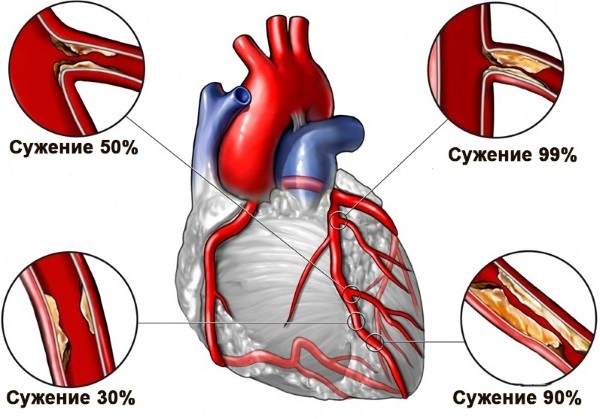
According to medical statistics worldwide from pulmonary embolism 0.1% of the population dies each year. The pathology is characterized by blockage of blood vessels in the pulmonary circulation by thrombotic masses.
The disease is accompanied by numerous symptoms, arises as a result of various factors. A cardiologist will help to establish a diagnosis. Without timely assistance, a person will face serious complications, up to and including death.
Record content:
- 1 What is pulmonary embolism?
- 2 PE reasons
- 3 Classification of thromboembolism
- 4 Stages
- 5 Symptoms and external manifestations
- 6 How to determine the likelihood of a blocked pulmonary artery before the examination?
- 7 Emergency care for pulmonary embolism
- 8 Diagnostics
-
9 Treatment
- 9.1 Conservative therapy
- 9.2 Measures for massive pulmonary embolism
- 9.3 Surgery
- 9.4 Installing a cava filter
- 10 Complications
- 11 Forecast
- 12 Video about TELA
What is pulmonary embolism?
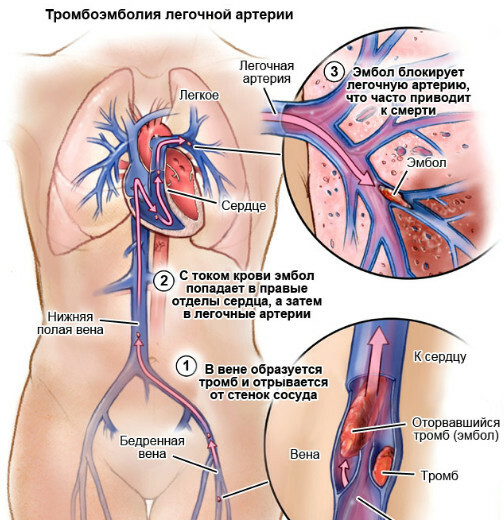
Pulmonary embolism is a disease in which blood vessels become clogged with thrombotic masses. Clots are more likely to form in the lower or upper extremities, rarely in the region of the heart.
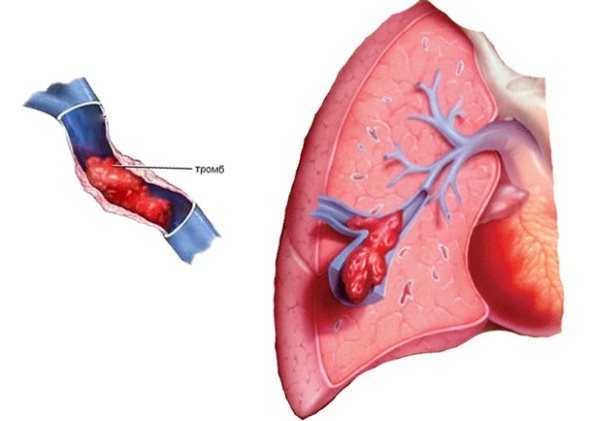
When exposed to provoking factors, the thrombus breaks off and moves along the bloodstream. Where it clogs a blood vessel depends on numerous circumstances, including the size of the clot.
PE reasons
Pulmonary embolism (the symptoms of the disease depend on the degree of its development) in most cases is a secondary pathology that occurs due to the formation of a blood clot. A common source of the pathological condition is blockage of deep veins in the lower extremities.
Thromboembolism occurs against the background of the following provoking reasons: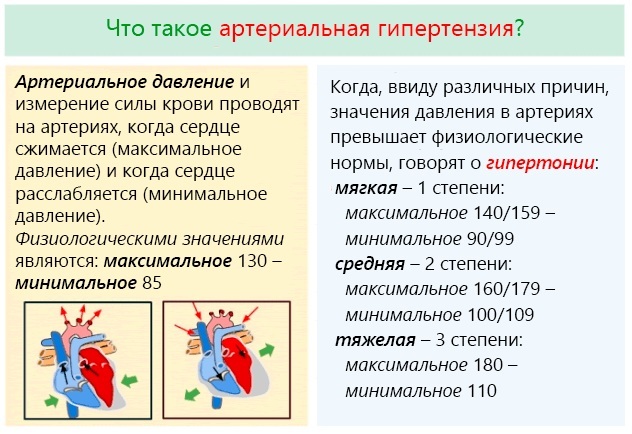
| Name | Description |
| Arterial hypertension | A pathological condition increases the risk of a blood clot and rupture of a blood vessel. |
| Injury | The likelihood of thrombus formation is minimal, but it is present, especially when the rheological properties of the blood are disturbed. The same applies to hematomas that appear after injuries of various kinds. |
| Bad habits | This is more true for those who abuse alcohol, tobacco and drugs. |
| Gender | The disease is more common in the stronger sex. |
| Wrong way of life | We are talking about poor nutrition, lack of sleep, stressful situations and overexertion at work and at home. |
| Hematological diseases | Pathological processes, under the influence of which the property of the blood changes. |
| Excess weight | The increased body weight increases the load on the heart, which leads to the occurrence of stagnant processes. Atherosclerotic deposits appear on the walls of blood vessels, which trigger the formation of blood clots. |
| Malignant neoplasms | The tumors put pressure on the blood vessels. |
The reason for the appearance of PE is also the increased density of the connective tissue. The same applies to the age of 55, uncontrolled intake of certain medications (oral contraceptives, anti-inflammatory drugs).
Classification of thromboembolism
Pulmonary embolism is classified on the basis of numerous characteristics (the severity of the ongoing pathological process, the extent of the lesion, the rate of development of the disease).
There are the following types of PE:
| Name | Description |
| Non-massive | Pathological processes affect the small branches of the pulmonary artery. The condition manifests itself as postoperative pneumonia. Non-massive PE provokes shortness of breath in the patient, chest pain. The patient needs a comprehensive diagnosis to prevent complications of the pathology. |
| Submassive | A form of the disease that manifests itself when the lobar branches of the pulmonary artery are blocked. Clinical symptoms of cardiovascular failure appear. |
| Massive thromboembolism | A severe pathological condition provokes a decrease in blood pressure. Shortness of breath appears, symptoms of heart failure intensify. In most cases, the patient dies. |
Given the course of pulmonary embolism, the following types of disease are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Lightning fast | The disease develops rapidly. As a result of obstruction of the main trunk, the patient's death occurs within a few minutes. |
| Sharp | Pathological processes occur suddenly and progress rapidly. The work of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems is disrupted. The same goes for the brain. The patient has a pulmonary infarction. |
| Subacute | The disease affects large and medium-sized blood vessels. There are signs of impairment in the functioning of the respiratory system, heart failure. As the pathological processes progress, the symptoms intensify, the risk of death is high. |
| Chronic | Pathology is characterized by periodic relapses. The pressure in the blood vessels of the small circle gradually increases. Manifested by pulmonary infarction, pneumonia, pleurisy, heart failure. |
In the chronic form of the disease, the majority of patients within a year after the diagnosis face myocardial infarction, which negatively affects the quality of life. Therefore, it is important to diagnose the disease in the early stages of development in order to timely start treatment and prevent complications.
Stages
Pulmonary embolism (symptoms of a pathological condition cannot be ignored, it is important to be examined and start therapy) also differs in severity as follows:
| Name | Description |
| Mild degree | Symptoms of the disease are sluggish. Pathological processes affect small vessels. Mild thromboembolism can be confused with other diseases (bronchopulmonary pathology, heart failure). |
| Average | The onset of violations does not proceed with lightning speed, but the patient needs an ambulance. The average degree of thromboembolism is accompanied by severe shortness of breath, tachycardia, and low blood pressure. The nasolabial triangle turns blue, and painful sensations appear in the chest area. |
| Severe stage | Symptoms at this stage are lightning-fast and pronounced. The patient loses consciousness, convulsions appear. |
Only a cardiologist can establish an accurate diagnosis, it is important to consult a specialist in a timely manner and undergo a full examination.
Symptoms and external manifestations
Clinical signs of pulmonary embolism will help the cardiologist determine the degree and stage of the disease. Establish a preliminary diagnosis and assign the patient the most informative examination.
The symptoms of pulmonary embolism are as follows: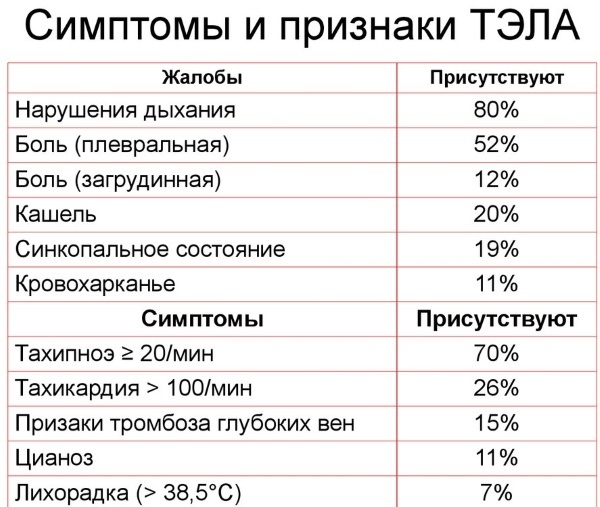
| Name | Clinical manifestations |
| Brain disorders |
|
| Cardiac symptoms |
|
| Respiratory disorders |
|
With inflammation of the lungs and mucous membranes, the patient's body temperature rises. An enlarged liver, impaired intestinal motility, belching, vomiting, and a hard abdomen may also be indicative symptoms.
How to determine the likelihood of a blocked pulmonary artery before the examination?
There is no clear cause for pulmonary embolism, there are numerous provoking factors, and symptoms may indirectly indicate the development of other pathologies. However, there are clinical signs of PE that should be looked at.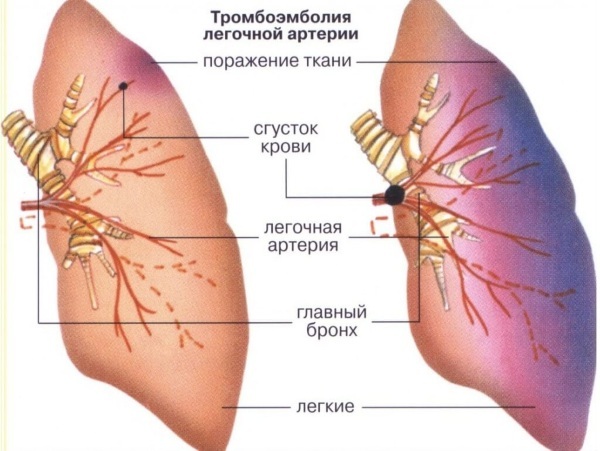
They will help you to timely suspect a disease and go to the hospital for medical assistance:
- lower extremities swell asymmetrically;
- pain syndrome appears along the veins during palpation of the legs;
- the heart rate increases (more than 94 units per minute);
- pain syndrome occurs in the leg on one side;
- the phlegm that comes out during coughing contains blood impurities.
It is necessary to monitor your condition for people who have already had heart problems in the past. If diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis. The same applies to the elderly, over 65 years old, people who have suffered a head injury or surgery. Blockage of the pulmonary artery can also occur against the background of malignant processes in the human body.
Emergency care for pulmonary embolism
Treatment of pulmonary embolism is carried out strictly according to the doctor's prescription, but before the arrival of a specialist, it is important to correctly and quickly provide an ambulance to the patient:
- Lay the person down on a flat surface.
- Create all conditions of rest.
- Free neck from clothing.
- Ensure the maximum flow of fresh air into the room.

If necessary, the patient should be given artificial respiration. It is also important to monitor your blood pressure and heart rate.
Diagnostics
A cardiologist will help to establish an accurate diagnosis and choose the most effective treatment. It is important for the first violations in the work of the heart to go to the hospital, to undergo a comprehensive examination.
To diagnose pulmonary embolism, patients are prescribed the following examination methods:
| Name | Description |
| Electrocardiography (ECG) | A diagnostic method that allows you to assess the work of the cardiovascular system, to identify irregularities in the rhythm and conduction of electrical impulses. |
| Chest x-ray | An examination method, thanks to which the specialist identifies numerous pathological changes in the structures and work of the heart. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | The specialist determines the exact location of the thrombotic mass. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | The study allows you to carefully view the branches of the pulmonary artery and identify the location of the thrombus. |
| Angiopulmography | An x-ray is taken using a contrast agent to locate the site of the thrombus. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | A specialist examines the heart. Assesses the state of the ventricles, rhythm, organ function. |
| Scintigraphy | The most informative method that allows you to determine the impaired blood circulation in the lungs. |
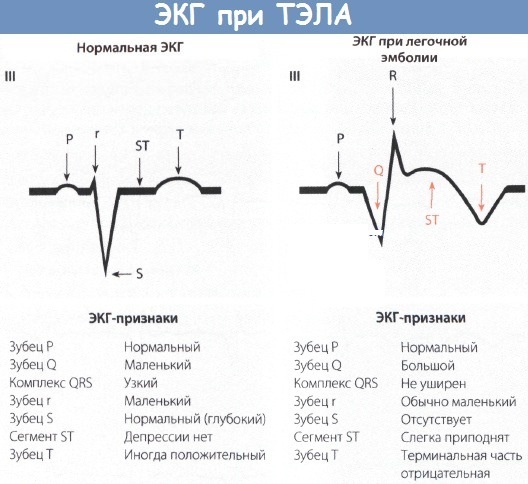
Differential diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is necessary because the disease accompanied by similar symptoms with other pathologies (bronchial asthma, myocardial infarction, acute pneumonia). Additionally, the patient may need to consult other specialized doctors (angiosurgeon, cardiac surgeon, pulmonologist, endocrinologist, oncologist).
Treatment
Thromboembolism therapy is necessary to save the patient's life and prevent the development of chronic pulmonary hypertension. The treatment regimen is selected by a cardiologist after a comprehensive examination based on the established diagnosis.
The specialist prescribes special drugs, taking into account the person's condition. In an emergency, surgery is performed.
Conservative therapy
Treatment is carried out to prevent complications of pulmonary embolism. The patient is placed in intensive care, he is shown complete rest.
For pulmonary embolism, the following drugs are prescribed:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Anticoagulants | Heparin, Warfarin | The medicine has an effect on the blood clotting process, preventing the formation of blood clots. The drug is administered intravenously. The adult dosage depends on body weight and is 1 thousand. Sword. The maximum daily volume of the drug should not exceed 60-80 thousand. IU. The course of therapy lasts 10 days. |
| Thrombolytics | Urokinase, Streptokinase | The medicine is used intravenously or intra-arterially. The contents of the vial are dissolved in water for injection, respectively. The adult dosage is 250,000-600,000 IU over 10-20 minutes. The average duration of therapy is 4-5 days. |
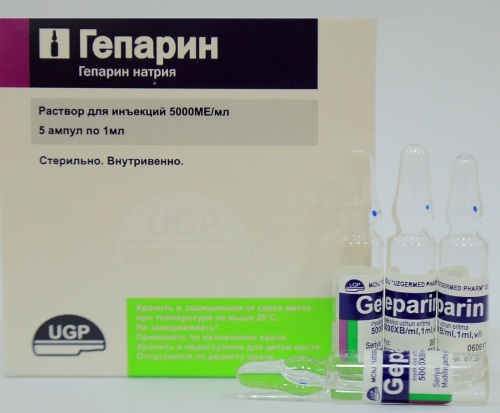
An individual treatment method is selected for each patient; it is important for a specialist to preserve a person's life and gas exchange in the lungs.
Measures for massive pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (symptoms will help the doctor determine the stage and degree of development of pathological processes) of a massive type, depending on the condition that has arisen in the patient, requires the following activities:
| Name | Description |
| Patient's heart stopped | Artificial heart massage, lung ventilation and defibrillation are performed. |
| Decreased oxygen levels | An oxygen mask is applied. The patient inhales a gas mixture containing oxygen (40-70%). This procedure is called oxygen therapy. |
| Disturbed breathing | Severe hypoxia requires mechanical ventilation. |
| Reduced blood pressure | Hypotension is eliminated with special droppers with saline solutions. Also used are drugs to increase blood pressure, vasoconstrictor drugs (Dopamine, Adrenaline). |
Massive thromboembolism is characterized by a 50% cessation of blood circulation in the lungs, so the patient needs urgent medical attention. Pathological processes affect the main branch. There is a high likelihood of shock and the development of systemic hypotension.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is carried out in emergency situations or according to certain indications. The procedure is complicated and can lead to complications and even death of the patient.
The operation is carried out according to the following indications:
- massive thromboembolism;
- conservative therapy does not give a positive result;
- pathological processes have spread to the pulmonary artery or affected large blood vessels;
- the patient has severe hypotension.
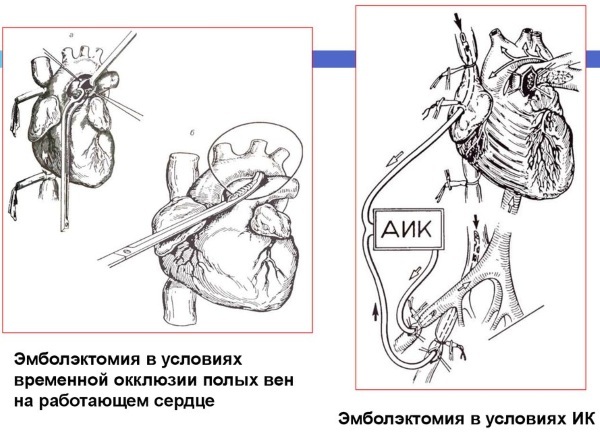
Surgical intervention for pulmonary embolism is carried out by the following methods:
| Name | Description |
| Embolectomy | The surgeon removes thrombotic masses. The operation is indicated for the acute form of the disease. |
| Endarterectomy | During the manipulation, the specialist removes the inner walls of the affected vessels. The operation is performed for chronic thromboembolism. |
Surgical treatment of PE is difficult and life-threatening for the patient. After the operation, a person will have a long period of rehabilitation.
Installing a cava filter
During the operation, the surgeon installs a special device. The mesh is placed in the lumen of the inferior vena cava. Kava filter helps prevent recurrence of the disease in high-risk patients. A special mesh retains thrombotic masses, they do not enter the pulmonary artery.
The patient is injected with light anesthesia; during medical procedures, he does not feel painful sensations or discomfort. The kava filter is installed within 60 minutes. The vein specialist passes the mesh, places it in the vena cava lumen, and removes the catheter. After the operation, the patient is advised to adhere to bed rest for 1-2 days.
Complications
Pulmonary embolism (symptoms at an early stage require a mandatory visit to a cardiologist and undergoing a comprehensive examination) without timely and correctly selected therapy leads to serious consequences.
In 30% of cases, death occurs due to pronounced changes that have affected the cardiovascular and respiratory system.
Massive thromboembolism is fatal in 100% of cases.
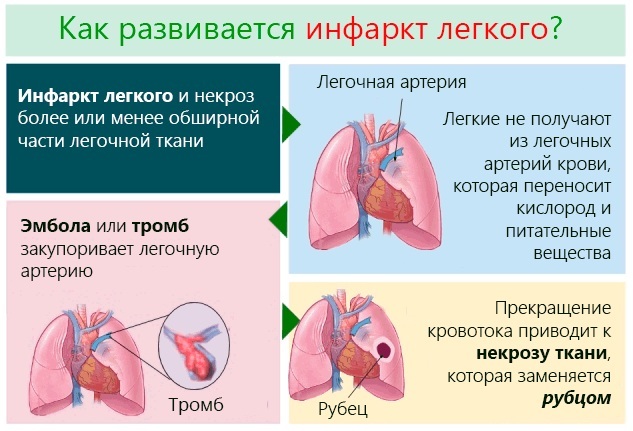
A complication of PE is not only death, but also other pathological conditions:
| Name | Description |
| Lung infarction | The pathological condition is characterized by the death of a certain area of the lung tissue. The main reason is impaired blood circulation, clogging of the branches of the artery with thrombotic masses. |
| Pneumonia | A disease in which the inflammatory process affects the lung tissue and alveoli. The patient develops a fever, weakness, chest pain, severe cough. |
| Chronic pulmonary hypertension | A pathological condition that is dangerous to human life, characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure in the area of the vascular bed of the pulmonary artery. |
Pleurisy, acute renal failure, embolism of blood vessels also occur against the background of blockage of the pulmonary artery by thrombotic masses. Therefore, the first symptoms of pathology cannot be ignored; it is important to consult a cardiologist in a timely manner.
Forecast
Pulmonary embolism is a serious medical condition that requires emergency medical attention. It is in 3rd place among all pathologies leading to the death of a person.
The prognosis for such a disease depends on numerous factors, including:
- speed of medical care;
- the presence of concomitant diseases;
- the presence of risk factors.
Death in the first 2 weeks after the onset of PE occurs as a result of serious complications from the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Pulmonary embolism requires qualified and timely assistance from a cardiologist. Otherwise, the disease will lead to serious complications, including the death of a person.
In the early stages, the disease is difficult to identify, many symptoms are similar to other disorders. Therefore, it is necessary to visit a doctor for preventive purposes, especially if there are prerequisites for this pathology in the anamnesis.
Video about TELA
The mechanism of development of pulmonary embolism: