A pathological condition of a person, in which his mental functions are distorted so much that he cannot adequately perceive reality, is called psychosis. In this case, the patient (it can be equally a man, woman or child) in his behavior demonstrates reactions that are contrary to the situation.
Certain painful symptoms are also manifested, namely, hallucinations and delusions. Most often, psychosis is not an independent disease, but a symptom of some kind of mental disorder.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Psychosis videos
Views
The classification of psychoses, based on the cause of the disease, is not entirely accurate, but perhaps the most illustrative.
| Types of psychoses by origin | |
Endogenous (functional) - arising from internal disorders in the body or hereditary factors:
|
Exogenous - provoked by a variety of external factors:
|

This systematization is simplified, since it is often difficult to attribute the cause of psychosis to only internal or exclusively to external factors.
Stages and degrees
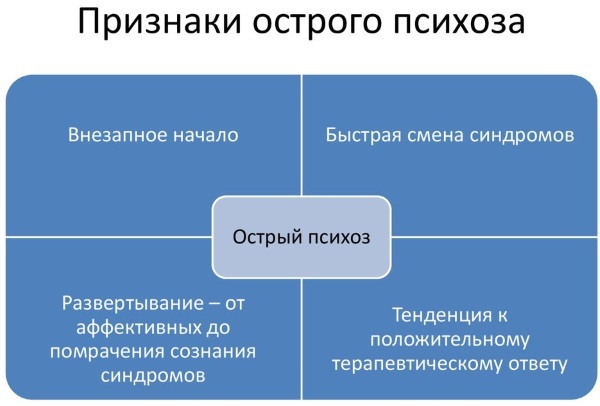
Psychosis in its development usually goes through certain stages:
- Prodromal, or anxious, stage: the appearance of early signs of the disease in the form of certain symptoms, at first rare, but with a gradual increase in symptoms. This can be anxiety, agitation, sleep disturbances, apathy, detachment, strange behavior, or unusual expressions of emotion. In women, the onset of the disease may coincide with periods of hormonal fluctuations (puberty, pregnancy and childbirth, menopause).
- Stage of untreated psychosis - from the onset of persistent symptoms until the psychosis is treated.
- Acute stage - the peak of the disease, the symptoms are maximally expressed.
- Residual stage - a gradual decrease in the intensity of symptoms (may last for several years).
Symptoms
Psychosis (symptoms and signs in women and men are quite variable) begins with obvious changes in the character and behavior of a person.
He becomes irritable, withdrawn, shows distrust, anxiety, fear, often expresses strange ideas, begins talk out loud, and these conversations are not like rhetorical questions to oneself, but more like conversations with the invisible opponent. May laugh for no reason or suddenly cut off the phrase and begin to listen to something.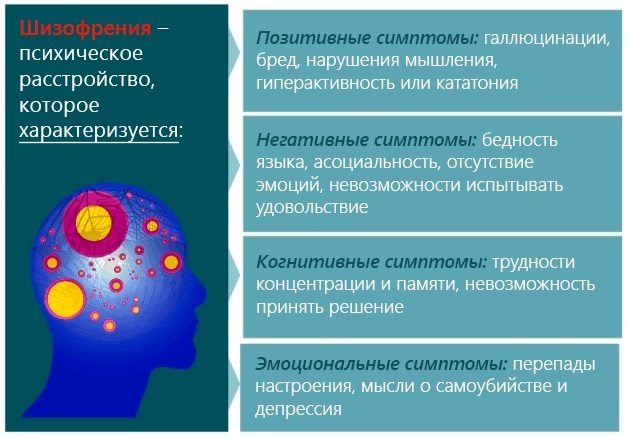
Disease performance decreases, but bursts of excessive activity may also occur when the patient takes on several things at once, talks a lot and moves, while being in an unreasonably increased mood.
Then his mood can change dramatically, and the person again loses interest in everything, becomes lethargic and apathetic, feeling melancholy and depression. Very often, the patient has serious problems with sleep: difficulty falling asleep, early awakening, as well as a lack of a sense of sleep, when it is difficult for a person to understand whether he has just slept or not.
The main symptoms of psychosis | ||
| Hallucinations are a disorder of the perception of reality, in which the arising images and sensations do not have a really existing source or stimulus. | Visual (optical) - usually occur against the background of clouding of consciousness. | A person can see both individual spots and flashes, and more complex images: objects, scenes, paintings, landscapes; colored or black and white, stationary or moving. |
| Auditory (acoustic) - the most common form of hallucinations. | Voices and sounds (noise, calls, beeps, whistles, crackles) of different volume and localization. In this case, the voices can be either narrative or commentary, or of an ordering nature, belong to one or several people. | |
| Tactile (tactile) | Feelings of touching the surface of the skin (hot, cold, wet, grasping, pressing) or the presence of animate (insects) or inanimate (glass, sand) objects on or under the skin. | |
| Olfactory | Sense of a variety of odors, most often repulsive (fumes, rot, excrement). | |
| Flavoring | Unreasonable appearance of gustatory sensations in the oral cavity, as a rule, unpleasant (bitter, burning, salty tastes). | |
| Visceral | Feeling of the presence of foreign objects in the internal organs, mobile or not. | |
| Delusional ideas - representations, reasoning and conclusions that do not correspond to reality, but do not lend themselves to correction (the patient cannot be convinced that he is mistaken). | Persecution delirium | The patient is convinced that he is being followed with the aim of causing him any harm. |
| Delirium of greatness | The patient is confident in his superiority due to the presence of certain talents and qualities, high birth, power, wealth, valuable inventions or ideas. | |
| Self-destruction delirium | A person is convinced of his guilt and sinfulness, or that he has an incurable disease or physical handicap. | |
| Movement disorders | Psychomotor agitation | This state is characterized by increased motor activity, senseless, chaotic movements, impulsivity, grimacing. |
| Lethargy (stupor) | The patient maintains immobility of posture and gaze for a long time, does not eat and does not react to anything. |
Since the listed signs are added to the usual state of the psyche, they are referred to as the so-called positive (productive) symptoms of psychosis, which is well corrected with medication.
Negative disorders damage the healthy functions of the body, lead to a change in the character of a person, his personal qualities, irreversible loss of any abilities.
These symptoms include:
- apathy, lethargy, lack of emotions, desires and impulses, decreased tone, self-isolation;

- thought disorder, impairment of memory and attention, loss of creativity, and sometimes the ability to work in general;
- rudeness, irritability, aggressiveness, personality degradation.
Reasons for the appearance
- Biochemical cause - failure in the production and exchange of neurotransmitters. Thus, excessive activity of the dopamine function of the brain provokes an increase in the positive symptoms of psychosis, while a decline in dopamine activation aggravates negative symptoms.
- Genetic predisposition: if one of the parents suffered from mental disorders, the likelihood of a similar illness in the child is 25%. In case of illness of both parents, this probability reaches 50%.
- Certain personality traits, such as, for example, emotionality, impressionability, anxiety and a tendency to control everything, can alleviate the onset of psychosis under equal concomitant unfavorable conditions.
- Social factors: regular stress, difficult life circumstances, childhood traumas (incidents of violence, negative emotional climate during growing up in a family or school).
- Anomalies of intrauterine development, including abuse of alcohol and drugs by the expectant mother, birth trauma
- Traumatic brain injury, intracranial tumors, vascular pathologies.
-
Chronic and acute intoxication: alcoholism, drug addiction, overdose or intolerance to drugs (hormones, anticholinergics, anti-tuberculosis drugs), poisoning with pesticides, toxins.
- Somatic diseases. In this case, mental disorders can be the result of a wide variety of injuries: intoxication, hypoxia, hormonal imbalance, hyperthermia, as well as stress as a result of fear for their health and a life.
Psychosis (symptoms and signs in women and men are generally similar) is not particularly tied to the gender of the patient. There is evidence, however, that women are 2 times more likely to suffer from bipolar disorder, while among men psychoses as a result of intoxication and trauma are more common.
Diagnostics
Early diagnosis of psychosis is extremely important, since the sooner adequate treatment is prescribed, the greater the likelihood of complete recovery and the absence of relapses in the future.
In psychiatry, there are the following diagnostic methods:
- Clinical, which include observing the patient and collecting as much detailed information as possible about the symptoms of the disease, as well as about cases of mental disorders among relatives. As a rule, these methods are sufficient in the absence of brain damage. Difficulties can arise with the differentiation of similar in symptomatology, but in essence different diseases. In this case, additional research methods come to the rescue.
- Psychometric methods that imply the use of standardized scales, questionnaires, tests and tasks that have passed scientific research to assess the patient's condition.
- Laboratory the methods are based on the search for specific biological markers of mental disorders. Thus, the presence of certain gene abnormalities does not yet indicate the presence of schizophrenia, but speaks of a certain probability of its occurrence. In addition, a close relationship has been found between the immune and nervous systems. It turns out that certain substances in human blood (antibodies, enzymes, proteins) can react to painful processes in the brain. It is on this knowledge that the Neurotest blood test and some other neural tests are based, which serve to clarify the diagnosis and control the course of mental disorders. Such research can be done in commercial psychiatric clinics. Their cost is over 3,500 rubles.
- Instrumental methods such as tomography and electroencephalography will not show any abnormalities in the case of endogenous diseases. They are used to a limited extent and according to indications - for example, when it is necessary to make sure that a mental disorder is not associated with damage to the brain, blood vessels, or neuroinfection.
When to see a doctor
When alarming symptoms appear, indicating the onset of a mental disorder, you should immediately consult a psychiatrist - a district therapist or a consultant in private clinics.
Psychoses are treated only with medication and do not go away on their own. If a person refuses to admit the problem and go to a doctor, you can try to assess his condition to start with a visit to a psychologist.

Psychosis (symptoms and signs in women and men can both increase gradually and appear suddenly, sharply) can become a dangerous condition in the event of delay and aggravation of the human condition and lead to suicide. The danger exists not only for the life of the patient himself, but also for those around him if the patient is aggressive or is not aware of his actions.
In acute psychoses, it may be necessary to call a psychiatric ambulance team. The patient's condition requires immediate hospitalization even without his consent, if he is absolutely helpless, or dangerous, and also in the event that the lack of psychiatric care will lead to a significant deterioration in his condition and irreversible consequences.
Prophylaxis
There are no ways to prevent endogenous psychoses - anything can be the impetus for the development of the disease. You can only try to avoid relapses, strictly adhering to the doctor's recommendations, avoiding stressful situations if possible, emotional turmoil and physical overload - in other words, leading a measured, orderly lifestyle in a safe, predictable surroundings.
As for mental disorders caused by some external circumstances, then for their prevention you need to be attentive to your health, monitoring somatic diseases, and, in general, to maintain a healthy Lifestyle.
Treatment methods
The principles of psychosis treatment are mostly the same: drug therapy is considered the only reliable method. However, the approach to the treatment of a particular patient must be strictly individual, taking into account age, gender, and the presence of somatic diseases.
It is very important to establish a relationship of trust with the patient. In this case, he will not hide the symptoms of his disorder and try to violate the recommendations given by a specialist.
Medications
With regard to drugs, the main role in the treatment of psychosis for several decades now has been assigned to psychotropic drugs (neuroleptics or antipsychotics). Before the discovery of antipsychotics, herbal remedies (henbane, belladonna, opiates) were used in the treatment of psychosis, then lithium salts, electroconvulsive therapy and lobotomy.
The first antipsychotic, chlorpromazine, was synthesized in 1950 and was first used as an antihistamine. After discovering its effectiveness as an antipsychotic agent, it is widely used along with other first generation antipsychotics such as haloperidol, stelazine, mazheptil and others.
These drugs coped well with the main symptoms of psychosis: delusions, hallucinations, psychomotor agitation. But along with this, they did not affect negative symptoms, and often the patient after a course of treatment could not return to a full life.
Another significant disadvantage of classical antipsychotics is that they cause serious side effects (extrapyramidal disorders) that reduce patient's quality of life: tremors, twitching of the limbs, inability to relax, muscle stiffness and other motor violations.
To reduce these extremely unpleasant phenomena, psychiatrists have to prescribe a number of additional corrective drugs (akineton, cyclodol and others). In addition to the disorders already mentioned, taking first-generation antipsychotics can be accompanied by other equally serious side effects.
Here are just a few of them: drooling or dry mouth, decreased pressure, fainting, nausea and constipation, weight gain, drowsiness, fatigue, memory impairment, decreased sex drive. Amenorrhea and galactorrhea are common in women, and erectile dysfunction and ejaculation are common in men.
At the end of the 80s of the last century, atypical antipsychotics were introduced into clinical practice, which proved to be both more effective and much better tolerated, since they do not cause extrapyramidal side effects phenomena. These drugs are olanzapine, asenapine, risperidone, leponex and others.
Atypical antipsychotics have side effects (weight gain, decreased potency, increased blood sugar and hormone levels), but they depend on the dosage and occur when it is increased. Another significant drawback of these drugs is their high cost due to their production abroad.
However, if you consider that when taking atypical antipsychotics there is no need to prescribe correctors, the cost of treatment with one with a new generation drug are comparable to the costs of prescribing 3-5 classic drugs and average $ 100-200 per month.
The duration of treatment for endogenous psychoses is determined by the attending physician. In this case, the period of hospitalization, as a rule, does not exceed 2 months, but after discharge there is a need for supportive treatment with low doses, which can last from 6 months to 2 years. In the chronic course of the disease, it will take many years to take drugs.
Other methods
Psychosis, whose symptoms and signs in women and men do not leave a chance for a fulfilling life, can be significantly alleviated with drug therapy. In this case, social rehabilitation and psychotherapeutic work must necessarily act as an auxiliary means.
Social rehabilitation is a special complex of programs aimed at teaching patients who have suffered a mental disorder in ways to interacting with people around you and various skills required in everyday life: using transport, cleaning the house and self-care, shopping.
Rehabilitation can help to keep or find a job, to continue and finish their studies - in short, to avoid, if possible, a decline in the quality of life.
Psychotherapy by itself cannot cure psychosis, but it can affect the future life of patients. She is able to help patients who are acutely inferior to treat themselves better, to avoid self-isolation.
It can be useful to work in groups, among people who understand what it means to be mentally unhealthy, which means they are able to provide support and give hope for recovery.
Possible complications
It is hardly possible to ignore the symptoms of psychosis. But if a person does not receive adequate treatment for a long time, this will ultimately destroy his life and the lives of his loved ones.
If the consequences of psychosis, the symptoms of which were arrested at an early stage of its development, are completely reversible, then prolonged stay of a person alone with a mental disorder can lead to personality degradation or suicide. Family members of the patient may also suffer - both mentally and physically.
Such a serious, difficult to treat disease like psychosis, with a competent approach to treatment, is not a sentence. With the help of modern drugs, it is possible to quickly stop such unpleasant symptoms as hallucinations and delusions, while avoiding destructive consequences for the individual.
Adequate drug treatment, coupled with psychotherapy, will allow both women and for men to a full life, provided that they see a psychiatrist at the first sign diseases.
Psychosis videos
Signs of the onset of psychosis:



