Content
- ECG indications
- What does an electrocardiogram consist of?
- How to decode an ECG
- ECG analysis
- What is PQ interval
- The norm of the PQ interval in children and adults
- PQ interval pathologies
- Mobitz I
- Mobitz II
- Survey video
Electrocardiography is one of the methods for studying the activity of the heart. Its essence lies in the registration of electrical potentials arising in the myocardium before its contraction. One of the indicators displayed on the ECG, namely the PQ interval, can say a lot about the normal or pathological state of the cardiac conduction system.
ECG indications
ECG is a non-invasive and painless research method that has no contraindications. The procedure is carried out in a planned or emergency manner.
Planned electrocardiography is prescribed:
- before surgery;
- during pregnancy management;
- during preventive examinations of the population;
Also, periodically, electrocardiography must be passed to persons with special health conditions or occupational hazards:
- in the presence of atherosclerotic plaques;
- hypertension;
- high blood cholesterol levels;
Emergency electrocardiography is performed to detect pathological processes in the heart, some of which require immediate intervention.
Emergency ECG is prescribed for:
- sharp pain localized behind the sternum or in the upper abdomen;
- suddenly developed shortness of breath;
- identified during the primary diagnosis of heart murmurs;
- with discomfort in the work of the heart.
What does an electrocardiogram consist of?
To understand the elements that make up the electrocardiogram, it is necessary to understand the processes occurring in the heart before and during its contraction.
To contract the heart muscle, an electrical impulse must first propagate through it. During the propagation of this impulse, the muscle becomes a source of electric current, which is conducted to the surrounding tissues and to the surface of the body.
If electrodes are placed on both sides of the heart, then it is possible to register and display on paper the potential difference that occurs during the propagation of excitation. The resulting scheme will be called an electrocardiogram.
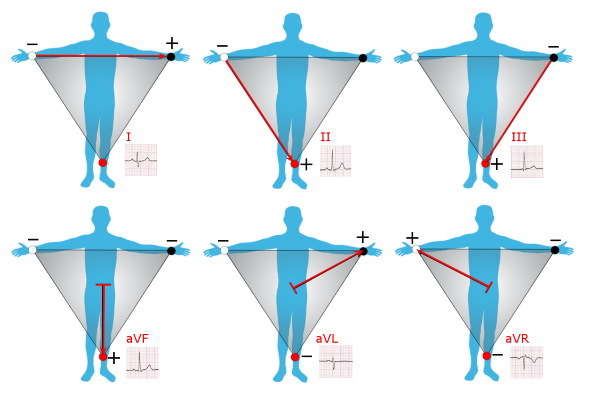
In practice, three methods of positioning the electrodes are used, called standard leads:
- In the first lead, the electrode on the left hand is positive, and on the right - negative.
- In the second lead, a positive electrode is placed on the left leg, and a negative electrode is placed on the right arm.
- In the third lead, the negative electrode is located on the left arm and the positive electrode is located on the right leg.
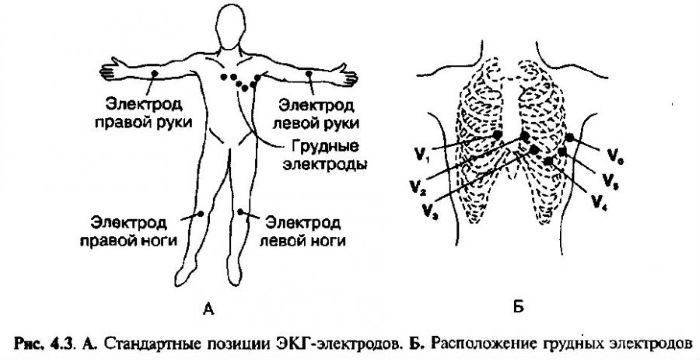
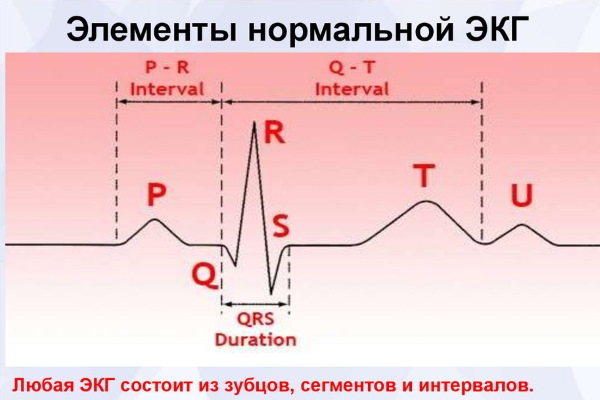
When recording electrical phenomena occurring in the heart for some time, an image is obtained, consisting of teeth, segments and intervals. The teeth represent a set of positive and negative peaks and reflect the processes of changing the potential difference between the electrodes.
Distinguish the teeth P, Q, R, S, T, they give the following information:
- The P wave occurs during atrial depolarization. Depolarization is a process that precedes muscle contraction. Normally, in the second standard lead, this tooth is positive.
- The QRS complex consists of two negative (Q and S) and one positive (R) waves. They correspond to the propagation process of ventricular depolarization.
- The T wave occurs when the resting potential of the cardiomyocytes (heart cells) of the ventricles returns to its original level and there is a repolarization. Normally, in the second standard lead, the T wave is positive.
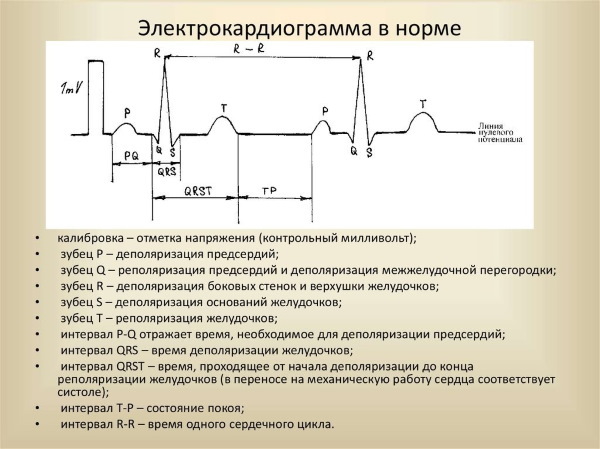
Segments are straight line segments connecting adjacent teeth to each other:
- The PQ segment occurs due to a delay in the impulse in the atrioventricular node; its duration can be used to judge the work of the cardiac conduction system.
- The ST segment corresponds to the time during which both ventricles are in a depolarized (excited) state.
Intervals consist of a tooth or several teeth and a segment:
- The PQ interval value is defined as the distance between the beginning of the P wave and the QRS complex. It displays the time interval spent on the propagation of excitation from the atria to the ventricles.
- The values of the QRS complexes on the cardiograms are represented by intervals from the Q wave to the S wave, and corresponds to the process of ventricular excitation.
- The QT interval belongs to the distance from the starting point of the Q wave to the end of the T wave. It reflects depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles.
How to decode an ECG
Decoding an electrocardiogram includes an assessment of intervals, teeth and segments.
The duration of the intervals, the amplitude of the teeth, their frequency and rhythm have rigid limits of the norm, and a deviation from these norms can tell about many pathologies. It is important to understand that only a doctor can diagnose a pathological change on the electrocardiogram, because the readings of the cardiogram can change.
The PQ interval on the ECG, the norm of which also has rather strict values, can be differentiated according to the age categories of patients. Children's norms of the indicator, for example, are less than those of adults. This factor is due to the peculiarities of children's physiology and the faster conduction of impulses of intracardiac excitations.
ECG analysis
In the process of analyzing the electrocardiogram, the doctor receives information about the heart rate (HR), the basic rhythm, the presence or absence of extraordinary contractions and violations of the electrical pulse.
The patient should understand that many factors can affect the result of the electrocardiogram. Any stressful factors, be it emotional overexcitement, physical activity or a cup of coffee before the examination, can significantly distort the real picture. Ideally, at the time of examination, the patient should be asleep, be in a calm, unexcited state.
In order for the results of the study to be reliable, a number of rules should be adhered to:
- refusal from strong tea, coffee and energy drinks a few hours before the examination;
- lack of physical and emotional stress;
- no excessive load on the gastrointestinal tract. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, you should postpone a hearty breakfast. If the procedure is performed during the day, it is better not to eat food several hours before the ECG;
- do not worry directly during the examination. The ECG procedure is absolutely painless and harmless, and excessive emotional stress can affect the reliability of the results;
- smoking and drinking alcohol is prohibited a few hours before the examination;
- you should not use drugs that affect the cardiovascular system.
A competent specialist, seeing deviations from the norm in the ECG indicators, will make sure that all the above rules are met, and only after that will he make a final diagnosis.
What is PQ interval
The PQ interval is the distance from the beginning of the positive P wave to the beginning of the negative Q wave (or to a positive R wave if the Q wave is not pronounced or absent). This interval reflects the process of impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node.
This interval displays the time during which the electrical impulse propagates from the place where it was generated. (atrium) to the ventricles, which, thanks to this "signal", contract and push a portion of blood into the main vessels.
The atrioventricular node serves as an intermediate point through which the electrical impulse passes. Normally, it is delayed at this intermediate point in order to prevent the simultaneous contraction of the atria and ventricles.
The norm of the PQ interval in children and adults
The PQ interval on the ECG (the norm for adults is 0.12-0.20 s) should vary strictly within a certain range. Anything that goes beyond it is pathology.
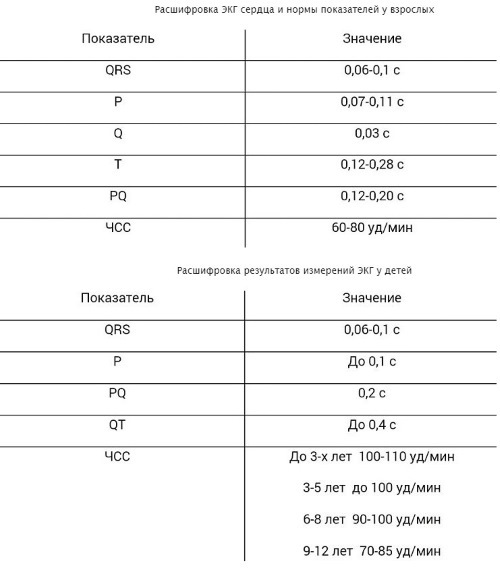
However, it should be understood that the value of this parameter depends on the heart rate (the higher the heart rate, the faster the pulse propagates). Therefore, it is more correct to assess the nature and state of the atrioventricular junction as the ratio of the duration of the PQ interval to the duration of the entire heart systole (PT).
The ECG in children has some peculiarities. Differences from the electrocardiogram in adults are most pronounced at an early age, after 13-14 years, its characteristics are more and more approaching the standard norm. The PQ interval in children is shorter due to the higher heart rate compared to adults.
The PQ interval and heart rate values when decoding the ECG for children are normally based on the following indicators:
| Age (years) | Heart rate (beats per minute) | Interval (s) |
| 0-1 | 120-140 | 0,09-0,12 |
| 1-2 | 110-130 | 0,10-0,12 |
| 3-4 | 90-110 | 0,11-0,13 |
| 5-7 | 80-105 | 0,12-0,14 |
| 8-11 | 75-95 | 0,12-0,14 |
| 12-15 | 70-90 | 0,12-0,16 |
PQ interval pathologies
Changes in the PQ interval indicate pathologies of the cardiac conduction system. This interval can be either shortened or lengthened. In some cases, there is a dissociation of the P wave with the QRS complex.
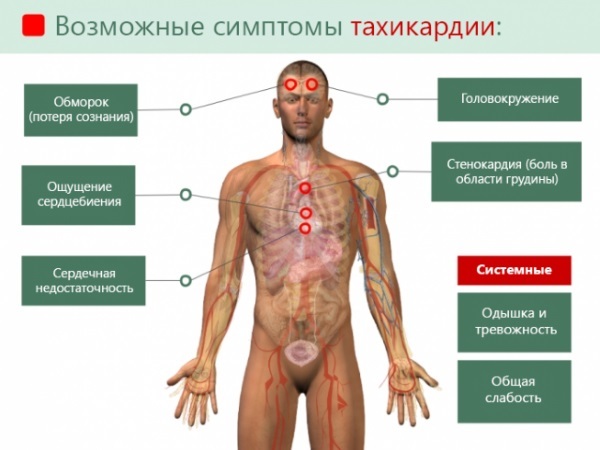
A shortening of the interval indicates a faster than normal conduction of excitation from the atria to the ventricles. This can be dangerous by the development of tachycardia attacks.
The lengthening of the interval, on the contrary, indicates the difficulty of conducting excitation between the atria and ventricles. These pathologies are called atrioventricular conduction blocks. They qualify as both physiological and pathological.
A shortening of the interval may indicate the presence of a syndrome of premature excitation of the ventricles. This syndrome is associated with the presence of additional (abnormal) pathways through which excitation from the atria reaches the ventricles. As a result, the impulse propagates without physiological delay, faster than necessary.
There are two types of this syndrome: CLC syndrome and WPW syndrome., it is possible to differentiate them among themselves according to the peculiarities of the QRS complexes. It is possible to recognize the accelerated conduction of impulses on the ECG by measuring the duration of the PQ interval. Its normal values should be less than 0.11 sec.
The PQ interval on the ECG (its norm for children is less than for adults) during diagnosis depends on the age of the patients. With this pathology, the QRS complex and the T wave remain unchanged.
The danger of this phenomenon is the possibility of developing arrhythmias (paroxysmal tachycardia). During the course of the disease without attacks of tachycardia, the patient may not be aware of the presence of additional pathways in the heart for a long time.
An increase in the interval can occur in cases of the presence of atrioventricular blocks. Distinguish between partial (1 and 2 types) and complete (3 type) blockade. Functional or organic factors can cause blockages.
Functional reasons include the use of certain drugs that reduce intracardiac conduction, intense sports. Examples of organic causes are myocardial infarctions, infectious diseases of the heart muscle, myocardial ischemia, and heart defects.

The PQ interval on the ECG (the norm against the background of partial blockades is violated) in the first type increases, since the conduction of excitation is slowed down, but all impulses from the atria reach the ventricles. The blockade of this type is physiological and is quite often observed in young patients and athletes.
Often this type of blockade does not have any clinical manifestations and does not affect the daily life of people. On the ECG, this type of blockade manifests itself as an increase in the PQ interval (duration is more than 0.2 s).
If a blockade of this type is detected, it is advisable to undergo an additional examination in order to exclude the possibility of concomitant pathologies. Treatment before identifying the factors that provoked the development of pathology is not prescribed.

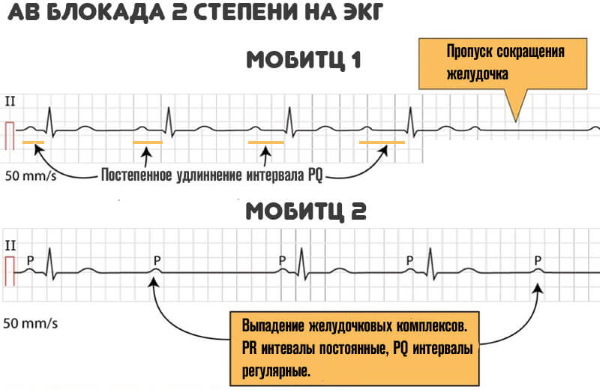
In the second type of disorder, not all impulses from the atria reach the ventricles. It is clearly seen on the ECG record that there are no QRS complexes following some P waves. There are two variants of the manifestation of the blockade of the second type: Mobitz I and Mobitz II.
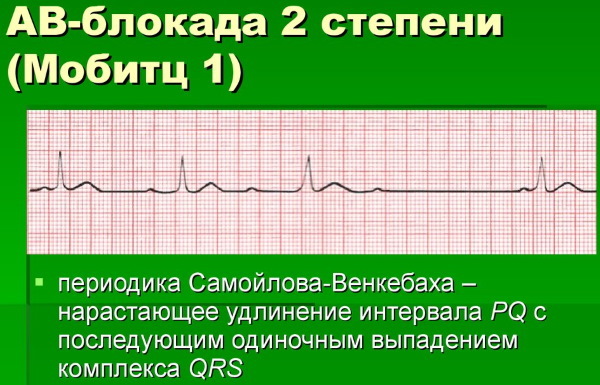
Mobitz I
This type of blockade of the second type can be physiological for young people and athletes. On the ECG, it manifests itself as an increase in the PQ interval with each contraction. The interval increases until the atrial impulse is blocked (on the cardiogram, this is displayed as the absence of a QRS complex).
Also, as with the first type of blockade, patients may not be aware of the presence of disturbances in the work of the cardiac conduction system and may not experience any clinically manifested signs.
If a blockade of II degree of type Mobitz I is detected, a second examination should be carried out, including daily monitoring of the heart rate and repeated electrocardiogram recording. Treatment is prescribed after identifying the cause of the blockade.
Mobitz II
This type is always pathological. The pulse transit time is constant, but the pulses are periodically blocked. This is reflected as the absence of some QRS complexes. Most often, the violation of the passage falls on every third (3: 1) or fourth (4: 1) excitement. In severe cases, the blockage occurs in every second contraction (2: 1).
The condition of patients with this pathology can be very different. Some patients notice a sharp deterioration in the condition, darkening in the eyes, coinciding in time with a falling QRS complex. A number of patients may not even be aware of these problems.
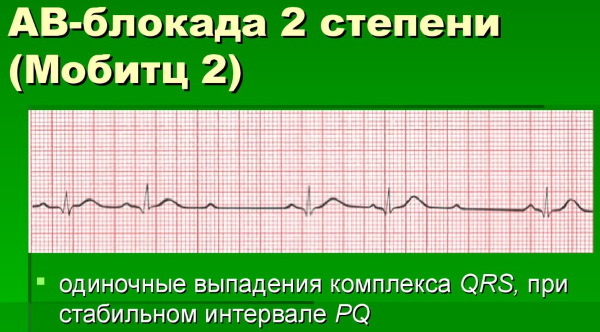
The severity of the blockade and the risk of going into full (third-degree blockade) depends on the reasons for the development of the pathology. Treatment is also prescribed based on the etiology of the disease. The blockade of the third type is characterized by a complete violation of the impulse conduction. On the ECG, it looks like a disconnection between the P waves and the QRS complexes.
Cardiac activity in these patients is maintained by a rhythm generated by the ventricles. Depending on the cause of the development of the third degree blockade, treatment methods can be both medication and surgical (implantation of a pacemaker). If this type of block is congenital, most patients do not need a pacemaker.
Violations of the cardiac conduction system can cause sudden cardiac arrest and death. These disorders can be both congenital and acquired.
In the case of acquired diseases, early diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment can affect the favorable outcome of the disease. That is why the ECG should be carried out periodically to make sure that its indicators (in particular, the PQ interval) are in accordance with the norm.
Survey video
ECG PQ interval:



