Disturbances in the structure of the uterus are quite rare. The main representatives of this pathology are the two-horned and saddle-shaped uterus.
Record content:
- 1 General information
- 2 The reasons for development, the mechanism of formation
-
3 Diagnostics
- 3.1 Ultrasound
- 3.2 Hysterography
- 3.3 Hysteroscopy
- 3.4 MRI
- 4 Saddle-shaped uterus and pregnancy
- 5 Features of childbirth
- 6 Treatment
- 7 Treatment during pregnancy
- 8 Saddle uterus videos
General information
This feature of the structure of the uterus is characterized by its formation at the bottom of a depression in the shape of a saddle. This malformation is not so common, about 1⁄4 of the total number of abnormalities in the structure of the uterus.
Normally, the uterus is an unpaired organ, pear-shaped. It is represented by muscle fibers, from the inside, the uterus is lined with a mucous membrane. And on the outside it is covered with a serous membrane. The uterus consists of a body and a fundus. The bottom with normal development is straight, has no outgrowths and depressions.
The saddle uterus is a separate form of the bicornuate uterus, but it is not divided by septa.
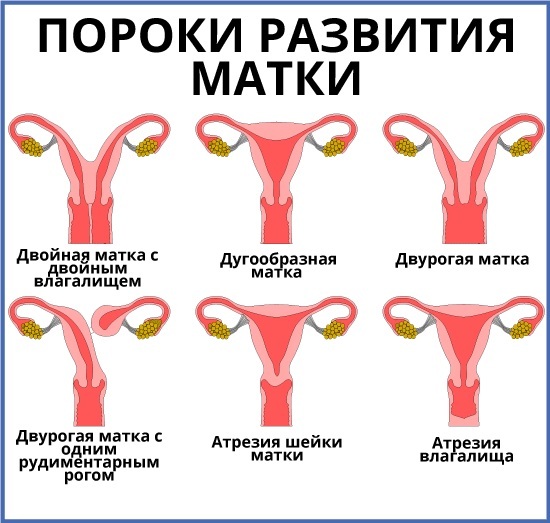
This developmental feature is a lighter form than a two-horned uterus and a more favorable prognosis for conception and subsequent childbirth.
This structure is often combined with the underdevelopment of the urinary system, reproductive organs (ovaries, fallopian tubes), as well as an anatomically narrow pelvis.
The reasons for development, the mechanism of formation
The formation of the uterus in the fetus during embryogenesis begins between 10 and 14 weeks of gestation.
At the stage of embryogenesis, the uterus is represented by two cavities, which are separated from each other by a septum. At this stage, the uterus has a two-horned structure, then gradually changes towards the saddle. By the time of birth, the uterus should take on the shape of a pear. If this does not happen, for any reason, the uterus may remain saddle-shaped. The severity of this deformation is different.
The etiology of the occurrence of the saddle uterus has not yet been established, but there are many factors that can affect the formation of fetal organs during intrauterine development. A pregnant woman can be exposed to these factors during gestation. The main effect on the fetus is exerted by a negative effect that occurred in the 1st trimester of pregnancy.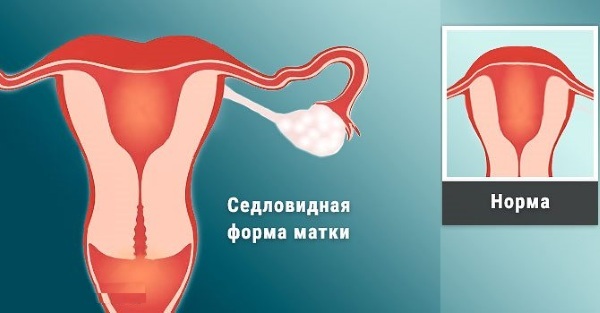
| Factors | Examples of |
| Intoxication of the body | Distinguish between narcotic, alcoholic, nicotine and drug intoxication of the body. Drug intoxication occurs when taking antibiotics, antiviral, antimalarial, anti-tuberculosis drugs. And also with the introduction of chemotherapy drugs into the body. These drugs have a pronounced teratogenic effect on the formation of fetal organs. |
| Exposure to chemicals | It occurs when poisoning with chemical compounds (mercury, lead), while working at chemical plants. |
| Trauma | Mostly these include injuries to the abdomen or pelvic organs. A case is described when a pregnant woman jumped from a height into the water and received a closed abdominal injury as a result of the child at the time of birth had multiple malformations of organs and systems. |
| Infectious diseases | These include flu, rubella, measles, chickenpox. These infections have an impact on the development of the fetus, especially in the 1st trimester, when the baby is not protected by the placenta. |
| Venereal diseases | Syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia |
| Chronic diseases of the reproductive organs | Polycystic, ovarian dysfunction, fibroids, endometriosis, adnexitis, salpigoophoritis, endometritis. |
| Placental pathology | Distinguish between incorrect attachment of the placenta (marginal, lateral, low-lying), detachment of the normally located placenta. |
| Pathology of pregnancy | Toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy, preeclampsia. |
| Age | If the first pregnancy occurs after the age of 35, the risk of developing fetal malformations increases. |
| Endocrine diseases | Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism. |
| Radiation exposure | Occupational hazards, radiation treatment in oncology. |
| Chronic stress | Long-term psycho-emotional impact, strong emotional upheaval. |
All these factors lead to impaired oxygen supply to the fetus. This leads to chronic oxygen starvation, during which the normal development of the child's organs and systems stops.
Diagnostics
The saddle uterus is a pathology, the main feature of which is that a woman does not experience any pathological symptoms throughout her life. The only thing that can induce a woman to see a doctor is long and unsuccessful attempts at conception. In addition, the diagnosis of uterine malformations is carried out with the usual miscarriage.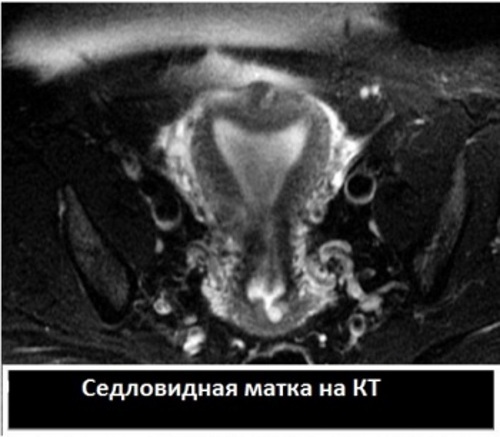
Sometimes a woman may have problems with her menstrual cycle. If the defect is combined with other diseases, their course may be aggravated.
Diagnosis is carried out using pelvic ultrasound, hysterography, hysteroscopy and MRI.
And also with a strong severity, it is possible to diagnose with the help of a vaginal examination. It helps not so much to detect the fact of the underdevelopment of an organ, but to suspect its presence. In this case, the doctor can send the patient for additional diagnostics.
These methods allow us to assess the level of underdevelopment of the organ and choose the tactics of treatment or management of pregnancy (when it occurs).
Ultrasound
Currently, ultrasound is used to diagnose uterine malformations. This procedure allows you to assess the condition of the organ without the use of invasive intervention.
During the study, the structure of the uterus, its size, location, as well as the condition of the uterine appendages and their structure are assessed. A study is carried out using a vaginal sensor, this allows you to better examine the features of the endometrium of the uterus.
If a malformation is present, an increase in the width of the uterus is recorded on ultrasound, as well as the presence of two M-echoes in the area of the tubular corners.
Like other research methods, ultrasound is not without its drawbacks. During the scan, cases were identified when malformations were not visualized and the saddle uterus was taken for normal. But, despite this, ultrasound is the safest, most affordable and cheapest method of examining the pelvic organs.
To obtain more reliable results, ultrasound is performed in the second half of the menstrual cycle. During this time period, the myometrium is visualized better than in the first phase.
Hysterography
Hysterography is another method for diagnosing disorders in the structure of the reproductive organs. It is an X-ray study.
Diagnose by introducing a contrast agent into the uterine cavity. In this procedure, a catheter is inserted into the woman, through which the substance enters the abdominal cavity and is distributed.
During the study, the structure of the uterus, its size, the condition of the fallopian tubes, and the presence of neoplasms are assessed. If a woman has a saddle-shaped uterus, then a convex uterine fundus will be visualized. This phenomenon resembles the shape of a saddle, arch or ridge.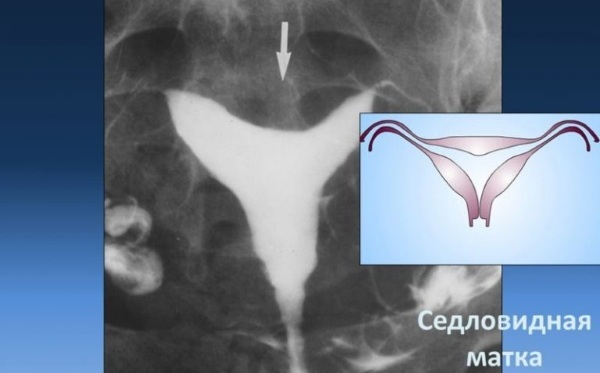
Despite the informational content of this method, it has some drawbacks.
These include:
- Radiation exposure.
- Inability to diagnose during pregnancy.
- Invasiveness.
- The risk of developing allergy to the contrast agent.
- Bleeding.
After the procedure, a woman may feel slight pain (as during menstruation), bloody discharge.
Hysteroscopy
The saddle uterus is also diagnosed with hysteroscopy. This is the introduction of a special tube (hysteroscope) into the uterine cavity for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
During this procedure, it is possible not only to detect defects in the structure of the uterus, but also to evaluate condition of the mucous membrane, patency of the fallopian tubes, the presence of polyps or foci of chronic inflammation.
Before the procedure, the woman is given general anesthesia. Then, in a small operating room, a study is carried out using a hysteroscope, which is equipped with a device for displaying an image on the screen.
With hysteroscopy, the bulge of the fundus of the uterus is observed. As in X-ray, this bulge looks like an arc. Hysteroscopy can be prescribed both for diagnosis and for the treatment of the saddle uterus (if it is impossible to carry it).
Despite the diagnostic effectiveness, hysteroscopy is not prescribed for all women. Its conduct is justified when it is impossible to carry out other methods of examination, with a pronounced malformation of the uterus, as well as with prolonged infertility. The main disadvantage of hysteroscopy is its invasiveness.
MRI
MRI is performed as an additional method of examining a woman. The method allows you to identify the structural features of the uterus, its structure, size, the presence of any pathological elements.
Contraindications for the procedure are:
- Pregnancy.
- The presence of metal structures in the body.
- Claustrophobia (fear of confined spaces).
No additional preparation is required for the patient during an MRI. The only drawback of magnetic resonance imaging is the rather high cost of the procedure.
Saddle-shaped uterus and pregnancy
The saddle uterus is a pathology in which conception and gestation are possible. It all depends on the degree of underdevelopment, as well as the presence of concomitant gynecological diseases.
It is possible to give birth with this pathology, but it is necessary to constantly be under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist. Since the saddle uterus several times increases the likelihood of developing pathologies of pregnancy.
This could be:
- Chronic fetal hypoxia. Hypoxia has a strong effect on the development of fetal organs and systems and can cause their underdevelopment. Often, against the background of hypoxia, the formation of heart defects occurs.
- Malformations of fetal organs.
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy. It is characterized by the attachment of the ovum outside the uterine cavity. With a saddle structure, this complication is more common than in women with a normal uterine structure.
- Neonatal fetal death.
- Placental abruption.
- Incorrect location of the placenta (lateral).
- Bleeding. They can be massive with abruption of the normally located placenta or directly during childbirth.
- Improper placement of the fetus in the uterine cavity. Most often, the pelvic and transverse position of the fetus is distinguished. In most cases, this is an indication for operative delivery.
- Weakness of labor, unproductive contractions.
- Birth trauma.
- Complications in the early postpartum period.
These risks can be significantly reduced if you are regularly observed in the antenatal clinic and all the doctor's recommendations are followed. If there are any pathological symptoms, the woman is placed in the hospital for "preservation".
Features of childbirth
Labor management with a saddle uterus has its own characteristics. To begin with, the woman in labor is hospitalized shortly before giving birth. This is usually 2 weeks. During this time, the woman is examined and the method of delivery is chosen.
With a saddle uterus, the likelihood of premature birth (before 37 weeks) is higher. Therefore, in the presence of symptoms (discharge of mucous plugs, abdominal pain, training contractions), a woman can be put on hospital observation after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
The choice of delivery depends on the severity of the underdevelopment of the uterus, the condition of the woman, the presence of pregnancy pathology.
Natural childbirth in women with a saddle uterus is possible. But in order for the process to be successful, their competent management is necessary. An obstetrician-gynecologist should assess the condition of a woman and a child and, if hypoxia or bleeding occurs, decide on a caesarean section.
With natural childbirth, uncoordinated contractions are possible, this can lead to severe overwork of the woman in labor and, as a result, to unproductive labor. therefore in women with a saddle uterus, epidural anesthesia is recommended.
If the changes are significant, and there is also a pathology of pregnancy (gestosis entwined with an umbilical cord, fetal hypoxia), a cesarean section is performed. And also an indication for surgery can be a clinically narrow pelvis of a woman in labor.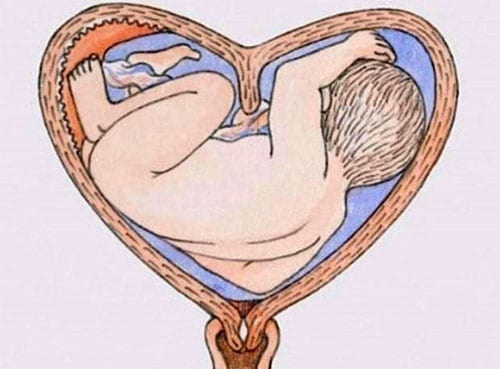
Caesarean section is performed both as planned and urgently (if pathological changes began to develop directly during childbirth).
Treatment
The saddle uterus is a pathology that can lead to long-term infertility. Treatment of this pathology is aimed at the possibility of conceiving and carrying a child.
Therapeutic measures for developmental defects consist in the use of surgical intervention. For this, the method of hysteroscopy or laparoscopy is used. Before the operation, a woman performs a number of important diagnostic procedures to assess the state of the body and its readiness for surgery.
The following studies are assigned:
- Clinical and biochemical blood tests.
- Blood test for syphilis, HIV infection, viral hepatitis.
- Study of blood clotting.
- Examination by a dentist and rehabilitation of chronic foci of infection.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- Fluorography.
Before the operation, the doctor may offer the woman hospitalization in a hospital for several days to undergo the necessary examinations. During the operation, the surgeon gives the anatomically correct shape to the uterus, suturing the defects.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. For this, the drug for anesthesia is administered intravenously. The operation, as a rule, does not take a lot of time.
The early recovery period after surgery rarely threatens any serious health consequences. A woman's fully reproductive health is restored within 6-8 months after surgery. But pregnancy planning is recommended to start one year after treatment.
In addition, medication may be required after surgery. These include pain relievers, antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and haemostatic agents. And antibacterial drugs can also be prescribed (to prevent the addition of a bacterial infection).
Treatment during pregnancy
If the pregnancy has already begun, then in this case, surgical treatment of uterine malformation is not performed. Instead, special attention is paid to the management of pregnancy throughout its duration. A woman should be observed in an antenatal clinic for the entire period of pregnancy and undergo the necessary examinations at a specified time.
Registration of a pregnant woman must be no later than 12 weeks of pregnancy. If a woman has a saddle uterus, registration can be at 9-10 weeks of pregnancy.
The saddle uterus is a pathology in which violations are possible not only from the mother's body, but also from the fetus. Therefore, during the management of pregnancy, special attention is paid to the examination of the uteroplacental blood flow using echography. This allows you to assess the state of the blood vessels of the placenta and identify violations in the supply of oxygen to the fetus.
In late pregnancy, starting from the 28th week, fetal CTG is performed, at the time prescribed by the obstetrician-gynecologist. This allows early detection of fetal hypoxia and a decision to carry out emergency delivery (if there is a pronounced oxygen deprivation).
In addition to intensive observation, medications are prescribed. This is especially important in the early stages of pregnancy, when the risk of miscarriage remains.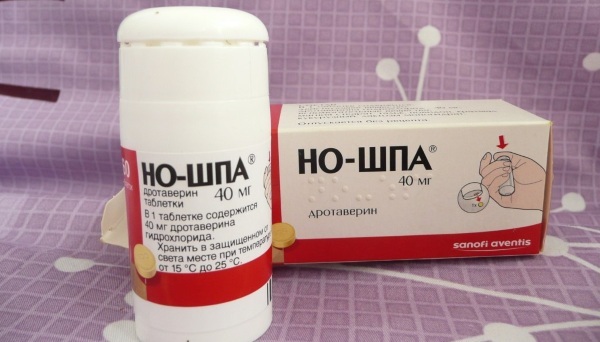
| Group of drugs | Examples of |
| Antispasmodics | No-shpa (1 tablet 2 times a day). Taking this drug can reduce the tone of the uterus. |
| Vitamins and minerals | Folic acid, B vitamins, calcium (up to the 3rd trimester of pregnancy), magnesium. Can be taken alone or as part of a multivitamin complex. |
| Progesterone preparations (with the threat of spontaneous abortion) | Urozhestan, Dyufaston |
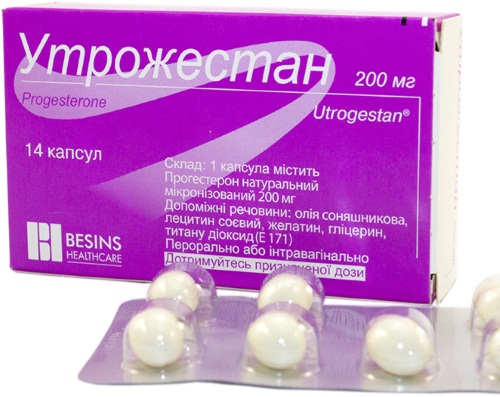
If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, strict bed rest is prescribed, and, if necessary, hospitalization in an obstetric hospital.
And also, if there is a threat of premature birth, it may be necessary to install an obstetric scribe. The scribe is a ring that is placed on the cervix to prevent premature disclosure.
The midwife scribe is filmed just before delivery, usually 2 weeks before the expected due date. The ring can be removed in the antenatal clinic and in the maternity hospital.
Such a pathology as the saddle uterus is dangerous by the development of infertility, miscarriage, premature birth, weakness of labor and an increased risk of perinatal mortality. But with proper management of pregnancy, these complications are minimal.
In order to minimize the risks of possible complications, a woman must strictly follow the recommendations of her doctor and observe complete physical and sexual rest.
Saddle uterus videos
Saddle Uterus Lecture: