What is it? Scarlet fever in children is a childhood illness that belongs to the class of bacterial infections. It is characterized by inflammatory processes in the lymphoid tissue of the palatine tonsils, nonspecific abnormalities in the body's thermoregulatory system and intoxication syndrome, an abundant skin rash on the areas of the body and face( see photo).
A causative agent associated with the classification of beta-hemolytic bacteria of the Streptococcus class, characterized by great aggressiveness. Getting inside the body produces very poisonous erythrotoxins, called in medicine "red poison".The consequence of exposure is inherent only in this class of streptococcus and is due to pathological processes that alter the mucous and skin.
The first description of the disease dates back to 1675.The English physician Thomas Sydenham described the detailed symptoms of scarlet fever, but he called the disease a purple fever. And only in time, it became known as the beautiful name "Scarlet"( scarlet) scarlet fever, which means scarlet or red.
Scarlet fever in children, photo
Children under the age of 16 are exposed to the disease - babies and one-year-olds suffer very seldom. The disease is transmitted the fastest and most common of all routes of infection - airborne. Especially dangerous is an infected child in the first days of illness.
The bacterium is able to maintain activity in the environment for a very long time, therefore all objects with which the patient contacted could be contagious. Carriers can be perfectly healthy children, but they are carriers of the pathogen.
The incubation period of scarlet fever varies from 2 days to 7, depending on the state of health of the child for the period of infection - the presence of ARI or ENT pathologies, signs of hypothermia. The latency period can be extended to a two-week period. For example, in the period of any disease, the treatment of which uses antibiotics.
Contents
- 1 Symptoms of scarlet fever in a child, rash
- 2 Symptoms of scarlet fever in children, photo
- 2.1 Scarlet fever with worn-out symptoms
- 2.2 Clinical signs of scarlet fever in young children
- 3 Complications of scarlet fever
- 4 Methods of diagnostic examination
- 5 Treatment of scarlet fever in children, prevention
Symptoms of scarlet fever in childrenchild, rash
Symptoms of scarlet fever in children and clinical signs depend on the form of its manifestation:
- Foringual or extrafarious, each of which mIt can occur with a clearly expressed symptomatology( typical form) and a latent form( atypical).
- The infectious process of typical scarlet fever can be expressed in mild, moderate and severe form of the flow, which in turn can be manifested with predominance of separately expressed components - toxic, septic, or mixed( toxic-septic).
- Atypical form of infection differs "blurred"( subclenic) and residual( rudimentary) manifestation.
The general nature of symptomatic of scarlet fever in children is the onset of the disease in acute form. The first hours are characterized by a rapid rise in temperature to 40 and above. At the same time, signs of infection toxins appear on the body - nausea, vomiting, perspiration and sore throat. All this is accompanied by:
- impairment of the child;
- with migraine and weakness;
- with tachycardia and abdominal pain.
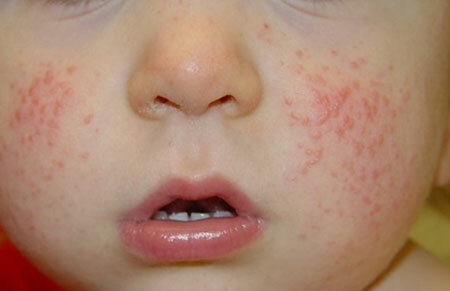
At the onset of , high fever can cause the child to have excessive excitability, mobility, a sense of euphoria, or vice versa - lethargy, drowsiness and apathy. Literally after a while, the first rashes appear on the face and neck, gradually spreading through the body, hands and feet. In some cases, the rash may not immediately manifest itself, but may be delayed for a couple of days.
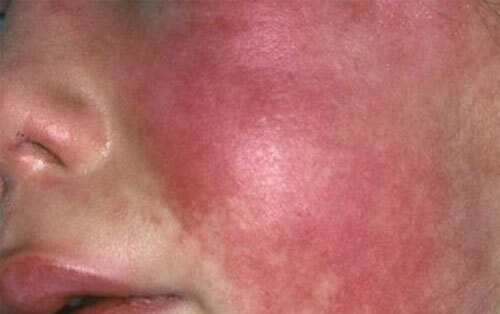
Symptomatic of infectious rash has its own peculiarity, manifested by exanthemal small-scale eruptions on hyperemic skin. It is more pronounced in the lower abdomen, along the sides of the body, the flexion zones of the arms and legs, skin folds - brightly saturated. It may appear as small-spotted foci or merge into solid erythematous spots.
This is very clearly expressed on the skin surface of the cheeks - the bright red merged rashes look very contrasting compared to the light skin of the nasolabial triangle, also covered with a small-point rash. With your finger( lightly pressing on the cheek) you can notice a whitish trace in the form of a strip that gradually changes color to the color of the original scarlet brightness( white dermagrophasm is a characteristic symptom of the disease).
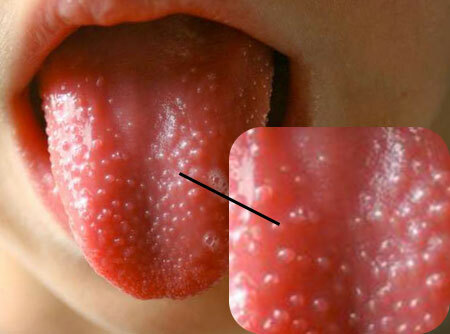
The rash in scarlet fever in children can manifest itself in different ways. Small, small white tubercles with cloudy contents inside( a miliary rash), are capable of merging and forming large bubbles. Frequent localization - hands.
Papular rash, small-spotted or hemorrhagic. With the latent form of the disease( atypical), rashes may not be. Everything depends on the severity of the pathology and the degree of exposure to streptococcal toxins.
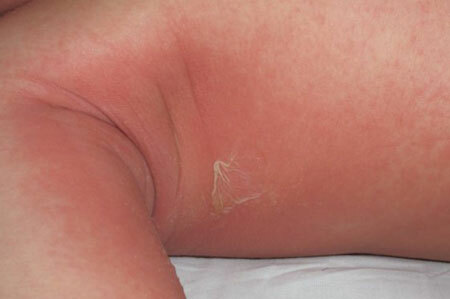
After 5-7 days the patient feels better, the temperature drops, the rashes pale and disappear. Begins the process of small peeling in places of delicate skin( on the folds, neck, ear lobes, groin), consistently extending to the whole body.
On the palms and feet, exfoliation is more intense, leaving large layers. In very young children, peeling may be completely absent.
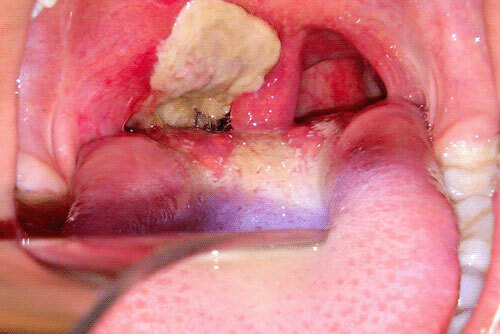
Almost always scarlet fever is accompanied by angina , as the throat and lymphoid tissue of the tonsils are the main routes of infection. But even if the infection struck the body in a different way, the development of angina is guaranteed in 99% of cases. A special difference is due to a limited inflammatory process that does not spread to the mucous membrane of the hard palate, and the completion of the process in a week.
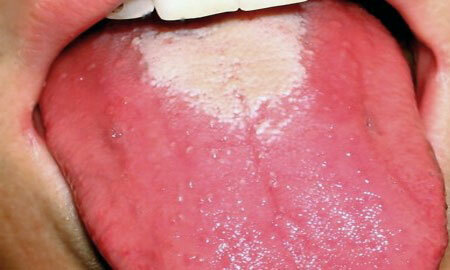
The development of necrotic tonsillitis is accompanied by necrotic foci of gray-green plaque on the areas of the tonsils. By the end of the 10th day the condition is normalized, but for a long time the dryness of the mucous cover of the mouth remains, causing the child to have a constant thirst. When examining the oral cavity, the lagging of the tongue is marked with a dirty yellow coating.
On the third day of the disease the plaque shifts to the center and tongue and acquires a rich scarlet color with raspberry edematous papillae. This symptomatology lasts from 7 to 12 days.
Symptoms of scarlet fever in children, photo
symptoms of scarlet fever in young children, photo 4
Light form of
Are characterized by moderate subfebrile condition. Intoxication signs and eruptions are not very pronounced. They flow together with catarrhal sinus and the main symptoms of the disease for seven days.
Scarlet fever, moderate
The course with the manifestation of a full complex of symptoms accompanied by severe exanthema, catarrhal or purulent sore throat. Symptomatics is characterized by:
- severe fever;
- malaise and pain in the head;
- by apathy towards food and frequent vomiting;
- heart palpitations;
- with plaque and necrosis in the lymphoid tissues of the tonsils;
- is painful when swallowed;
- is an abundant scarlet fever.
The disease does not develop further, after a week and a half the condition and temperature are normalized, the initial symptomatology disappears.
Severe Toxic, Septic and Mixed Forms
In severe toxic forms of the disease, the symptoms manifest themselves in a hyperpyretic temperature, which overshoots the thermometer. Patients strongly lose weight, violations in the psyche are noted, manifesting themselves:
- symptoms of overexcitation or vice versa, patients are severely retarded;
- marked with severe vomiting, sometimes accompanied by convulsions;
- meningeal symptoms and neurogenic syncope;
- persistent increase in blood pressure and tachycardia;
- elements of hemorrhagic exanthema;
- with catarrhal purulent angina;
- manifestations of ITH( infectious-toxic shock).
With severe symptoms of toxicosis, deep fainting is noted - scarlet fever is pale, followed by cyanosis of the skin, cooling of limbs and filiform pulse. At an early detection of the disease and adequate treatment, the intoxication syndrome quickly stops.
Septic form of the disease is added aseptic components - necrotic phenomena of angina with the spread of necrotic processes from the tissue of the tonsils to the soft palate, mucous membrane of the mouth and nasopharynx. Accompanying the development:
- submandibular lymphadenitis;
- periadenitis - inflammation of the tissues adjacent to the lymph nodes;
- suppuration of lymph nodes - adenophlegmons.
The swallowing process is accompanied by a sharp pain, the child is not able to ingest food and drink. Cracks appear due to the dryness of the mouth and the thinness of the tongue on the lips. Breathing of the nose is hindered by the strong formation of a purulent mucus discharge. As a result of the spread of infection from the throat, it is possible to develop purulent sinusitis and otitis, manifestations of symptoms of an increase in the heart( scarlet heart).
Recovery is slow. In a week and a half or on the fourth, because of the development of metastatic abscesses( septicopyemia), or purulent complications, a fatal outcome is possible.
In mixed form, from the fourth day of the disease, the course is accompanied by mixed severe signs of toxic and septic scarlet fever.
Rapid and hypertoxic form of the disease
Rapid scarlet fever in children fully justifies its name developing catastrophically quickly, manifesting itself:
- with severe intoxication syndrome;
- fever with high temperature;
- with severe mental disorders;
- with syncope and delusions;
- with abundant vomiting and convulsions;
- tachycardia and coma.
The life of a child who has fallen into a coma can break off in the first days and even hours of illness. Sometimes, against the background of cyanosis of the skin, the main symptom of scarlet fever is invisible, which contributes to the setting of a false diagnosis.
Hypertensive - hemorrhagic variety - a rare disease. To intoxication syndrome, hemorrhagic skin eruptions and a rash on the mucous membranes are attached. The totality of such manifestations often leads to death.
Scarlet fever with worn-out symptoms of

This group includes several types of scarlet fever, with no obvious symptoms of the disease, minor signs or rapid disappearance. Such patients are the most dangerous. Difficulties in diagnosing contribute to the unhindered spread of infection. Therefore, the probability of meeting with pathology is much higher than how timely it is revealed.
According to clinical manifestations, such pathologies of erased forms are subdivided into a kind of residual( rudimentary) manifestation, a disease without rash and scarlettiasis tonsillitis.
Residual form , rudimentary is characterized by the easiest clinical picture. The main symptomatology is poorly expressed. The first two days of the illness may be a small temperature or remain normal throughout the illness.
In the lymph nodes there may be a slight increase and signs of a minor tachycardia, which is replaced by the end of the week by a decrease in the heart rate. Of all scarlet fever symptoms, the disease can be determined by the condition of the throat, its intense reddening of the spot and moderate pain symptoms while swallowing the food.
Eruptions on the skin are meager and pale, can be localized only in certain zones - the abdomen and flexion surfaces of the extremities in the form of pinpoint hemorrhages. The skin of the nasolabial triangle may be normal or slightly pale.
As a rule, scarletotic symptoms quickly disappear. Peeling may be delayed, or absent altogether. In children who have suffered this type of disease, complications can subsequently develop in the form of nephritis, otitis and other diseases.
Scarlet fever without manifestation of rash
Characterized by the absence or poor manifestation of the main sign - rashes, but with a severe manifestation of all other symptoms, the development of necrotic tonsillitis with early purulent complications.
Extra-pharyngeal type of the disease
Very rare type of pathology, unlike other forms of scarlet fever in children, infection occurs due to penetration of the pathogen into wound skin or mucous cover trauma, postoperative wound burns, during labor or in the process of complications with open purulent foci. Such babies are not dangerous to others, since they do not isolate the pathogen by coughing or sneezing.
Fast latent period( several hours, day) complicates timely diagnostics. Clinic of the disease has its own characteristics - the absence of signs of tonsillitis, inflammatory reactions and the appearance of rashes in the areas of penetration of the pathogen.
Clinical signs of scarlet fever in young children
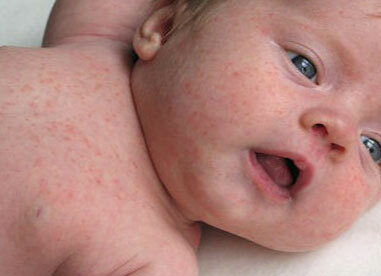
Small patients and infants tend to manifest septic type of the disease, but the intoxication syndrome manifests itself poorly. In some cases, the disease occurs with a slight subfebrile condition, scanty symptoms of angina and a pale rash.
But, in other, similar circumstances, it can be expressed by signs of necrotizing angina or nasopharyngitis, multiple purulent-necrotic consequences.
Complications of scarlet fever
The most severe consequences of scarlet fever transmitted by children - in the form of streptococcal sepsis, adenophlegmons and mastoiditis, with the inclusion of etiotropic benzylpenicillin preparations into the curative program, is practically reduced to zero. Today, it can be:
- sinusitis or otitis media;
- toxic myocarditis, which develops at an early stage of the disease;
- nephritis, manifested in the second week by moderate signs of proteinuria, leukocyturia, erythrocyturia or cylinduria;
- "child" pneumonia and bronchopneumonia;
- infectious processes in bone tissue and brain.
Early diagnosis of the detection of scarlet fever in children, treatment and prevention, help to prevent more serious complications in time.
Diagnostic examination methods
For a precise diagnosis of the disease, a number of diagnostic tests should be performed.
- Expanded blood clinic, helping to identify the cause-the indicators of the reaction of ESR, leukocytosis and neutrophileosis confirm or refute the bacterial nature of the infection.
- Bacteriological study confirms the diagnosis, highlighting the pathogen in the mucosa secretions from the oropharynx.
- Express-method is the most promising technique, revealing by means of the coagglutination reaction, the antigen of the pathogen within half an hour.
Treatment of scarlet fever in children, prevention of
With easy flow of scarlet fever in children, treatment is performed on an outpatient basis. In difficult cases, to avoid possible complications, children are hospitalized.
An activity restriction mode and a balanced vitaminized diet with thermal and mechanical processing of food are prescribed. It should be soft mashed, do not contain irritating ingredients and not capable of causing an allergic reaction. The diet is dominated by a dairy-vegetable diet.
Drugs of the penicillin group are widely used as a drug therapy. The age-related dosage and tolerability of the particular drug are taken into account. The course of treatment of scarlet fever with antibiotics lasts up to 7 days.
In toxic forms with pronounced symptoms of intoxication, antitoxic serum is introduced in the first two days. To increase protective immune functions, gamma globulin is prescribed.
In case of complications, a therapeutic treatment of the disease caused by the complication is carried out.
Prevention of
Prevention of scarlet fever in children today is not done by vaccination. Specific prophylaxis is - gamma globulin, applied to weakened babies who were in contact with patients with scarlet fever.
If treatment of scarlet fever in a child with antibiotics was prescribed in time, the isolation time can last up to 10 days.
A child is discharged from the hospital after all the inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx have been stopped and the final recovery is complete. Children are admitted to children's institutions after 12 days. In addition, weekly quarantine is introduced in groups of children in contact with the patient.