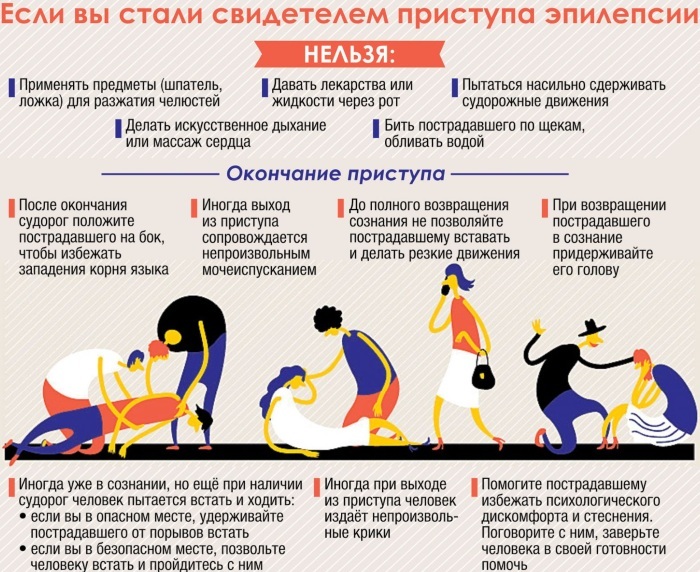
delirium - it is a mental disorder that is accompanied by confusion. The man suddenly develops a violation of orientation in time and space, the inability to adequately express thoughts, to concentrate, hallucinations appear, accompanied by a sense of fear and unmotivated aggression. As a rule, this pathology is reversible when the full therapy.
Overview
Delirium refers to a fairly common disease. According to foreign scholars, almost a third of mentally healthy people who took part in the study, at least once in their lives experienced the syndrome. Up to 10% of patients treated hospital general imposes specific complaints. Delirium as a transitory mental disorder Symptoms occur because of diffuse metabolic disordersLeading to acute failure of brain function. The severity of the condition in this mental illness range from mild stupefaction to a coma.
Causes
Delirium develops due to disorders of the brain normal functioning under the influence of various factors.
The causes of the disease are divided into 3 groups:
- intracranial pathology;
- somatic disorders;
- toxic damage.

intracranial pathology
This group of causes of delirium include:
- brain injury;
- circulatory disorders of nervous tissue due to thrombosis or embolism respective arteries;
- hemorrhage into the cavity between the meninges;
- inflammatory diseases of the brain of various genesis;
- transient ischemia;
- cancer formation;
- brain abscess.
Comaticheskaya pathology
Somatic pathology that can cause delirium, a very diverse and affect all organs and systems.
The most common causes of this group of factors should be considered:
- disease of the cardiovascular system ( myocardial infarctionexpressed heart failure);
- infection accompanied by severe intoxication (flu, malaria, typhoid fever);
- metabolic disorders (acidosis, Alkalosis, uremia);
- endocrine organs disease (diabetes, pathology of thyroid and parathyroid glands).
toxic damage
Formulations of the pharmaceutical industry, and alcohol are combined in a group of toxic factors. The most dangerous drug capable disrupt the normal functioning of the brain, are as follows:
- antidepressants;
- hypnotics;
- anti-TB drugs;
- drugs for the relief of seizures;
- anticholinergics.
Large doses of these agents, or a combination increases the risk of delirium. Alcohol often causes mental disorder when massive intoxication or cancel state.
symptoms
Despite the variety of reasons that can be a trigger for the development of delirium, the clinical manifestations of this disease are relatively constant. The main symptoms are:
- stupor - a condition characterized by acute onset and fluctuating course. It worried sick mostly at night or after a severe fatigue. Consciousness can clear when resolving the main pathologic process. Mild disorders of thought and attention can be revealed only in the course of a thorough examination. However, in severe dizziness patient only responds to emerging hallucinatory experiences, accompanying this incoherent speech.
-
Violation of orientation in timeAnd space and with regard to the self depends on the level of consciousness. In severe disease the patient may be disoriented time.

- confusion of thought It appears at approximately the same time, with the dimming of consciousness. Dkliry progression of the disease makes the thinking is absolutely not connected.
- impaired perception often accompanied by delusions or erroneous interpretations. The last characteristic in relation to unfamiliar people or objects. Patients developing visual hallucinations, often frightening content, causing the patient a strong sense of fear. There may be complex hallucinations, which in addition to the visual image there are also false tactile and auditory stimuli.
- Changing emotional behavior. Dominated by anxiety, irritability, feeling of hopelessness and indifference.
- become evident violation of psychomotor functions. They may be in the form of lethargy or hyperactivity.
- For severe delirium is characterized by profound amnesia.
Diagnostics
For diagnosis using large and small criteria. The former include dizziness, the second group includes:
- amnesia;
- hallucinations;
- speech disorders;
- changes in sleep;
- increased or decreased psychomotor activity.
Large set of criteria and any two small makes it possible to diagnose delirium. The survey is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms.
Differential diagnosis includes the following pathologies:
- decompensated dementia;
- depression in the elderly;
- mania;
- schizophrenia.
After carefully collected history and examination is expedient to carry out the following diagnostic measures:
- to conduct a general analysis of blood and urine;
- identify the content of sugar in the blood;
- determine the urea and electrolytes;
- investigate the liver function, endocrine system;
- determine the level of alcohol and psychotropic substances;
- to conduct X-ray examination of the chest;
- perform electroencephalography, which is able to detect the characteristic of slow waves of cerebral activity;
- conduct sampling and investigation of the cerebrospinal fluid;
- to investigate the structural changes in the brain by computed tomography.
Treatment
Treatment of patients with delirium is carried out in specialized clinics. Correction of the basic somatic pathology is the main goal of treatment. During this period, you need to normalize metabolic processes, fluid and electrolyte balance, optimize the power to abolish all drugs, the use of which is not caused by necessity.
In order to reduce violations of perception in a hospital is necessary to create certain conditions:
- patient ward should be well illuminated at night;
- the number of staff should not exceed a few people that the patient could remember them;
- to reduce the patient's sense of fear is often necessary to soothe;
- carefully monitor the dynamics of the patient's condition.
For the symptomatic treatment of patients with acute symptoms of mental disorders used antipsychotics. Acting on the dopamine receptors in various parts of the brain, they have the following properties:
- have a tranquilizing effect;
- reduce the response to external stimuli;
- an overwhelming sense of fear;
- help to reduce aggression;
- reduce agitation.
However, antipsychotics can cause the development of delirium, so for the treatment of mental disorders used the minimum dosing regimen.

Also, these drugs are able to:
- cause hypotension, leading to ischemic conditions;
- have a damaging effect on the liver cells;
- lead to epileptic seizures;
- increase the risk of pneumonia, especially in older patients;
- provoke allergic reactions and photosensitivity;
- reduce immunity by inhibiting leukocyte germ in bone marrow tissue.
Given the pronounced side effects of antipsychotics, they are used strictly on the evidence and under the control of vital signs.
Treatment of delirium tremens has its own characteristics. The main symptoms develop 3-4 days after cessation of drinking.
During this period, the patient should already be in a specialized hospital. Medical assistance should be carried out without delay and shall include:
- Sedatives with an antiepileptic effect. Early treatment administered intravenously, with a gradual decrease in dosage and by oral route of administration. The duration of this treatment should not exceed 2 weeks.
- For the prevention of encephalopathy using vitamins of group B.
- Patients with delirium tremens, a sharp dehydration, so one of the priorities is to fluid resuscitation and electrolyte component.
- It is necessary to adjust the level of glucose in order to prevent complications in the nervous system.
Drug treatment helps eliminate psychiatric symptoms in about 3 days. However, the patient may experience anxiety symptoms over a long period. They need to be adjusted because of the high likelihood of the resumption of the use of alcohol. After the treatment the patient should assess the degree of motivation to over treatment alcoholism.

complications
Delirium is characterized by the following complications:
- causing injury or mutilation;
- violation of the functions of internal organs;
- brain edema;
- metabolic disorders.
Delirium tremens is dangerous:
- the development of epileptic seizures;
- the emergence of cardiovascular disease;
- infectious pathologies;
- self-harm.
prevention
Major preventive measures to prevent the development of delirium is timely diagnosis and proper treatment of systemic diseases.
In addition, a healthy lifestyle, abstinence from alcohol or drugs, Rational methods of drugs can reduce the risk of mental disorder.
Forecast
After the resolution of the underlying disease, trigger the development of delirium, the latter symptoms may persist for the next few days. The prognosis for patients with mental illness depends on the etiology. If toxic delirium he favorableThen patients with cancer pathology or severe heart failure mortality rate can be up to 50% at the end of the year.
Found a bug? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter