Content
- Causes of the prolonged squeezing syndrome
- Symptoms of the long-term soft tissue compression syndrome
- Classification and stages of development of the syndrome of prolonged compression
- Etiopathogenetic links and factors
- Diagnostics
- First aid. Rendering algorithm, rules
- IV epinephrine or norepinephrine for heart failure
- Inpatient anti-shock therapy and further treatment
- Complications
- Forecast
- Prolonged Compression Syndrome Video
Prolonged pressure syndrome is a massive soft tissue injury. Without the absence of first aid, the pathological condition entails persistent hemodynamic disorders, traumatic shock, uremia. Prolonged pressure syndrome requires the right therapy, since without treatment, the risk of serious complications, up to and including death, increases.
Causes of the prolonged squeezing syndrome
In most cases, the syndrome of prolonged compression occurs with closed mechanical injuries to parts of the body.
The causes of the pathological condition are the following factors:
| Name | Description |
| Traumatic causes | Electric shock, frostbite of the extremities, burns, severe concomitant injury. |
| Ischemic | Arterial embolism, thrombosis, tourniquet syndrome, positional compression syndrome. |
| Hypoxic | Overstrain or severe hypoxia of muscle tissue. Great physical exertion, convulsions, tetanus, chills, epileptic seizures, delirium tremens. |
| Infectious | Pyomyositis, sepsis, bacterial or viral myositis. |
| Dismetabolic | Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hypokalemia. |
| Toxic | Treatment with certain drugs, substance abuse, insect or snake bites. |
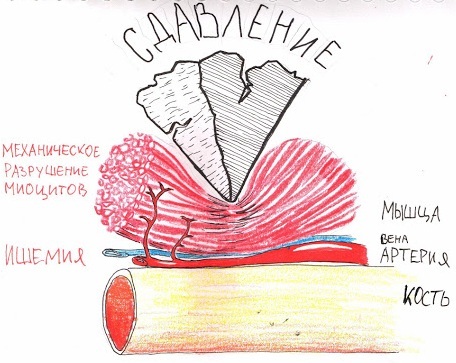
There are also genetic factors, against the background of which the syndrome of prolonged squeezing develops.
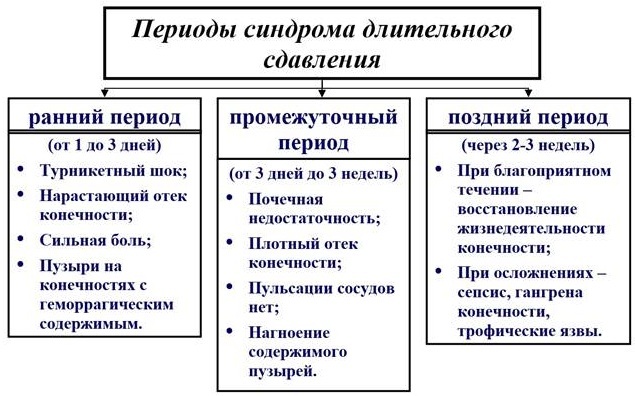
Symptoms of the long-term soft tissue compression syndrome
The clinical picture of the syndrome of prolonged compression depends on the degree of damage to the soft tissues.
The following periods of the appearance of signs of a pathological condition are distinguished:
| Name | Symptoms |
| The first period (compression) |
|
| Second period (toxic) |
|

In the third period of the development of clinical signs, prolonged compression syndrome provokes serious complications, as a result of which a person can die. Accompanying symptoms are vomiting, fever, anemia. Kidney function is disrupted, necrotic foci appear, muscles are exposed. The victim's consciousness is inhibited, hysteria and psychosis appear. At the fourth stage, there is a complete restoration of the work of all internal organs and systems of the human body.
Classification and stages of development of the syndrome of prolonged compression
Prolonged pressure syndrome (first aid is provided by a qualified medical team) in medicine classified by the degree of damage to soft tissues, the course of pathological processes and depending on the provoking factors.
| Name | Description |
| Mild degree | The terms of squeezing soft tissues are 2-3 hours. A slight endogenous intoxication develops. Oliguria disappears in a few days. The prognosis is favorable. |
| Medium severity | The time of squeezing soft tissues is 2-6 hours. Moderate endotoxicosis is present. Acute kidney damage persists for 1–2 weeks after mechanical injury. The prognosis in this situation depends on the speed of the first aid provided.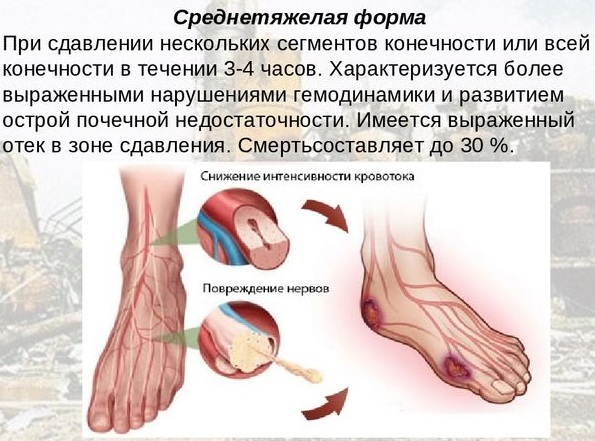
|
| Heavy | Prolonged pressure syndrome was observed for more than 6 hours. Severe endogenous intoxication intensifies, multiple organ failure develops with acute kidney damage. Intensive treatment is carried out, the victim is prescribed hemodialysis. In the absence of therapy, the patient will face negative complications and a disappointing prognosis. |
In medicine, there is a classification of the syndrome of prolonged compression, depending on the localization of the lesion:
- thoracic region;
- abdominal area;
- head;
- upper and lower limbs;
- pelvic region.
 Prolonged pressure syndrome (first aid provides a specific algorithm of actions to save life) in any situation requires the urgent attention of doctors in order to prevent serious complications.
Prolonged pressure syndrome (first aid provides a specific algorithm of actions to save life) in any situation requires the urgent attention of doctors in order to prevent serious complications.
Etiopathogenetic links and factors
In most cases, the main cause of the development of the syndrome of prolonged compression is mechanical injury, which with high likely to be obtained at work, as a result of an accident, earthquakes, during an explosion and at the time of other emergency situations.
During prolonged compression of soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves are damaged. Necrotic areas appear as a result of ischemic processes. First aid to victims must be provided immediately, at the scene.
In medicine, the following etiopathogenetic links of the prolonged compression syndrome are distinguished:
- Painful shock sets in.
- Capillary permeability increases.
- Proteins and plasma are released from the vascular bed.
- The normal tissue structure is impaired.
- Damaged tissue swells.
- The amount of the liquid part of the blood (plasma) decreases.
- Hemodynamics is impaired.
- There is a malfunction in the functioning of the system that is responsible for blood clotting.
- Blood clots form.
- Due to tissue decay, toxemia develops.
- Trace elements from damaged tissues penetrate into the blood.
- The acid-base balance is disturbed.
- Myoglobin appears in the blood and urine.
- Hydrochloric acid hematin is formed from methemoglobin.
- Tubular necrosis develops.
- Kidney cells die.
- Acute uremia develops.
- Mediators of the inflammatory process enter the systemic circulation.
- Multiple organ failure develops.
When blood vessels constrict and normal muscle circulation is disrupted, sensory arousal occurs. This applies not only to the affected, but also to healthy tissues.
Diagnostics
Examination of the victim begins with a thorough examination and examination by doctors of the existing clinical signs. After a visual examination, a physical diagnosis is assigned to the person.
Laboratory examination for prolonged pressure syndrome involves the following measures:
| Name | Description |
| General urine analysis | The results obtained will help establish the condition of the kidneys.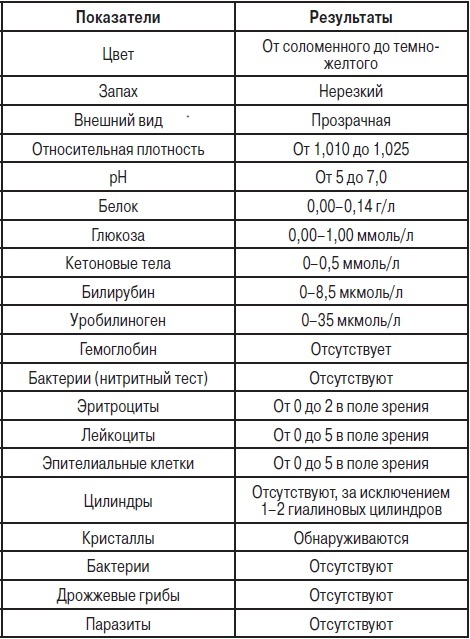
|
| General and biochemical blood test | With the development of an inflammatory process or other pathological changes in the human body, blood parameters change. |
| Microbiological research | Testing allows you to establish the type of infection present and select the most effective drugs. |
Diagnostics will allow not only to establish the condition of the victim, but also to determine the accompanying pathological changes inside the body. Based on the results of the examination, an individual therapy scheme is drawn up for the patient.
First aid. Rendering algorithm, rules
Prolonged pressure syndrome requires complex treatment. The initial stage is to provide first aid to the victim.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Removing a person from the rubble and transporting him to a safe place.
- The imposition of a tight bandage or tourniquet on the affected area of the body, slightly higher from the place of squeezing. A necessary measure that will help prevent a person's death from severe bleeding.
- Fracture immobilization using special splints or improvised items.
- It is necessary to stop the bleeding and conduct a thorough examination of the whole body of the person.
- All wounds are mechanically cleaned and treated with antiseptic agents.
- A sterile bandage should be applied to the wound.
- A cold compress should be applied to the affected area.
- Provide the victim with access to oxygen, give him water and warm him up.
- During transportation, the patient must be immobilized as much as possible in order to prevent possible complications.


 First aid is provided by a medical team, therefore, in emergency situations, the victims are injected with drugs:
First aid is provided by a medical team, therefore, in emergency situations, the victims are injected with drugs:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Pain relievers | Ketorol, Analgin | Medicines reduce pain. The tablets are taken orally, swallowed whole and washed down with a sufficient amount of water. The dosage of the drug depends on the severity of the pain syndrome. Adults are advised to take 10 mg per day. The maximum dosage of the drug is 40 mg per day. The therapy continues for 5 days. If necessary, the drug is administered intramuscularly. |
| Detoxification drugs | Polyglyukin, Disol | Medicines are given intravenously through an IV line. The dosage depends on the condition of the person and is 10-20 ml / kg per day. |
| Diuretics | Mannitol, Lasix | The drug is administered by intravenous stream or drip. The dosage of the drug is selected individually from 500 ml to 1.5 g / kg. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone | Medicines help prevent the development of heart failure. Adult patients are prescribed 20-30 mg per day. The maintenance dosage is 5-10 mg. If a person is in shock, the medication is administered intravenously or in a stream. |
If necessary, penicillin antibacterial drugs are administered to the patient at the first aid site.
IV epinephrine or norepinephrine for heart failure
Prolonged pressure syndrome (first aid requires emergency medical measures) can provoke acute heart failure. We are talking about a pathological condition that is a consequence of stagnation of blood in the small or large circle of blood circulation.
For this reason, the functioning of all internal organs and systems deteriorates. In a state of shock, the patient is injected intravenously with epinephrine or norepinephrine to intensify the contraction of the heart, increase the conductivity of myocardial tissue and the frequency of contractions.
Norepinephrine (1-2 ml) is pre-diluted with glucose or saline (150-200 ml). The finished medicine is administered through a dropper (20 drops / min). In this case, the patient needs to check blood pressure every 15-20 minutes. With intravenous administration of the drug, the therapeutic effect occurs in 2-3 minutes.
Inpatient anti-shock therapy and further treatment
After providing first aid for the syndrome of prolonged compression, the victim is hospitalized without fail for further treatment. A thorough examination is prescribed and, based on the results of diagnostics, therapy is selected:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Diuretics | Furosemide, Uregit | The medicine is taken orally. The tablets are not chewed and washed down with a little water. Adults are recommended to take 1-4 tablets 1-2 times a day. It all depends on the patient's condition. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Diprospan, Betamethasone | Intramuscularly, the drug is injected in a dosage of 1-2 ml deep into the gluteus muscle. |
| Broad spectrum antibiotics | Ampicillin, Erythromycin | The recommended dosage for patients is 250-500 mg 4 times a day. Treatment lasts an average of 7-14 days. |
| Antiplatelet agents | Cavinton, Pentoxifylline | The medicine is taken orally, washed down with a sufficient amount of liquid. The adult dosage is 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 2 months.
|
| Cardiac glycosides | Strofantinus, Korglikon | The drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The adult dosage is 250 mcg as a single dose. Subsequent appointments include 100 mcg / h. Before use, the medicine should be diluted with glucose or isotonic sodium chloride solution. |
| Antihistamines | Suprastin, Clemastin | The medicine is taken orally, washed down with water, mainly with meals. Adult patients are prescribed 25 mg 2-3 times a day. In severe or urgent cases, the drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. |
| Antiarrhythmic drugs | Verapamil, Kordaron | The tablets are swallowed whole, not crushed and washed down with water. An adult is prescribed 80 mg 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts at least 7 days. |
| Immunostimulants | Imunorix, Likopid | The medicine should be taken before meals or after meals. During an exacerbation, adult patients are prescribed 800 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 2 weeks. Supportive therapy is carried out using 800 mg of the drug once a day for 60 days. |
Additionally, physiological saline, sodium bicarbonate, albumin or hemodez are injected through a dropper. Substitution therapy is in progress. Fresh frozen plasma or blood substitutes are injected into the victim's blood. DIC syndrome will help prevent heparin therapy (Curantil, Trental).
In severe and urgent cases, extrarenal blood cleansing is performed. Patients are shown hemodialysis, ultrafiltration, plasmapheresis. In the absence of positive results, surgery is performed. During medical procedures, the surgeon removes necrotic foci, dissects the fascia. In case of emergency, the damaged part of the body is amputated.
Complications
Prolonged squeezing syndrome (first aid is provided by a medical team at the scene of the incident) in the absence of first aid and subsequent therapy in the inpatient department will lead to serious consequences:
- pulmonary embolism (PE);
- peritonitis;
- myocardial infarction;
- irreversible tissue ischemia in the damaged area of the body;
- pulmonary edema, the development of an inflammatory process (pneumonia);
- sepsis.
The consequences of the syndrome of prolonged squeezing will be minimal if the doctors restored the functioning of the kidneys in a short period of time. Otherwise, their irreversible damage can even lead to death.
Forecast
The prognosis for long-term compression syndrome depends on the speed of the first aid provided. The degree of damage to the victim's body matters, how extensive the pathological processes are. The same applies to the course of the syndrome of prolonged compression and the individual characteristics of the human body.
After therapy, the patient will have a long rehabilitation period with massage procedures to restore the functionality of the body. Additionally, a complex of physiotherapy exercises is selected. Patients are advised to attend physiotherapy procedures, to carry out spa treatment.
Physicians cannot predict the course of prolonged pressure syndrome, and what the prognosis will be. Every day the number of people who have an accident, become victims of natural disasters or receive mechanical injuries is increasing. In this situation, every minute counts. The sooner a person is provided with first aid, the more chances he has for life.
Prolonged Compression Syndrome Video
About crash syndrome:



