Content
- What is schizoaffective disorder, who is predisposed to psychosis
- Causes of Schizoaffective Disorder
- Types of schizoaffective psychosis, their symptoms and signs
- Manic
- Depressive
- Mixed
- How does the disease proceed in men and women, in adolescents
- Difference with schizophrenia
- Differential diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder
- Drug treatment
- Psychotherapy
- Forecasts
- Schizoaffective Disorder Videos
Among mental diseases, the share of endogenous (internal) psychoses is significant and reaches almost 12%. Due to the dual nature of the symptoms, a number of scientists suggest that the manifestation of schizoaffective disorder be considered one of the variants of schizophrenia with unusually pronounced affective signs. However, this type of psychosis was nevertheless isolated as a separate nosological unit with a complex train of symptoms, which requires the doctor to conduct in-depth diagnostics to prescribe therapy.
What is schizoaffective disorder, who is predisposed to psychosis
When diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder (psychosis), many patients believe that it is already schizophrenia. Meanwhile, schizoaffective psychosis is a transitional clinical form between two psychotic diseases of the chronic type. Pathology is an intermediate condition, combining episodes of schizophrenia (delusions, hallucinations) with signs of affective bipolar disorder (mania, depression, mood disorders).
The author of the term "schizoaffective disorder" (SHAR) in 1933 became Jacob Kazanin, since in some of his patients he managed to fix changes in mood in parallel with psychopathological symptoms characteristic of schizophrenia. For a long time, SHAR was considered a subtype of schizophrenia, but today the pathology has become an independent disease that has taken a certain place in the ICD 10 classifier.
The diagnosis is made only when the simultaneous appearance of psychosis and disorders is established moods in a certain ratio - more than 50% of affective symptoms should be combined with 2 or more signs schizophrenia.
The manifestations of schizoaffective disorder include a complex of psychotic episodes characteristic of both the state of passion and schizophrenia:
- signs of deep depression against the background of general depression, feelings of fear, anger;
- illogical behavior when the expression of emotions does not correspond to the situation;
- catastrophic weight loss due to appetite problems;
- development of addiction to alcohol or drugs;
- acceleration of speech, while the patient "swallows" the endings of words;
- the appearance of suicidal and delusional thoughts, auditory and voice hallucinations;
- inability to fall asleep, concentrate, think logically.
Schizoaffective disorder is a combined form of psychopathological syndrome that manifests itself in both schizophrenic and melancholic or manic episodes. The clinical picture is characterized by a milder course compared to schizophrenia.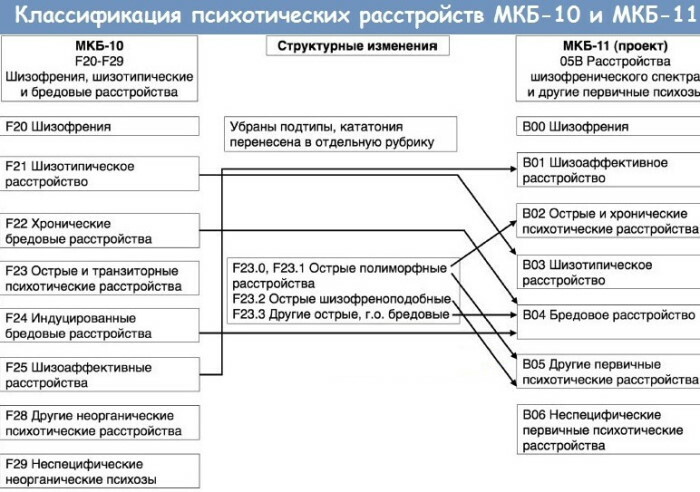
The development of endogenous psychosis takes place in stages, characterized by an increase and decrease in manifestations:
- Stage 1. During the pre-manifest period, against the background of internal discomfort and general anxiety, sleep is disturbed, and the mood becomes unstable. The feeling of one's own “I” also changes, which can happen quite sharply.
- Stage 2. The affective-delusional stage is characterized by the appearance of delusional attacks similar to the reality of hallucinations. With a large specific gravity of pathological sensations, some patients believe that they are damaged.
- Stage 3. If derealization does not turn into an acute form, then there is a decline in the process and an exit from the state of psychosis. This stage is accompanied by the appearance of residual symptoms - affect (sadness or hypomania) or manifestations of the schizophrenic type.
- Stage 4. The uncomplicated form of psychosis is characterized by the onset of a period of remission. The acute form is characterized by the progress of total depersonalization with the manifestation of disorders of consciousness, a feeling of stunning, which can be replaced by a coma.
Depending on the form of the course of schizoaffective disorder, the nature of its symptoms changes. The disease begins with vivid affective sensations, then there is an attachment of disorders schizophrenic type, and in the clinic of combined pathology, symptoms of one of the its forms.
| Dominant form | How does it manifest |
| Affective | Affect dominant type early manifests (before 15 years) with a sharp change in mood, active gestures and facial expressions, over-expressed emotional reactions. A person can completely lose appetite, become sloppy, and a pessimistic attitude leads to the appearance of suicidal thoughts. |
| Schizophrenic | The schizodominant type is characterized by the predominance of manic-delusional symptoms, manifested by illogical behavior, sometimes frightening. The patient is sure that the course of his thoughts is known to others, and they can influence his subconsciousness. The patient has hallucinations and delusional ideas, dementia develops. |
 With the dominance of schizophrenic manifestations, the duration of the attack increases - at least six months. The increase in schizodominant symptoms occurs gradually with a predominance of mood changes, a change in hysteria with aggression. Until the appearance of clinical signs, 2 years may pass, but the threat of a sharp onset of exacerbation, not caused by any external provoking aspects, is not excluded.
With the dominance of schizophrenic manifestations, the duration of the attack increases - at least six months. The increase in schizodominant symptoms occurs gradually with a predominance of mood changes, a change in hysteria with aggression. Until the appearance of clinical signs, 2 years may pass, but the threat of a sharp onset of exacerbation, not caused by any external provoking aspects, is not excluded.
Schizoaffective disorder is a borderline mental state in the continuum between the classic type of schizophrenia and manic-depressive psychosis. In the case of a predominance of affective symptoms, an attack of SHAR provokes the action of external factors. However, with the onset of remission and the decline in manifestations, specific episodes go away, and those around in a person's behavior do not notice dangerous changes.
Causes of Schizoaffective Disorder
Specialists have not yet been able to establish the exact reasons for the development of pathology, but only to indicate a specific set of individual characteristics of an organism that increases the likelihood of formation BALL. Such psychoses are most often diagnosed in persons with a hereditary predisposition who have a gene for the risk of developing schizophrenia. The occurrence of episodes of schizoaffective disorder is recognized as a genetically determined fact.
The dormant gene that provokes the disease can cause mental problems under the influence of the following factors:
- a particularly severe stressful situation, low social status;
- living in hunger and poverty, as well as living completely alone;
- due to the outbreak of hostilities or forced migration.
Pathology is characterized by prolonged periods of a psychotic state. Exacerbations of the disease sometimes stretch for months, and a person has to go to the hospital. The presence of alcohol and drug, as well as chemical addiction significantly increases the threat of the emergence of a ball, but determine the root cause of psychosis (mental sphere or addiction) can only be a specialist in a psychiatric hospitals.
According to scientists, in addition to the influence of stress, the cause of the onset of schizoaffective psychosis is often obtained in childhood trauma, as well as a failure of the chemical processes of the brain, when the properties of neurotransmitters change or the percentage increases dopamine.
Types of schizoaffective psychosis, their symptoms and signs
The uniqueness of the psychopathological syndrome in the presence of symptoms of two types - psychotic symptoms of the type of schizophrenia and signs of depressive-manic disorder that changes mood. Depending on the prevailing emotional background and the characteristics of the clinical picture, there are 3 main forms of the disease - manic, depressive, mixed. Each type of mental disorder differs in the originality of symptoms, which complicates the task of the diagnostic process.
Manic
Manic schizoaffective disorder is characterized by an abrupt onset with the appearance of vivid symptoms against a background of high spirits. This is a condition when episodes of schizophrenia are accompanied by manic manifestations, the patient has a sharp agitation, disinhibition. For example, a person may give away all of their possessions or spend all of their savings.
The main symptoms include the following episodes:
- the appearance of incoherent speech, scattered attention, unwillingness to rest and sleep;
- due to hyperactivity, the patient rapidly changes topics of conversation;
- a sharply increased mood does not extinguish even in inappropriate situations.
Patients suffer from delusions of grandeur, some have delusional ideas that are cosmic or magical in nature, accompanied by visual and auditory hallucinations. At the stage of exacerbation of the disease, a person is dangerous to others, he needs treatment in a psychiatric clinic.
Depressive
In this variant of schizoaffective disorder, there is a combination of schizophrenic manifestations with depressive symptoms.
This form of psychosis can be called moderate or prolonged depression, the syndrome is diagnosed by the presence of the main manifestations:
- a depressed state and a feeling of melancholy, a decrease in energy potential;
- loss of interest in life against the background of rapid fatigue and insomnia;
- heightened feelings of guilt, inability to concentrate, memory problems.
 The clinical picture is accompanied by episodes of wide-ranging delusions, as well as the negative nature of hallucinations (accusatory orientation). However, the manifestations of psychosis of the depressive-paranoid type are purely individual, the protracted course of a poorly controlled disease threatens with sudden attacks of aggression, suicidal attempts.
The clinical picture is accompanied by episodes of wide-ranging delusions, as well as the negative nature of hallucinations (accusatory orientation). However, the manifestations of psychosis of the depressive-paranoid type are purely individual, the protracted course of a poorly controlled disease threatens with sudden attacks of aggression, suicidal attempts.
Mixed
Only a psychiatrist, based on the results of diagnostics, will be able to accurately establish the type of mental illness, the severity of its course, in order to prescribe the correct treatment regimen with modern drugs. Moreover, a mixed variety of endogenous pathology signals the manifestations of manic and depressive disorders. Moreover, in time, the attacks of both forms of psychosis alternate, which leads to the need to take into account the characteristics of the manic and depressive phases during the choice of meta therapy.
How does the disease proceed in men and women, in adolescents
Despite the fact that representatives of both sexes suffer from this type of disorder, endogenous psychoses are less common in the male category of patients. The reason for the appearance of SHAR in men is more often dependence on alcohol or psychoactive substances. The clinic of male pathology has a peculiar specificity, manifested by the early onset of symptoms (adolescence), a decrease in working capacity due to the severity of the manifestations of the disease.
Due to the more emotional brightness of the female psyche, women are more likely to suffer from psychoses, especially during pregnancy, as well as menopause. If in men the symptoms of the schizophrenic type debut at the age of 20-25, then in women psychoses develop 5-7 years later.
A sluggish illness progresses imperceptibly and much more slowly, signaling episodes of bright affects of a depressive or manic type without much impact on performance. True, it is easier for patients to control the volitional sphere, building personal relationships, but with the onset of menopause, the threat of schizophrenic symptoms increases.
Schizoaffective disorder is a mental disorder whose symptoms are dangerous to ignore. Indeed, in adolescents, the debut of psychosis occurs, as a rule, at the age of 16 against the background of hormonal disruption, provoked by stressful and traumatic situations.

Psychosomatic pathology starts imperceptibly, manifested by isolation, aggressiveness, conflicts with peers, and enthusiasm for super ideas. A teenager's academic performance is rapidly falling, he may start smoking, use alcohol or drugs, become addicted to the game.
Difference with schizophrenia
Despite the simultaneous presence of symptoms of two types of psychosis, SHAR is recognized as a separate diagnosis with its own characteristic features:
- rather long duration (at least 1 month) of the first episode with the simultaneous presence of symptoms of schizophrenia and mood swings;
- the emergence of self-care problems and social difficulties are less noticeable to others than in the case of schizophrenia.
The clinic of endogenous disease is characterized by a special way of development. At the pre-manifest stage, the onset of symptoms of a psychopathological syndrome occurs, with the onset of an acute period, which can last up to 8 months, an attack begins. The exacerbation ends in remission in the absence of residual consequences - a state of apathy, passivity, flattening of emotions, desocialization.
Differential diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder
Since the clinic of pathology includes signs of two types of psychopathological syndromes, it is important to correctly diagnose the patient's condition. The main difficulty lies in differentiating SHAR from schizophrenia, the treatment of which is carried out according to a completely different program.
Therefore, to confirm schizoaffective disorder, at least one proven psychotic episode, which is not accompanied by a pronounced symptom of impaired mood.
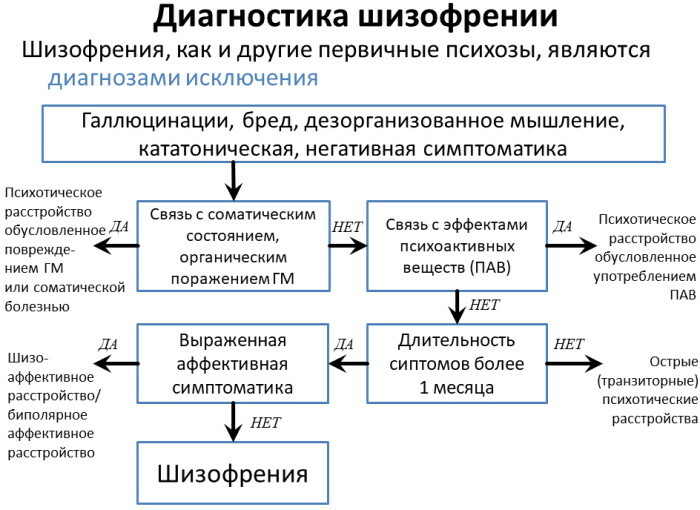
The diagnosis is confirmed if the following manifestations are found:
- obvious symptoms of an affective state;
- at least one attack within 2 weeks;
- time combinations of schizophrenic and affective symptoms.
In addition, the doctor needs to make sure that the patient did not use psychotropic substances, did not suffer from organic damage to the brain or central nervous system. It is also necessary to exclude drug and alcohol dependence, and if neurological diseases are suspected, the results of additional examinations will be required.
Drug treatment
Schizoaffective disorder is a special type of psychosis with a predominance of affective disorders rather than psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. At the stage of the acute course of the disease, the patient needs hospitalization. The decision on the choice of the method of dealing with the manifestations of psychosis is made depending on which form of pathology is dominant.
Therefore, the treatment regimen includes a combination of several groups of specific medications:
- To stop the manifestations of depression, antidepressants are prescribed. The action of the drugs improves mood, removes the state of melancholy and anxiety, relieves the feeling of apathy against the background of relieving emotional stress.
- Schizophrenic symptoms are eliminated with antipsychotics (antipsychotics). The drugs relieve the arrival of delusional ideas, the appearance of hallucinations, smooth out the intensity of affective episodes.
Antipsychotics for schizoaffective disorders - The connection of tranquilizers (anxiolytics) helps to get rid of fear and anxiety. The sedative effect of certain drugs has a beneficial effect on sleep.
- Reception of normotimics relieves affect, normalizes mood and stabilizes the emotional background.
- To increase the productivity of sleep, to ensure a good night's rest, it is necessary to prescribe sleeping pills.
In the acute stage of schizoaffective psychosis, it is advisable to combine several medications in order to stop the severity of symptoms. Usually doctors for these purposes prescribe antipsychotics in combination with antidepressants.
The choice of antipsychotic and the dose of admission depend on the intensity and nature of the delirium. With a sharp severity of delusional manifestations, the dose of the drug is significantly increased. After exiting the acute period, normotimics are connected, and with the onset of remission, the patient is recommended to switch to outpatient treatment, but under the supervision of a psychiatrist.
Psychotherapy
Thanks to an integrated approach to the treatment of psychosis in the hospital, the patient receives psychiatric help, which allows him to quickly return to a normal lifestyle. Despite the fact that the method is considered auxiliary, psychiatric help accelerates and consolidates the action. medicines, increases the duration of the remission period, adaptation of the patient in the environment of healthy members society.
The use of talking therapy helps to normalize thinking. Through one-on-one conversation with a psychiatrist, the patient learns to understand his condition in order to successfully confront the symptoms of schizoaffective disorder.
The method of family and group psychotherapy helps to reduce social isolation, provide support for the joint overcoming of the disease. If the patient has difficulties in expressing his problems, the method of art therapy (music, dance, art) will help him.
Thanks to psychotherapeutic techniques, it is possible to smooth out the influence of the root cause of the disease, to reduce the negative impact of stress. To ensure full contact, the psychotherapist begins to work with the patient only after the severity of the attack has been removed.
Forecasts
The course of schizoaffective syndrome is characterized by cyclicality - at the onset of the disease, the attacks do not last long, followed by a rather long remission. However, in the absence of timely treatment, a gradual manifestation of personality changes occurs. By analogy with the manifestations of the disease, the prognosis is ambiguous, depending on the dominant form and type of psychosis.
If symptoms of the affective type predominate, the correct combination of medications will help an early onset of prolonged remission. In the case of the schizodominant form, there is no need to expect a favorable prognosis. Experts, on the basis of many years of medical practice, argue that a patient with schizoaffective disorder can be in society, since this condition does not threaten others with acute symptoms forms of schizophrenia.
Schizoaffective Disorder Videos
Schizoaffective disorder. Difference from schizophrenia:



