Content
- Definition and concept of human existential needs
- Types and characteristics of existential needs
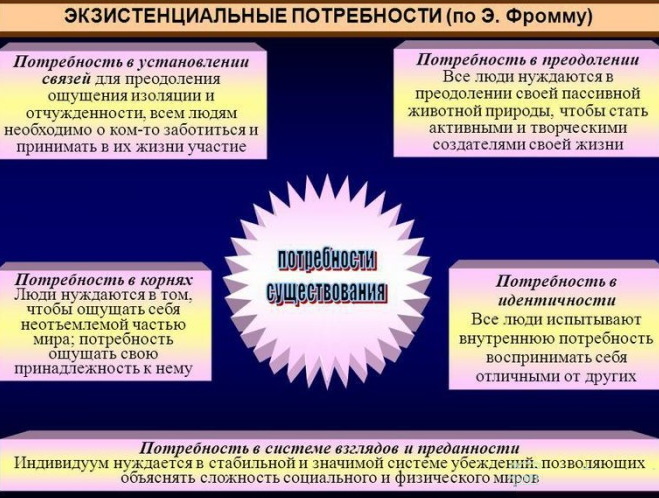
- Establishing connections
- Transcendence
- Rootedness
- Self-identity
- System of values
- Modern interpretation of social existential needs
- The existential needs of a person, according to the concept of E. Fromm
- The existential needs of a person according to the theory of A. Maslow
- Maslow's pyramid of needs
- Examples of existential needs
- Video about existential needs
Conditioned by the squeak of its own place in life, the socio-biological needs of psychoanalysts are called existential. They affect the inner world of a person, mental-behavioral and emotional aspects of the person. This concept was introduced into everyday life by the German-American philosopher and reformer of psychoanalysis Erich Fromm.
Definition and concept of human existential needs
The first attempts to formulate and outline the range of such psychoemotional factors of an individual's behavior go back to ancient philosophical teachings.
Ancient Greek and Roman authors sought to separate the true socio-biological needs from those inspired by time, formed under the influence of passing social traditions or foundations.
The fundamental difference and a clear identifying feature of existential needs lie in the psycho-emotional roots, not the physiological nature. They are not considered basic because they are not required for biological survival. But without their satisfaction, the mental and psycho-emotional state of the individual will be depressing.
The existential needs of a person are a philosophical category most convincingly formulated by E. Fromm. In 1955 g. he published Healthy Life, which defines such actions as addressing typically human dilemmas.
Existential needs according to E. Fromm are presented in the table:
| Need | a brief description of |
| Building and strengthening ties | Social and family relationships are implied. Socialization of the individual improves the psycho-emotional state, instills self-confidence, and provides a sense of security. |
| Individualism | For a person, self-identification is important, which consists in realizing his own difference from the people around him. Fromm considered the thirst to satisfy such a need a key behavioral motive. |
| Formation of the worldview system | For a confident orientation in the social environment, an individual needs a clear scale of value coordinates. In this capacity, scientific theories and hypotheses, philosophical teachings, and religious beliefs are used. |
| Regulation of your own behavior | To satisfy sublimated existential needs, it is necessary to go beyond natural instincts, natural physiological reflexes, giving priority to spiritual aspects. They must determine the behavior of the individual. |
| Return to the roots | This implies the individual qualities that are laid down from childhood by the social environment. Satisfaction of such a need creates a feeling of one's own need and security, which positively affects the development of the individual. |
 The desire to satisfy the listed existential needs forms a balanced and harmonious personality. Their presence radically distinguishes people from representatives of other biological species that inhabit the planet.
The desire to satisfy the listed existential needs forms a balanced and harmonious personality. Their presence radically distinguishes people from representatives of other biological species that inhabit the planet.
Types and characteristics of existential needs
Generally distinguish bodily-biological, social-personal, spiritual-mental needs. Each psychological school offers its own classification of existential needs. Theories of A. Maslow, K. Alderfer, E. Fromm and some others.
American psychologist David McClelland proposed his own system for classifying existential needs, based on the methodology he developed for studying the driving forces of a personality. Below are the most common and frequently used types of psycho-emotional needs.
Establishing connections
It is natural for a human person to strive to integrate into ongoing social processes, to become an integral part of a social formation. It is psychologically important to feel your own involvement, closeness with your own kind, unity.
Loneliness and isolation from society are unnatural, since humanity is a collective species. Establishing close relationships is especially valuable with loved ones or helpful people.
In the second case, satisfaction is based on a mercantile interest, which gives rise to controversy about whether such a need can be considered existential. Erich Fromm will propose to separate psychological moments from other motives.
The existential needs of a person are, according to the American philosopher of German descent, the desire to establish social connections based on emotional attachment, love, and other related motives.
Dominance / submission-based communication hinders the formation of harmonious contact. This connection, according to E. Fromm, cannot be considered complete and healthy.
A typical example is the standard relationship between a boss and a subordinate. A specific form of establishing ties of this nature is marriage. The desire of one partner to rule, dictate and control falls on fertile ground when meeting with a person seeking to take a dependent and subordinate position.
Such relationships are called complementary and are considered to meet the needs of both participants in the existential connection of a complementary orientation. A strong union does not mean a healthy one. Making this connection is a common way to satisfy existential needs.
NS. Fromm identifies the following factors for healthy interpersonal relationships:
- love;
- respect;
- the trust;
- coincidence of life goals;
- common interests.
In a connection based on other impulses, emotional attachment either does not arise or quickly fades away.
Transcendence
The term is used in psychology and philosophy to describe the personality's overcoming of itself, going beyond the usual framework. This provides a sense of inner freedom. A purposeful person with the help of transcendence reaches his own landmarks.
Such a state is determined by opposite and mutually exclusive forms of behavior - constructive or destructive-destructive. The first implies the recognition of social values, care for the benefits and achievements created by civilization.
Such individuals try to supplement other people's inventions, creations, intellectual products. They strive to preserve and develop existing achievements, to take an active part in social processes, various spheres of public life. Such people have a positive effect on progress, make their own contribution to the future of humanity.
Examples of a creative approach to life:
- medical advances;
- writing activity;
- scientific developments;
- care for the environment;
- teaching or educational work.
Destructive and destructive behavior is aimed at suppressing and oppressing the will of other people, thoughtless use of resources. It implies a consumer attitude towards life.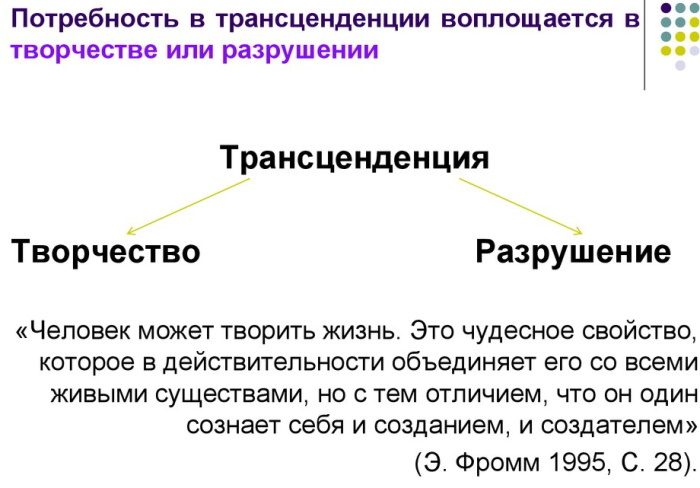
Such people value their own ego above all else, go on about personal ambitions, strive to satisfy exclusively physiological needs. Destructive behavior has a destructive effect on the psyche.
Rootedness
For personal growth, harmonious development, emotional stability, an individual needs a kind of fulcrum that creates a sense of security. This gives strength for creative achievements and new life challenges, allows you to withstand tense moments without falling into despair.
Being rooted provides a sense of security. The realization of such a need is considered by psychoanalysts to be a basic emotional need. Without rootedness, a feeling of mental isolation, helplessness inevitably arises, and depressive states develop.
Existential needs are aimed at a person's search for a place in life and awareness of their own role in the social environment. This is a kind of escape from moral loneliness, social non-recognition. Satisfaction brings awareness of their own relevance, self-respect.
The thirst for security, imbued with a sense of security and need pushes to establish unconstructive connections with vague social roles. An example is marriage, when a man associates his chosen one with his mother.
It is a subconscious choice driven by deep-rooted childhood memories of safety, security, and comfort. This behavior speaks of a latent or conscious unwillingness to take responsibility. The man tries to satisfy this existential need through marriage.
This desire has signs of psychoemotional adaptation to constantly changing living conditions. It is dictated by fear of the unknown, self-doubt. Explicit psycho-emotional reasons for the need make it possible to consider it existential.
Self-identity
The collectivism of human society E. Fromm compares it to the herd instinct. Thinking creatures of our biological species have a developed need to search for their own similarity to their own kind, belonging to a social group according to clear identifying characteristics.
As a result, individuality is partially lost, the boundaries of self-awareness are blurred. A striking example of such a behavioral reaction is when a person introduces himself as a relative or friend of a famous person. Thus, he negates his own significance.
Another illustration is the highlighting of a profession or social role instead of oneself. A person with such behavioral reactions introduces themselves as a doctor, lawyer, manager, and so on in order to increase their importance in the eyes of the interlocutor.
Self-identity from the point of view of psychoanalysis means the ability to accept one's own personality outside depending on the type of occupation, professional affiliation, social status, other similar factors. Exaggerating personal significance dilutes and devalues individuality.
System of values
She plays an important role in the formation and development of personality. The value system performs the function of a behavioral guide or a moral fulcrum. In crisis, difficult or critical life situations, a person turns to the formed value orientations, coordinating his own actions with them.
They allow you to avoid feelings of guilt, remorse, or regret for what you have done. The system of values in the aspect of existential needs provides psychological comfort and moral satisfaction from the realization of the correctness of the choice, the perfect deed.
It is the ability to take responsibility in difficult moments in life. With a developed and well-established system of values, any mistake is perceived as a new experience that the individual learns and adopts in order to avoid repetition in the future.
The existential needs of a person are the cornerstone of the harmonious development of the individual. The desire to satisfy them often leads to a revision or adjustment of their own value system. Armed with such moral and ethical guidelines, a person is distinguished by purposefulness.
He adequately perceives the realities of life, more easily adapts to the changing conditions of the surrounding world, directs efforts towards creation. Rational behavior based on a scale of values allows you to maintain psychosomatic health and a favorable emotional state.
Modern interpretation of social existential needs
Regularly conducted sociological studies of the value system of people are extremely important in the aspect of understanding the trends of social development, ensuring order, and educating the younger generation.
When analyzing the behavior of collective formations or individuals, the dominant role of existential needs becomes obvious. They serve as a determining factor in the behavior of an individual, influence the mores or traditions of cultural formations.
On their basis, normative value guidelines and legal regulation of social relations are formed. It is a powerful factor in collective or individual life.
Cardinal changes in the structure of societies, revision of the scale of human values in the XXI century. caused an increased interest in the study of existential needs, value systems. They are the main subject of research by psychologists and sociologists.
The existential needs of a person are a fundamental, multifaceted and widely interpreted concept. Each philosophical school interprets them in its own way. In classical works on psychoanalysis and sociology, existential needs are considered an important contribution to the life of social formations.
Significant phenomena and processes are associated with their satisfaction. Existential needs come in a variety of ways. As social development progresses, they acquire other expressions and numerous forms.
The circle of existential needs is constantly expanding. They are embodied in objects, material goods, abstract ideas. Some modern interpretations interpret existential needs as a standard or a tool for assessing reality.
They are positioned as an element of the cultural structure, consisting of behavioral algorithms, values, principles of interpersonal relationships. Existential needs are aimed at satisfying spiritual and psycho-emotional needs.
The existential needs of a person, according to the concept of E. Fromm
In the theory of the German-American psychologist and philosopher, such aspects of the personality are classified on the basis of the integration of the individual into social processes, social phenomena and relationships.
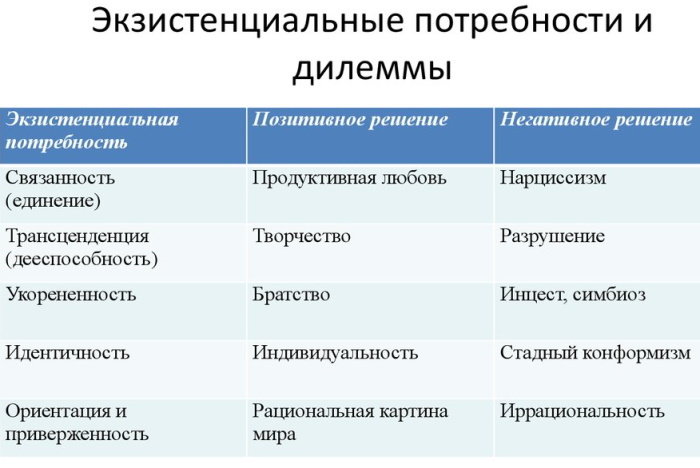
NS. Fromm highlights existential needs:
- Communication with the strengthening of interpersonal bonds. The foundation is love, friendship, family relationships.
- Thirst for creativity. Regardless of the type of activity or professional affiliation, a harmonious person strives to form a psychologically comfortable environment around himself.
- Deepening of root links. They provide strength and stability to life.
- Striving for assimilation. It implies a search for one's own similarity to other members of society.
- Cognition and development of the surrounding world. They are realized with the help of intellectual development, broadening one's horizons.
The author of the philosophical concept gives an important role to the influence of subconscious behavior on the formation of personality. The unconscious, according to E. Fromm, serves as a driving force and hidden potential.
The existential needs of a person according to the theory of A. Maslow
The most popular and widespread system for classifying existential needs belongs to the American founder of the humanistic school of psychology, Abraham Maslow.
His model of the hierarchy of human needs has found wide application in economic theory. Based on the pyramid A. Maslow studies consumer motivational factors and behavioral responses.
Maslow's pyramid of needs
The hierarchy of existential needs is divided into primary and secondary, higher and lower. In a special variety A. Maslow singles out prestigious needs driven by ambition.
They often regulate consumer behavior. To the primary needs of the pyramid A. Maslow's natural physiological needs are counted.
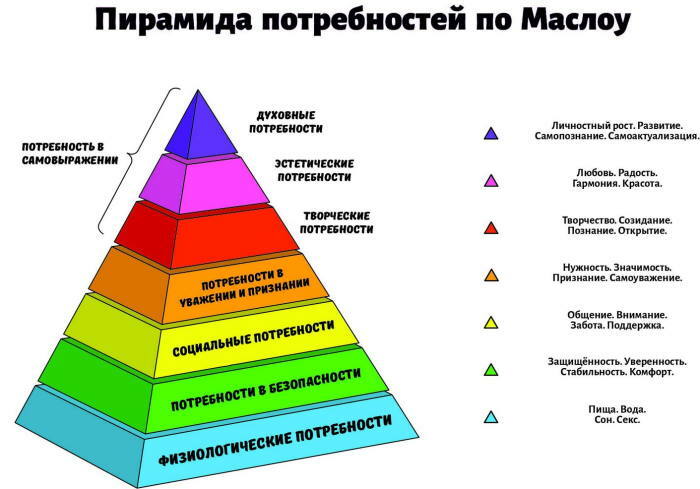
This includes satisfying natural reflexes and instincts:
- thirst;
- food hunger;
- recreation;
- reproduction of offspring;
- respiratory function;
- motor activity;
- search for clothes;
- arrangement of a warm and safe home.
According to the author's concept, the secondary needs include social moments - communicative ability, emotional attachment, participation in collective activities.
This category of existential needs includes spiritual needs aimed at self-realization. Career growth and social status are of great importance in modern society. People spend a lot of effort to satisfy them.
Examples of existential needs
Complementary partnerships are considered to be a visual reflection of such human needs and their satisfaction. Examples are the desire for unity with a social group, participation in social processes. It is based on inherent values.

Another typical example of existential needs is marriage, where the husband knows how to earn money and the wife knows how to manage the household. Anyone seeks to satisfy such needs in an affordable way. This is the natural desire of the individual. Without satisfying their needs, people tend to fall into depression, apathy, and lose interest in life.
Video about existential needs
The existential needs of a person are: