What is it? Sepsis is a purulent infection that spreads through the body, developing from the primary focus on the background of a weakening of the protective mechanisms and proceeding with a sharp oppression of the functions of a number of vital organs and systems. The problem of sepsis is relevant in connection with the increase in morbidity, difficulties in diagnosis and high mortality - then we will consider in detail what kind of disease it is.
The word "sepsis" of Greek origin means decay or decomposition. The term is used in various areas of clinical medicine, has a broad terminological interpretation, which is due to the variety of clinical manifestations of the disease. This condition is caused by penetration into the bloodstream and tissues of the pathogens of the infection and the products of their vital activity, is characterized by an inflammatory process throughout the body.
For many centuries, sepsis took the lives of the wounded and sick, it was considered to be the most severe, threatening complication of wound infection. Before the discovery of antibiotics, mortality as a result of the disease reached 100%.
But even now the lethality is also kept at a high level. In the United States, about 700 thousand sepsis cases are registered for a year, and 200-215 thousand patients die. This is not only a medical, but a demographic and economic problem.
Contents
- 1 Causes of sepsis
- 1.1 Classification
- 2 Symptoms of sepsis
- 3 Diagnosis of sepsis
- 4 Treatment of sepsis
- 5 Sepsis in newborns
- 6 Complications
- 7 Prognosis and prevention
Causes of sepsis
Sepsis is caused by various types of bacteria, viruses or fungi. Most often it is caused by streptococci and staphylococci, less often it can be provoked by pneumococci and E. coli. In its development, a significant role is assigned to the body's defenses, which can be reduced as a result of severe disease, loss of large amounts of blood, surgical intervention.
The root causes of general infection include:
- wound suppuration;
- exacerbated by local purulent diseases( boils);
- complications after childbirth and abortion;
- purulent inflammation of the urogenital system;
- acute or chronic suppurative processes of the oral cavity.
A septic reaction develops in peritonitis, pneumonia, infection of intravascular devices and catheters. Sepsis does not arise as a result of the direct influence of microbes and toxins on the body, but is the result of large disorders in the immune system, complete or partial loss of ability to suppress the pathogen outside the infectious focus, which makes the patient's recovery almost impossible without intensive treatment.
Classification
According to domestic and foreign publications, there are many points of view on the definition and pathogenesis of sepsis. Nowadays, the disease is divided into the clinical course, depending on the entrance gate of the infection, the type of pathogen and the localization of the primary focus.
The clinical course of sepsis is:
- fulminant, or acute;
- sharp;
- subacute;
- is chronic.
For fulminant sepsis is characterized by a rapid onset and rapid progression, often lethal outcome for 1-2 days. The acute form of the disease lasts from 6 to 14 days without remission. Subacute - from 2 to 12 weeks, signs are less pronounced. Chronic sepsis with relapses and periods of remission can be observed for several years.
Dependent on the entrance gate distinguishes:
- wound sepsis( accidental or postoperative wound);
- burn;
- postpartum;
- sepsis in pathologies of internal organs( pericarditis, pneumonia).
Regarding the localization of the primary septic source of sepsis:
- is dental;
- tonsilogenetic( primary focus in tonsils);
- otogennym( complication of otitis);
- is rhinogenous( the primary focus is located in the paranasal sinuses and oral cavity);
- with gynecological;
- umbilical( entrance gates have umbilical wound);
- cardiogenic( septic foci in the endocardium).
This also includes urosepsis with the location of infection in the kidney and urinary tract.
Infection is distinguished by the type of pathogen. According to this classification, it can be:
- staphylococcal;
- streptococcal;
- is colibacillary;
- pseudomonosal;
- anaerobic;
- fungal.
Sepsis may be secondary, developing with a purulent infection and primary, when the focus can not be determined. Admissibility of the emergence of the latter form is discrete, since an infectious source at the time of sepsis development may lose its clinical significance and may not be detected during a patient's examination.
Symptoms of sepsis
Almost all organs and systems of the body are affected by pathological processes that are observed in sepsis. Symptoms of sepsis are diverse and depend on its clinical form, the location of the primary focus.
As a rule, the disease begins acutely, with a rise in temperature to 39-40 ° C.Fever can be permanent, remitting or wavy. It is accompanied by a shaking chill, pouring sweats and a painful heart palpitations, which continues after the normalization of body temperature.
Changes to the central nervous system include drowsiness, confusion, excitement or inhibition, disorientation.
Among the organ damage most often manifested: arthritis and polyarthritis, endocarditis with the involvement of valves, polysergment pneumonia.
Sepsis accompanies kidney damage of a different nature. Changes are manifested in the form of damage to the renal tubules, oliguria. Drift of infectious sepsis into the kidneys can be expressed by cystitis, parainfritis, pyelitis.
On the part of the digestive system, often debilitating diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, seizure pain in the abdomen. Pathological processes in the liver and spleen are manifested in the form of jaundice, increased bilirubin.
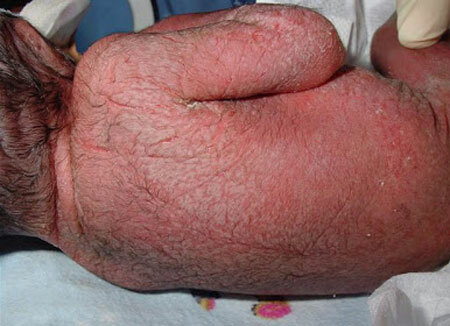
Almost obligatory in patients with sepsis is the defeat of the respiratory system. The severity of the condition can range from shortness of breath to the development of severe lung function disorders in the form of respiratory distress syndrome. Pathology is characterized by hemorrhagic or pustular rash on the trunk and extremities, which appears at the end of the 1 st week of the disease and lasts for a long time, fading and flaring up again.
Sepsis is a dynamic process that often develops in an unpredictable scenario, so there is no basic and unique diagnostic criterion.
Diagnosis of sepsis
The diagnosis of sepsis is based on exhaustive analysis, evaluation and comparison of clinical and laboratory data. The history, availability of the primary focus, entrance gates and comparison of the septic syndrome( fever, chills, severe intoxication, inadequate tachycardia) with multiple organ lesions is important.
Laboratory diagnosis is based on the definition of a marker of systemic inflammation - procalcitonin, which is considered to be the most effective indicator of sepsis. Usually in humans, this figure does not exceed 0.5 ng / ml. If the figure is more than 2 ng / ml, sepsis is diagnosed with a high probability.
A microbiological study is also conducted. For the diagnosis, not only blood is selected, but also material from wounds, tracheotomy tubes, drains.
To the diagnostic minimum, which the doctor should appoint to clarify the diagnosis include:
- an expanded blood test with the formula;
- general urinalysis;
- X-ray of the thoracic cavity organs.
Additional research methods: ultrasound, computed tomography, puncture.
Treatment of sepsis
In the treatment of sepsis an important role will be played by timely phased antimicrobial therapy. The choice of an antibacterial drug depends on the severity of the patient's condition and pharmacological characteristics of the drug, whether a community-acquired or hospital infection provoked infection, from the presence of the outbreak.
When treating sepsis with antibiotics, carbapenems( imipenem), cephalosporins( ceftriaxone) in combination with aminoglycosides( gentamicin), glycopeptides( vancomycin) are of the greatest importance.
Delay with the onset of the necessary antibiotic therapy increases the risk of complications and mortality. Preparations are prescribed by courses for 2-3 weeks, while using several drugs.
Treatment also includes detoxification therapy, nutritional support( enteral nutrition), immunotherapy, correction of tissue hypoxia, intensive care and resuscitation, according to indications - surgical intervention. Almost all patients with sepsis have a need for respiratory therapy.
To prevent damage to the lungs with symptoms of acute distress syndrome, a special mode of artificial ventilation is needed.
The organization of treatment is always complex. Therapy is carried out in a close alliance of a surgeon, therapist and resuscitator. One of the important tasks of treatment is the search for and sanation of primary and secondary purulent foci - without their elimination, even at the highest level of therapy, one can not expect the patient to recover.
Sepsis in newborns
In the structure of mortality factors of full-term newborns, an increase in the share of infectious pathology is observed. Among the causes of sepsis in neonates, not the last role in the violation of an adequate immune response belongs to intrauterine infection of the fetus.
The focus of infection in such cases is:
- microflora of the mother's birth canal;
- infectious inflammatory diseases in pregnant women;
- anhydrous period in childbirth more than 6 hours;
- out-of-hospital births.
The high risk of sepsis in children is diagnosed if the birth weight is less than 1500 g.
Complications of
Various complications arising during the course of a disease often significantly change the clinical picture and predetermine its outcome. The complications of sepsis include:
- septic shock;
- acute renal and hepatic insufficiency;
- bleeding;
- thromboembolism;
- pneumonia;
- pyelonephritis;
- endocarditis.
One of these complications is the result of a weakening of the compensating capacities of the body during the course of sepsis, others arise due to intoxication and spread of infection as a result of metabolic disturbances. Septic shock is the most common cause of death.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for sepsis is extremely serious. Especially it is disappointing in young children, in pregnancy, in people of mature age, with aggravating accompanying diseases.
Prevention is the timely treatment of wounds and purulent foci, the implementation of rules of aseptic and antiseptic in surgical operations.