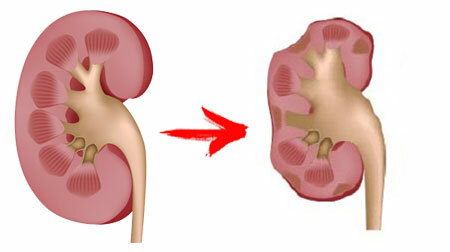
Kidney buds - what is this?
The kidney cyst is a common pathological condition that is most often diagnosed at the age of 40-50 years and older. According to statistics, the prevalence of the disease is 65-70% of all neoplasms affecting the renal parenchyma.
The kidney cyst in women is less common than in men, which is explained by the protective effect of estrogens and low levels of androgens. However, in menopause, the ratio of affected men to women is equalized.
Kidney of the kidney is an abnormality of the structure of the genitourinary system, characterized by the presence of liquid formation with thin walls, which can be either single or multiple. The formation of cysts occurs either in the prenatal period, or due to the action of various factors throughout the life of a person. This is what determines the division of cysts into hereditary and acquired ones.
Contents of
- 1 What causes cysts on the kidneys?
- 2 Symptoms of a cyst in the kidney
- 2.1 Types of kidney cysts
- 3 Diagnosis
- 4 Cyst on the kidney - what to do and how to treat?
- 5 What is a dangerous kidney cyst?
- 6 Prophylaxis of renal cyst formation
What causes cysts on the kidneys?
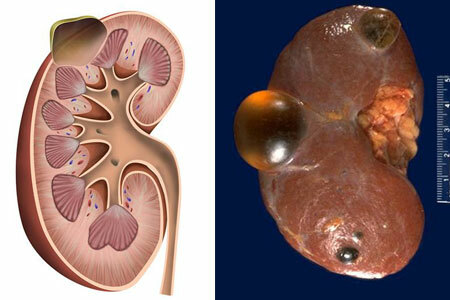
The causes leading to the appearance of a kidney cyst are very diverse. The formation of cystic congenital( inherited) character depends on the problems in the genetic apparatus of a person who is very vulnerable during the period of a woman's pregnancy. Especially dangerous at this time are the following factors:
- Smoking;
- Alcohol( in excess);
- Chemical agents( chlorine, heavy metals, etc.);
- Various infections;
- Radioactive effects, including solar energy and X-rays.
Other factors lead to the formation of acquired cysts. These include:
- Infectious-inflammatory diseases of the kidney;
- Injury of the lumbar region;
- Congestion of urine in the kidney;
- Dysplasia of connective tissue structures of the urinary system;
- Hormonal shifts( elevated levels of estrogen and a decreased level of androgens in men provoke increased production of epidermal growth factor, which determines the development of the tumor);
- Disturbance of blood circulation in the kidney with the development of foci of ischemia, the outcome of which is the formation of the cystic cavity.
Symptoms of the cyst in the kidney
The most common clinical sign of the kidney cyst is pain. They force the patient to seek medical help from a doctor. The pains are localized in the affected lumbar region, and they can be either permanent or periodic.
The second characteristic symptom of a kidney cyst is hypertension. Its development is associated with excessive stimulation of the renin-angiotensin system, the hormones of which affect the level of arterial pressure.
A distinctive feature of hypertension developing against the background of renal cysts is its malignant course and the ineffectiveness of many antihypertensive drugs. Such patients are helped only by representatives of the class of angiotensin-converting enzyme blockers.
The third important diagnostic criterion is the periodic or permanent detection of blood in the urine. Symptom may manifest macrogmaturia( urine visually has a red color) or microhematuria( outwardly the color of urine is not changed, but with microscopy it reveals an increased number of red blood cells).
Loss of erythrocytes in the urine leads to the development of anemia. The latter is also explained by the inhibition of the formation in the kidneys of erythropoietin, a substance necessary for the stimulation of erythropoiesis( the formation of erythrocytes) in the bone marrow.
In an objective examination of the patient, the physician can identify additional symptoms of the kidney cyst:
- Appearance of pain during effleurage in the corresponding lumbar region.
- Pain when feeling this area.
- Palpation of the displaced or enlarged kidney.
Types of kidney cysts
Classification of cystic formations in the renal parenchyma depends on several factors. Given the multiplicity of lesions, urologists distinguish:
- Single neoplasms;
- Multiple( usually do not reach large sizes).
According to the topografical anatomy this structure anomaly is divided into:
- Cysts of both kidneys;
- Neoplasms of one kidney( cyst of the right or left kidney).
Given the morphology of the cystic formations are:
- Simple;
- Parapelvic, located close to the renal sinus;
- Multilocular, the hallmark of which is the presence of several cameras inside the formation;
- Dermoid, related to abnormalities of embryonic development( in such cysts hair, nails, adipose tissue, bones, etc., ie, the derivatives of 3 embryonic leaflets) are found.
In a separate category, the multicystic kidney and spongy kidney are distinguished. In the first case, the entire renal parenchyma is affected by small cysts, leading to a significant decrease in the functional reserve of the organ. As a result, kidney failure develops in a short period of time.
With a spongy kidney, there are also multiple cysts, but they are localized in the collecting canals. This pathology refers to congenital states. Such children usually need early hemodialysis because of the rapid progression of renal failure.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of renal cysts is aimed at solving several problems:
- Immediate imaging of the neoplasm in the renal parenchyma.
- 2. Research of kidney function.
- 3. Early detection of the inflammatory process.
For the implementation of the first task, the following studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound scanning of the renal parenchyma;
- Computed tomography.
To investigate renal function, it is necessary to determine the concentration in the blood of the following substances:
- Glucose;
- Creatinine;
- Protein;
- Urea.
The solution of the remaining diagnostic tasks involves performing such tests as:
- General analysis of urine( inflammatory processes increase the number of leukocytes);
- General blood test( reveals inflammatory processes).
An increased risk of complications requires that such patients receive a coagulogram( this study assesses the state of the blood coagulation system) and electrocardiography.
The need for these diagnostic tests exists also when the patient enters the hospital, as sometimes a surgical removal of the kidney cyst may be required. And this is always associated with a certain anesthetic risk and the danger of bleeding( both during surgery and after).
Kista on the kidney - what to do and how to treat?
What to do when a cyst is found on the kidney? This is a natural question that arises in most patients with a similar diagnosis. The correct conduct of them is in active-expectant tactics.
This means that such patients are followed by dynamic ultrasound observation."Active" treatment of the kidney cyst begins as soon as a significant increase in the size of the neoplasm is detected - a percutaneous puncture of the kidney cyst is made with subsequent aspiration of the fluid.
If this intervention can not be performed, then this is an indication for surgical removal of the neoplasm.
All patients with kidney cysts are also taking other measures( it should be noted that the causes and treatment of kidney cysts are interrelated, if the underlying cause was infectious kidney disease, then it requires priority treatment):
- Treatment of concomitant infections complicating the course of the background disease;
- Organization of dietary nutrition;
- Coping with complications( stopping bleeding, performing analgesic therapy, etc.).
In extremely rare cases, the kidney cyst resolves itself. This is an additional argument in favor of active-expectant tactics. Most often this happens with inflammatory cysts.
A well-organized diet with a kidney cyst( diet table No. 7 according to Pevzner) is an important direction in the treatment and prevention of progression. Principles of dietary nutrition are:
- Exception from the diet of fatty, smoked and fried;
- Sharp restriction of salty foods( food is not recommended for dosage);
- Complete rejection of alcohol, spicy spices and sparkling sweet water;
- Enrichment of the ration with dishes cooked in the oven, steamed and boiled;
- Reduction in the diet of protein foods( meat and legumes), becauseit is excreted by the kidneys, which increases the load on them.
What is a dangerous kidney cyst?
The danger of renal cysts is the possibility of complications. The latter include:
- Chronic renal failure;
- Urinary retention in the kidney and its expansion( hydronephrosis);
- Pyelonephritis, incl.and purulent;
- Suppuration of the cyst;
- Hemorrhage in the cyst;
- Rupture of neoplasm and peritonitis;
- Anemia;
- Arterial hypertension.
Prevention of renal cyst formation
Renal cysts in women and men are multifactorial diseases, so prevention should be aimed at eliminating many causal conditions. Therefore, it is recommended:
- Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Treatment of foci of chronic infection( diseases of ENT organs and dentoalveolar system), which can become a source of inflammation of the kidneys.
- Preventing injuries to the lumbar region.
- Dynamic ultrasound observation of patients with kidney trauma.
- Exclusion of intense physical activity with increased activity.
- Normalization of the hormonal background in men.
More difficult to prevent is the prevention of congenital cysts. All activities should begin before and during pregnancy, when a woman should adhere to the following recommendations:
- In a timely manner, check for chronic urogenital infections and, if detected, treat before conception.
- Refuse to smoke, incl.and passive( toxic effect is not the nicotine, as previously thought, but directly the carbon monoxide).
- Avoid excessive drinking.
- Minimize the exposure to direct sunlight.