or senile senility, which denote the extreme form of personality decay.
- Alzheimer's dementia exists in two versions: normal, which begins after reaching the age of 65 years, and an early form that occurs much less frequently.
Worldwide( as of 2006), there were about 25 million cases of asthma, but given the low level of development of psychiatry and neurology in developing countries, the number of cases can be brought to 40 million. This means that the average risk of getting sick is 1: 180.
This is a pretty high figure. Given the development of medicine and the increase in the number of older people, especially in developed countries, the number of patients will only grow, and by some estimates, by the year 2050 the number of patients may be around 100 million people worldwide.
The causes of Alzheimer's disease, despite a very large number of studies, are 80% unclear. One thing is clear: at an early onset of the disease, heredity plays an essential role.
Three genes have been discovered that are responsible for the development of family and early forms, and if they are defective, the risk of developing an early form of dementia is almost 100%.
Unfortunately, most cases of the disease at a later age do not yet have an established cause, although there are many theories. Of great importance are risk factors that can increase the incidence of this disease.
About risk factors

Alzheimer's disease photo 2
As always, there are factors that can not be modified( modified), and there are factors that need to be changed, if the patient wants and certain efforts made. The permanent, non-modifiable factors of asthma include:
- Elderly, over 65 years of age. This is the main risk factor, and suggests that, in addition to age, nothing could be found;
- Presence of sick relatives( parents, sisters or brothers).As described above, there are gene mutations that make higher family cases than the average in the population;Genetic abnormalities in the E4 allele of the APOE gene. The only so far proven cause. Therefore, this is not even a risk factor, but a "verdict".Even if a child has found this defect, it guarantees him this disease in the future.
In addition to these factors, there are modifiable risk factors. They can be changed by the patient and even cease to exist. These include:
- Moderate memory impairment( cognitive impairment) that occurs at a young age. In the event that their therapy is carried out, progression is stopped, then this risk factor is reduced;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system and endocrine system, which is manifested by chronic hypoxia of the brain( atherosclerosis, diabetes, strokes, hypercholesterolemia, increased blood pressure);
- Harmful habits( mostly smoking);
- An interesting factor is the relationship between the level of education of the patient and the frequency of the disease. The more educated a person is, the more his brain is "trained", the less chance he has for dementia in old age. Apparently, it is a matter of a large number of inter-neural connections and a great perfection of the neural network for an educated person who has got used to solve various tasks;
- Chronic consequences of craniocerebral trauma and permanent trauma. It is known that with frequent attacks on the head, the risk of not only dementia but also other posttraumatic diseases( for example, the development of posttraumatic parkinsonism in the famous boxer Mohammed Ali) increases.
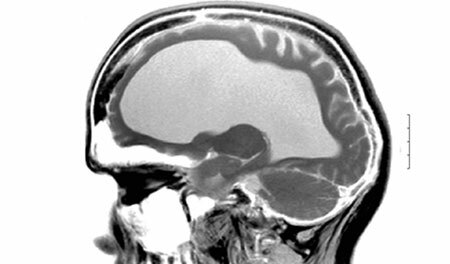
Symptoms and signs of Alzheimer's disease, photo

photo 3
Symptoms of Alzheimer's disease are very diverse, because it is about higher nervous activity. Let's try to talk about the most common symptoms, with a gradual increase in their severity.
It all starts with the fact that the patient, being in full mind, tells his family or colleagues that he has problems with memory: names, dates, geography. He often remembers where the glasses lie, the keys, but all this does not interfere with work or family matters. And, if the patient did not say, no one would notice anything.
When symptoms and signs of Alzheimer's disease begin to show mild - already relatives, colleagues, and testing can detect abnormalities. Most often they consist of the following violations:
- It is difficult to find words that denote objects. The patient often shows by hand;
- Forgotten names, information is remembered and reproduced "in pieces", with the loss of a significant semantic part;
- Decreased ability to plan, to organize;
- There may be a loss of interest from work or from favorite activities, "cooling down" to friends;
- Constantly losing things that used to be "at hand" all the time;
At the stage of moderate cognitive impairment, the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease develop:
- Patients are lost in previously known places, for example, in familiar neighborhoods, or at a metro station, but still remember where they live and can give the exact address of their residence;
- Patients experience difficulties in writing, invoicing, unable to conduct financial activities and pay for purchases;
- Patients forget their biography, confuse dates;
- There are insomniac disorders, the day is confused with the night.
With the progression of Alzheimer's disease, signs are becoming more pronounced - the patient does not remember the current date and time of the year, does not remember who he is by profession, is not able to properly dress in weather and season. I remember only important details about myself. While a person is still able to serve themselves, sometimes there may be problems in using the toilet.
Gradually lost contact with friends and acquaintances who live far away. There is an emotional "burnout" and flattening of feelings.
Then the patient can begin to confuse the names of relatives, put on shoes on the wrong foot. There is untidiness, suspiciousness, pettiness, inclination to litigation. Possible delusions, stereotyped obsessive movements. Insomnia increases, there is a change in eating behavior( gluttony).It is at this stage that older people who are left unattended are lost.
In a more severe stage of Alzheimer's disease, contact with the patient is difficult, the patient is untidy with urine and feces, loses the ability to actively move, and expresses one's thoughts. Need help with walking and even sitting, while eating.
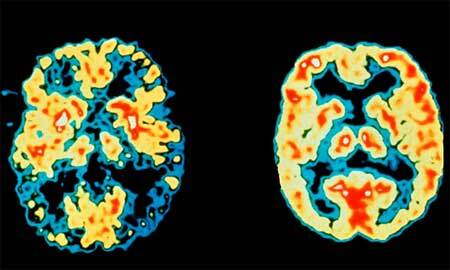
Stages of Alzheimer's disease

photo 5
Like any chronic, progressive disease, asthma has its own periodicity. There are many classifications, but the most convenient is the following, which reflects the stages of Alzheimer's disease, understandable for a person without medical education:
- Predmendency. Sometimes it develops 5-8 years before the onset of the disease, it is confused with "aging" and a general memory impairment. Does not interfere with work;
- Early dementia( not early Alzheimer's disease by age, but by symptomatic progression).The boundary between pre-dementia and early stage is the fact that the signs of the disease begin to attract attention of the surrounding people to the stage of early dementia, and there are difficulties at work;
- Moderate stage. Classical symptoms - speech disturbance, gait. Labor activity or very difficult, often impossible. The patient for the most part serves himself;
- Severe dementia. The patient needs constant care, contact with him at home is either difficult or impossible. The further development of Alzheimer's disease leads to the fact that a person goes to bed, the reflexes of oral automatism come to life, intercurrent diseases arise: infected bedsores, intestinal paresis, hypostatic pneumonia with fatal outcome.
The convenience of this classification is that it does not consider individual symptoms and signs of Alzheimer's disease, but is based on the reactions of others, the impossibility of work and the constant need for care and care.
How many live with Alzheimer's disease
With very good care, patients live quite a long time, the average life expectancy can be indistinguishable from the average in the population. The fact is that the average life expectancy for this disease, after diagnosis, is 7-10 years.
Therefore, the patient's life expectancy, if the disease began at age 65, can be 75 years or more. By the way, this term is 4 years longer than the average life expectancy in Russia, so the patient dies earlier from lack of care and exacerbation of concomitant chronic diseases
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease - drugs and techniques
 Treatment of Alzheimer's disease, the symptoms and signs of which we have considered, are currentlytime is impossible. There are groups of drugs that can only slow the progression of the disease and improve the quality of life of the patient. These funds include:
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease, the symptoms and signs of which we have considered, are currentlytime is impossible. There are groups of drugs that can only slow the progression of the disease and improve the quality of life of the patient. These funds include:
- Anticholinesterase drugs( rivastigmine, galantamine).A typical representative is Exelon, Donepezil. An increase in the concentration of acetylcholine slows the progression, and the formation of a pathological amyloid protein, which is formed in the brain of patients with Alzheimer's disease;Blockers of glutamate NMDA receptors. This is "Akatinol Memantine", which slows the atrophy of gray matter;
- Antidepressants( fluoxetine "Prozac", sertraline, lorazepam);
It is necessary to slow down Alzheimer's disease: treatment, preparations are good, but psychosocial methods of patient management are also very important. They include:
- Supportive psychotherapy aimed at relieving a depressive background;
- Therapy experienced positive memories;
- SIT-sensory-integrative therapy. Patients perform exercises that stimulate the visual, auditory, tactile areas of the cortex, that is, sensations;
- Art therapy, animalotherapy( patients are engaged in simple forms of art: modeling, drawing, communicate with animals).
Of course, complex therapy, a drug that provides the patient comfort, and then care, which soon becomes almost permanent, is very expensive. In developed countries, every case of this disease puts a heavy burden on the state budget, because the patient is already old, and soon loses the ability to work.
Therefore, the causes of the onset and treatment of Alzheimer's disease is information that can help relatives and friends in a timely manner to detect the signs of this ailment and pay attention to it.
The earlier the treatment is started, the longer the time goes to the invalidating stage of the disease.