Sinusitis - mucosal inflammation of one or more paranasal sinuses (maxillary, ethmoid, frontal and wedge).
symptoms of sinusitis
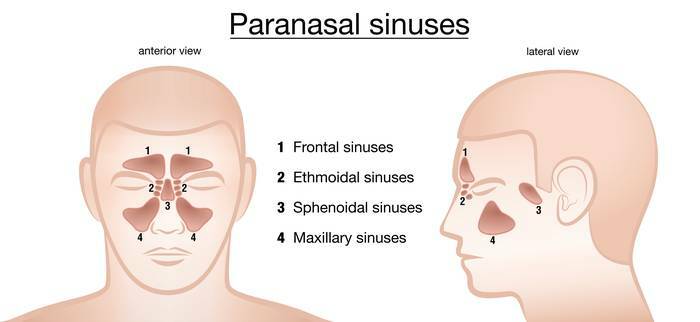
For the duration of sinusitis manifestations distinguish
- acute (3 months)
- relapsing acute (2 to 4 cases of acute sinusitis per year)
- chronic (more than 3 months).
The inflammatory process often involves the maxillary sinus (antritis). The second highest rate stands inflammation of the ethmoidal labyrinth cells (ethmoiditis), then the frontal (Front) And the wedge (sphenoiditis) sinus. Manifestations of the disease depend on the age of the patient.
In young children, for sinusitis usually is not accompanied by any symptoms.
Sinusitis is usually manifested nasal congestion, mucous or purulent discharge from the nose, sinus pain in the area. Often, the disease occurs with fever, symptoms of intoxication (weakness, headache, Loss of appetite), swelling of the cheeks and eyes from the affected sinus pain in the sinuses, copious purulent discharge from the nose. Sinusitis often develops after a viral infection, although it may be a period of general improvements between viral infection and the symptoms of sinusitis.
The most common symptom of the disease in all children, especially children under the age of 10 years - persistent runny nose. Increasingly, they are pus, but there may be watery. In young children, nasal discharge are often slimy or watery. In some cases, parents report bad breath in children.
Headache and pain in the sinuses are the main symptoms of sinusitis in adults and in children, they are observed in one third of cases and very rare in the middle and younger children. Almost half of young children accompanied by acute sinusitis acute otitis.
diagnosis of sinusitis
Diagnosis is carried out ENT doctor.
"Gold standard" diagnostic sinusitis in adults is allocation of paranasal sinus puncture at a large number of bacteria.
this method is not recommended for the diagnosis of sinusitis in children. In children, the diagnosis is based on the manifestations of the disease and ENT examination.
Of additional research methods sinus ultrasound used radiography in frontal and lateral projections, CT scan, Nuclear magnetic resonance. Informative method is the endoscopic examination of the paranasal sinuses.
sinusitis treatment
In acute viral sinusitis not require designation of antimicrobials, and in patients with bacterial sinusitis antibiotics are a mandatory part of the treatment.
Antimicrobial treatment of the disease should be aimed at removal of the pathogen (recovery sterility sinuses), prevention of complications of the disease and the transition in the chronic form. The drugs of choice for the treatment of sinusitis is amoxicillin and amoxiclav, cefuroxime. Alternative drugs for sinusitis are clarithromycin, azithromycin and doxycycline (used in children older than 8 years).
Antimicrobial therapy of recurrent and chronic sinusitis is not fundamentally different from the treatment of acute. Treatment should be comprehensive, combined with surgical methods. A must is to perform puncture sinuses.
Preschool children antibiotics is desirable to administer suspensions or syrups.
Duration of treating sinusitis, usually depends on the form and severity of the disease. In acute sinusitis antimicrobial treatment is carried out for an average of 7-10 days, with exacerbation of chronic sinusitis - up to 3 weeks.
In most cases, when properly administered antimicrobial therapy, there is a significant improvement in 48-72 hours.



