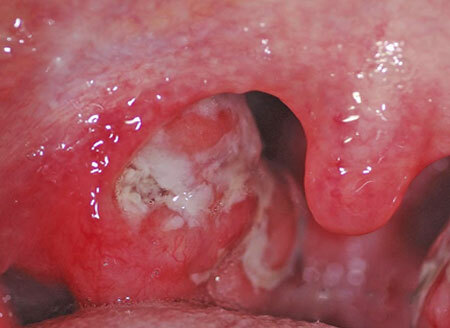
What is it? Paratonzillar abscess is the most severe stage of paratonzillitis, which is an inflammation of the cellulose surrounding the palatine tonsils.
The peak incidence of paratonsillitis falls on the age of 15 to 30 years, other age groups suffer much less. Pathology occurs with the same frequency in men and women.
About the disease and the causes of
If tonsils, which are usually called glands, are prone to frequent inflammation,( angina), the result is a chronic process( chronic tonsillitis).In 80% of chronic tonsillitis leads to the development of paratonzillitis with its transition to the paratonsillar abscess.
The appearance of a parathonsillar abscess is associated with anatomical features of the structure of palatine tonsils and surrounding tissues. In tonsils there are depressions - crypts, which are filled with purulent contents. Especially deep crypts are located in the upper part of the amygdala, where the inflammatory process with tonsillitis is most often observed.
Over time, the scar tissue forms on the site of the inflammatory foci, which prevents the normal outflow of the inflammatory fluid and pus from the indentations in the tonsils.
In the event of a new inflammation, the cleansing of the altered crypts slows down, and the infection from the tonsils spreads inward: through Weber's glands into the cellulose located around the tonsils, i.e.into the paratonsillar space.
The area around the upper pole of the tonsils, again, is most susceptible to the development of infection in it due to the pronounced looseness of its fiber, so the localization of the abscess is the most frequent there.
Given the fact that chronic local tonsillitis causes local and general weakening of the body's defenses - the development of inflammation in the paratonzillar space after infection can occur very easily.
Other causes of paratonsillar abscess can be any suppuration in the mouth: caries of the "wisdom teeth" of the lower jaw, periostitis, purulent inflammation of the salivary glands, as well as trauma to the pharynx and neck. Rarely the infection can get otogenmnym way, i.e.through the inner ear, and hematogenous - through the blood.
The risk group for the development of paratonsillar abscess includes the categories of patients suffering from the following diseases:
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Anemia;
- Immunodeficiency;Oncological processes, etc.
Against the background of the pathological conditions listed above, immunosuppression is observed. In the first place, local immunity suffers. Therefore, the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the tonsils occurs easily.
With the same ease they overcome other protective barriers, and fall into the bloodstream and the space surrounding the tonsils. Over time, the process from catarrhal to purulent, which is interpreted as a paratonsillar abscess.
Contents
- 1 Species and classification
- 2 Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess
- 3 Treatment of paratonsillar abscess
- 4 Complications of abscess
Types and classification of
Paratonzilit can appear as three clinical morphological forms that are consecutive stages of the inflammatory process. Detection and treatment of early forms of paratonzillitis can prevent the development of an abscess. But usually they masquerade as signs of usual sore throat with an acute respiratory infection of a viral origin.
Forms of paratonzillitis are as follows:
1. Ointment. This form is rarely diagnosed, as it is manifested by a slight sore throat, which can be explained by other causes, for example, hypothermia. Therefore, the disease easily passes into the next more severe stage.
2. Infiltrative. With this form, about 10-15% of all patients with paratonzillitis get to the doctor. It is characterized by the appearance of signs of intoxication, such as fever, headache, weakness, and local symptoms - pain and redness of the throat, pain when swallowing. As a rule, treatment for patients with paratonzillitis is prescribed at this stage.
3. Abscessive form of , which is the actual parathonsillar abscess. Develops in 80-85% of patients with paratonzillitis, if not carried out timely diagnosis and treatment. The parathonsilar abscess can have different localization. With this in mind, four types of abscess are distinguished:
- Supratonsillar and anterior - located above the amygdala, between it and the anterior palatal arch, observed in 70%( the most frequent appearance);
- Rear - develops between the amygdala and the posterior arch, the second in frequency - 16% of cases;
- Lower - formed between the lower part of the amygdala and the lateral part of the pharynx, observed in 7% of patients;
- Lateral or lateral, located between the middle part of the amygdala and the pharynx. This is the rarest localization, which happens in 4% of cases. But the heaviest, because with this arrangement, the worst conditions for self-breaking and cleaning the abscess cavity. As a result, purulent exudate accumulates in this space and begins to destroy surrounding tissues.
The side of the lesion in the abscess is not directly dependent. Thus, the left-sided paratonsillar abscess is observed with the same frequency as the right-sided abscess.
There are no anatomical prerequisites for more frequent abscess development from one side or another. Therefore, during the diagnosis should be guided by the severity and nature of clinical symptoms.
Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess
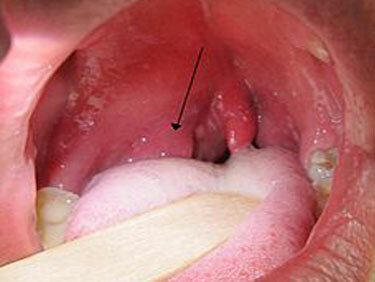
In paratonsillar abscesses, the symptoms appear primarily on the side of the formation of a purulent focus. Over time, they can move to the opposite side, which will lead to aggravation of the patient's condition.
On the development of suppuration of cellulose will indicate:
- Deterioration of general well-being;
- Temperature rise to high figures - 38,5-39 ° С( however, in patients with sharply reduced immunity the temperature can remain within normal limits or even lower - hypothermia);
- Increased pain in the throat. It becomes "jerking", spreading into the ear area, jaws;
- Increased pain when swallowing, which is so pronounced that the patient refuses to eat and drink so as not to provoke this gain. As a result, the body develops a deficiency of vitamins and other nutrients;
- Abundant salivation. It arises as a reflex to irritation of the salivary glands. Saliva flows from the mouth, as the patient is afraid of once again making a swallowing movement because of the pain. This leads to maceration of the skin around the mouth and formation of seizures in its corners;
- Putrid odor from the mouth, associated with the life of pyogenic bacteria, which led to the development of an abscess;
- Trismus of the chewing musculature - a spasm of muscles, varying degrees of severity, which does not allow wide opening of the mouth;
- Slurred speech, nasal congestion to prevent pain;
- Pain in the neck when turning the head is observed when the inflammation spreads to the muscles and lymph nodes of the neck. It always indicates the neglect of the pathological process;
- Crying when trying to swallow liquid food.
The general condition of the patient exacerbates the psychological tension associated with persistent severe pain, which exhausts emotionally, disrupts normal sleep, and leads to forced starvation.
Salivation makes you take a forced posture - either lying on your side, or sitting, tilting your head forward to ensure the flow of saliva without performing swallowing movements.
On the 4th-5th day of the development of the disease, spontaneous dissection of the "ripe" abscess may occur. The patient's condition thus sharply improves, the temperature falls, the painful pain in the throat disappears. In this case, an artificial surgical opening of the abscess is not performed.
The patient is recommended only rinsing and treatment of the opened cavity with antiseptics.
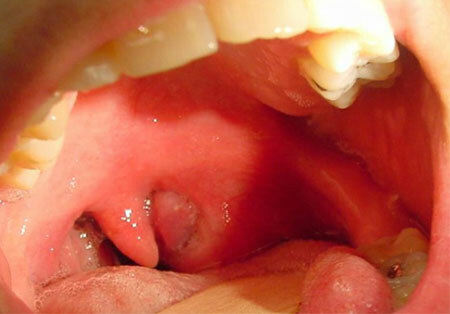
Parathonsillar abscess with typical top localization can be detected independently when examining the throat. It looks like a globular formation with a strained surface that swells above the tonsil up and toward the middle part of the pharynx.
Mucous over the formation is bright red, sometimes purulent white-yellow color is visible through it. With palpation, the fluctuation zone can be determined - purulent softening. Most often, a breakthrough occurs in this zone due to the enzymatic melting of the coating envelope.
Treatment of paratonsillar abscess
After the diagnosis of paratonsillar abscess, treatment is always performed in a hospital, methods of home therapy are impossible. In this case, a surgical dissection of the paratonsillar abscess is immediately performed.
Preliminary perform local anesthesia with a solution of dicain, lidocaine or other local anesthetic. Then make an incision with a scalpel on the most protruding site with the subsequent expansion of the abscess cavity with pharyngeal forceps and purging the purulent cavity.
At the final stage, the wound is treated with an antiseptic solution. For a better outflow of pus in the opened cavity, drainage is left( a rubber graduate), through which the pathological exudate comes out.
In case of a "cold" abscess, it is important to take into account the frequency of exacerbations in order to choose the most rational tactic. If a patient often has frequent sore throats during the interview, immediately remove the tonsils from both sides in order to prevent the recurrence of abscesses.
If the sore throats are not frequent, then the tonsils after opening the abscess are not removed, and it is recommended to do it 1-1, 5 months after the current treatment. In this case, the risk of inflammatory complications in the postoperative period is minimal.
After the performed operation, conservative treatment is performed. It involves taking medication and treating the open cavity.
The principles of conservative treatment of are:
- Bed rest regime, food is liquid, abundant warm drink. With severe pain and inability to swallow before opening an abscess, feed with special mixtures through the probe or prescribe intravenous drip 5% of glucose, dextran, 0.9% solution of sodium chloride;
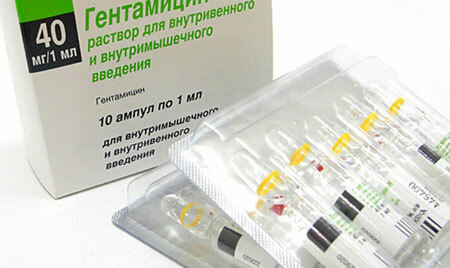
- Antibacterial drugs intake inside and intramuscularly: cefazolin, cefraxime, ceftriaxone, gentamicin, amikacin, penicillin, amoxicillin. The choice of antibiotic depends on the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of the disease, which allows us to assume the most likely causative agent of the abscess;
- In order to detoxify intravenously drip haemodesis and other drugs( this direction is indicated for patients with moderate and severe condition);
- Rinses of the throat with a solution of furacillin, miramistin and other preparations of the antiseptic series;
- For the prevention of fungal complications with antibiotic therapy appoint intraconazole;
- For analgesia use analgin intramuscularly, paracetamol inside;
- Antihistamines for the prevention of allergic organism;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs that help in addition to stop pain.
It should be noted that in the acute period, in the presence of severe pain, drugs are given parenterally - intramuscularly, intravenously or rectally( in the rectum).
Introduction by mouth( oral) is not allowed, becauseexacerbates existing clinical manifestations. Such a path is possible when the inflammatory changes subsided.
Complications of abscess
With paratonsillar abscess of throat complications will be options for further development of purulent process. When the infection spreads into the retropharyngeal space, a parapharyngeal abscess and phlegmon develop.
These complications can occur with breakthroughs of the paratonsillar abscess and with accidental damage to the pharyngeal wall during the dissection of the abscess. Parapharyngeal abscess can be limited and quickly cured with timely detection and surgical treatment. Without treatment, he is dangerous for the development of sepsis and phlegmon of the neck, as well as a sharp violation of breathing due to compression of the pharynx from the outside.
Neck phlegmon is a dangerous and life-threatening condition associated with anatomically possible rapid spread of infection over the cellulose of the neck.
Requires surgical treatment in the shortest possible time, as it can not independently break through due to depth of location, and therefore is dangerous for the development of mediastenitis and sepsis. Mediastenitis is an inflammatory process of the mediastinum, which includes the heart, large vessels( aorta, hollow and pulmonary veins), etc.
Purulent mediastenitis is a suppuration of the mediastinal tissue( area behind the thorax).One of the most severe forms of purulent infection of soft tissues.
Its feature is a complicated diagnosis in the early stages. Treatment consists in elimination of the original cause, surgical cleaning of the suppurated cavities. The success of treatment depends on the timeliness of their initiation. Delay creates a serious threat to life.
All purulent complications are subject to intensive treatment with antibacterial drugs. The proven effectiveness of cephalosporins 3 and 4 generation: cefoperazone, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefepime. Supplement the treatment with immunomodulating drugs.
With proper selection of antibiotics, their effectiveness can be assessed after 48 hours. If the patient's condition does not improve, then a change in antibacterial drugs is required.