Glomerulonephritis is a group of renal diseases having various clinical manifestations. However, for all the variety of symptoms, the result of untreated glomerulonephritis is one: a gradual or rapid formation of renal failure with possible development of uremic coma.
The function of the kidney can be restored only by eliminating the cause of the disease, prolonged symptomatic therapy and strict regimen. The most radical measure is kidney transplantation.
Contents
- 1 Glomerulonephritis - what is it?
- 2 Forms of glomerulonephritis
- 3 Symptoms of glomerulonephritis - nephritic syndrome
- 4 Diagnosis of glomerulonephritis
- 5 Treatment of glomerulonephritis
- 5.1 Consequences of glomerulonephritis of the kidneys
- 5.2 Prevention
Glomerulonephritis - what is it?
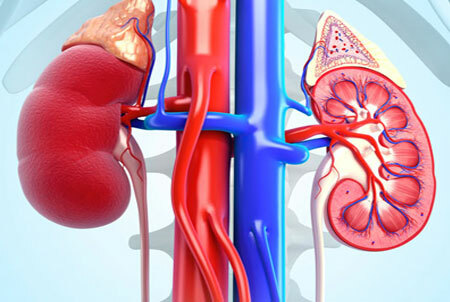
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory damage of renal glomeruli( nephrons) filtering blood plasma and producing primary urine. Gradually, the kidney tubules and interstitial tissue are involved in the pathological process.
Glomerulonephritis of the kidney is a long-term current pathology, without timely treatment leading to disability and serious consequences. Most often develops without severe symptoms and is diagnosed when there are abnormalities in the urine.
An inappropriate immune response to inflammation plays an important role in the development of glomerulonephritis.
Immunity produces specific antibodies directed against its own kidney cells, which leads to their damage( including blood vessels), the accumulation of metabolic products in the body and the loss of the necessary protein.
About the causes of
The disease of glomerulonephritis develops under the influence of the following factors:
- hereditary disorder of the structure of the glomeruli of the kidneys( primary, international classification of the disease N07);
- infections( ICD N08.0) - bacterial( angina, scarlet fever, bacterial endocarditis, pneumonia), viral( hepatitis, parotitis, mononucleosis, chickenpox), parasitic;
- toxic effects - drugs, alcohol, radiation exposure, often vaccines;
- autoimmune diseases( ICD N08.2, N08.5) - vasculitis, periarthritis, lupus erythematosus;
- diabetes mellitus( ICD N08.3) - diabetic vascular lesions spread to the kidneys, other endocrine diseases( ICD N08.4);
- tumor( ICD of diabetic glomerulonephritis N08.1);
- regular supercooling - "trench jade" - is caused by blood flow disturbance due to cold exposure.
The first manifestations of the disease are fixed 1-4 weeks after the provoking effect.
Forms of glomerulonephritis
Glomerular lesion always develops two-sidedly: both kidneys are affected simultaneously.
Acute glomerulonephritis is a rapidly developing nephritic syndrome. This variant gives the most favorable prognosis with appropriate treatment, rather than the asymptomatic course of the pathology. Recovery in 2 months.
Subacute ( rapidly progressive) nephron damage - acute onset and aggravation of the condition after 2 months due to the development of renal failure.
Chronic course - asymptomatic onset of the disease, often pathological changes are detected with already developed renal failure. A long-term pathology leads to the replacement of nephrons with a connective tissue.
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis - nephritic syndrome

Nephritic syndrome is a generalized name of 4 syndromes with varying degrees of severity with glomerulonephritis:
- Edema - swelling of the face, hands / feet;
- Hypertonic - increased a / d( difficult to give drug therapy);
- Urinary - proteinuria( protein) and hematuria( erythrocytes) in the analysis of urine;
- Cerebral is the extreme form of toxic damage to the brain tissue of eclampsia( a seizure is similar to epileptic, tonic convulsions are followed by clonic seizures).
Symptomatic disease depends on the rapid development of pathological changes in nephrons and the severity of a syndrome of glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis
The following symptomatic forms of acute glomerulonephritis are distinguished:
- Ointment - swollen eyelids in the morning, thirst, puffiness of limbs, accumulation of fluid in the abdomen( ascites), pleura( hydrothorax) and pericardium of the heart( hydropericardium), sudden increase in weight up to 15-20 kg and their elimination after 2-3 weeks.;
- Hypertensive - shortness of breath, hypertension up to 180/120 mm Hg.st., some reduction of heart tones, pinpoint hemorrhages in the eye, in severe cases, symptoms of cardiac asthma and pulmonary edema;
- Hematuric - reveals blood in the urine without concomitant symptoms, urine is the color of meat slops;
- Urinary - bilateral lumbar pain, oliguria( small amount of excreted urine), changes in urine composition, rarely elevated temperature( with the disappearance of the acute phase of the disease, the amount of urine increases);
- The unfolded is a triad of symptoms( urinary, edematous, hypertension).
Nephrotic glomerulonephritis
Severely developing nephrotic glomerulonephritis is characterized by pronounced combined signs:
- Pronounced edema, anasarca( fluid retention in the subcutaneous tissue);
- Significant loss of protein( up to 3.5 g / day or more in the urine) against hypoalbuminemia( low amount of protein in the blood - less than 20 g / l) and hyperlipidemia( cholesterol from 6.5 mmol / l).
Chronic glomerulonephritis
Chronic pathology is characterized by alternation of acute periods and temporary improvement. During the remission of the disease, only changes in the urine and hypertension speak.
However, this process gradually leads to the proliferation of connective tissue, shriveled kidneys and the gradual cessation of renal glomerular function.
In this regard, the following forms of chronic glomerulonephritis are distinguished:
- With retention of the renal functional - the stage of compensation - against a background of a satisfactory condition, cicatricial renal scarring progresses.
- With chronic renal failure - the stage of decompensation - increasing intoxication due to the accumulation of urea and creatinine in the blood. In severe cases, ammonia smells from the mouth and cachexia.
- uremic coma is the terminal stage of the development of chronic renal functional impairment: impaired breathing, high a / d, hallucinations / delirium.inoculation with periods of excitation, plaque from urea crystals on the skin.
Diagnosis of glomerulonephritis
Assays for glomerulonephritis:
- Urine examination - protein and erythrocytes( with nephron damage), leukocytes( inflammation sign) in the general analysis, Zimnitsky test - low specific gravity( no change in specific gravity indicates chronic renal failure).
- Blood test - general analysis( anemia, high ESR, leukocytosis), biochemistry( dysproteinemia, hyperlipidemia, hyperaemia - high urea and creatinine), analysis for streptococcal antibodies.
With the detected changes in urine and blood to clarify the diagnosis and the degree of severity of the disease appoint:
- ultrasound of the kidney, X-ray;
- computed tomography;
- biopsy( necessary for finding out the cause of the pathology);
- excretory urography( in acute phase);
- nephroscintigraphy.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis
Symptoms and treatment of glomerulonephritis are closely related - the therapy program depends on the form of the pathological process( chronic or acute) and the severity of the symptoms.
Treatment of acute form
- Strict bed rest.
- Antibacterial, antiviral treatment( for the infectious nature of the disease).
- Symptomatic means( diuretics, hypotensive, antihistamines).
- Immunosuppressive treatment( cytostatics).
- Dialysis - connection to the apparatus of an artificial kidney( with the rapid development of renal failure).
Treatment of chronic form
- Common restorative drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs( NSAIDs, corticosteroids).
- Anticoagulants( to reduce blood viscosity and prevent thrombosis).
- Regular dialysis with severe renal failure.
- Kidney transplantation with ineffective conservative treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis( does not eliminate further autoimmune destruction).
Diet
Therapeutic diet assumes important limitations:
- fluid( puffiness prevention);
- protein food( cottage cheese and egg albumen, fats up to 80 g / day are allowed, caloric content is obtained by carbohydrates);
- salt - up to 2 g / day.
Consequences of glomerulonephritis of the kidneys
Complications of glomerulonephritis are serious enough:
- Renal colic when the lumen is blocked by the ureter by a blood clot.
- Development of acute form of renal failure( with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis).
- Chronic failure of renal function.
- The uremic coma. Heart attack, heart failure.
- Encephalopathy / eclampsia attacks due to renal hypertension and hemorrhagic stroke.
Prevention
Recommendations for glomerulonephritis( avoid complications and prevent exacerbations) include:
- Complete treatment of streptococcal infections, sanation of chronic foci.
- Exclusion of overeating and the subsequent set of extra kilograms.
- Control of blood sugar.
- Motor activity.
- Salt restriction( this recommendation alone can prevent edema).
- Refusal of smoking / alcohol / drugs.
Glomerulonephritis is a dangerous disease comparable to a time bomb. His treatment takes months( in acute form) and years( with chronic).Therefore, kidney disease is easier to prevent than treat and combat disability.