Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) are caused by impaired brain development, which is manifested by deviations from accepted norms in behavior and causes difficulties in communication and learning. With the necessary correction in patients with ASD, it is possible to achieve the formation of the necessary behavioral skills and a significant improvement in socialization.
Record content:
- 1 Autism Spectrum Disorders: Symptoms or Disease?
-
2 Reasons for violations
- 2.1 Genetic factors
- 2.2 Psychological factors
-
3 What is on the autism spectrum? ASD classification
- 3.1 Childhood autism
- 3.2 Atypical autism
- 3.3 Asperger's Syndrome
- 3.4 Childhood Disintegrative Disorder
- 3.5 Other pervasive developmental disorders
- 3.6 Rett syndrome
- 4 Severity of Autism Spectrum Disorders
-
5 Features of symptoms and characteristics of children with ASD
- 5.1 Disruption of communication
- 5.2 Conduct disorder
- 5.3 Stereotypy in ASD
- 5.4 Associated features supporting the diagnosis
- 6 Differential diagnosis
-
7 Treatment of Autistic Disorders
- 7.1 Applied Behavior Analysis (PAP)
- 7.2 TEACCH
- 7.3 Speech and speech therapy
- 7.4 Drug treatment
- 7.5 Corrective work with children with ASD
- 7.6 Pedagogy and teaching
- 8 Video about ASD
Autism Spectrum Disorders: Symptoms or Disease?
ASD is a complex (spectrum) of diagnoses that are no longer used independently and, according to ICD-11 (from 2018), are combined into one new diagnostic unit - ASD (code 6A02). The disorder can be called both a disease (more precisely, a health problem), since it has a code in ICD-11, and a syndrome, that is, a complex of symptoms.
ASD is also called an alternative state of the psyche, which implies its acceptance as one of the possible behavioral norms (when such a state does not cause serious, intractable problems).
Prior to the appearance in ICD-11 of the term “autism spectrum disorder”, the term “autism” was used to define this condition. Due to changes in diagnostic criteria, there is an increase in the number of patients with a smoothed form of autism, which is often referred to as ASD.
The disorder may be accompanied by mental and physical retardation. Sometimes intellectual abilities persist, but develop unevenly: in some areas with a lag from the norm, and somewhere they are manifested in in the form of unusual abilities, for example, in the form of phenomenal memory, absolute hearing, which makes it possible to speak even of genius (syndrome savant).
Although this is observed in ASD only in isolated cases, it gives reason not to equate the disorder and mental retardation.
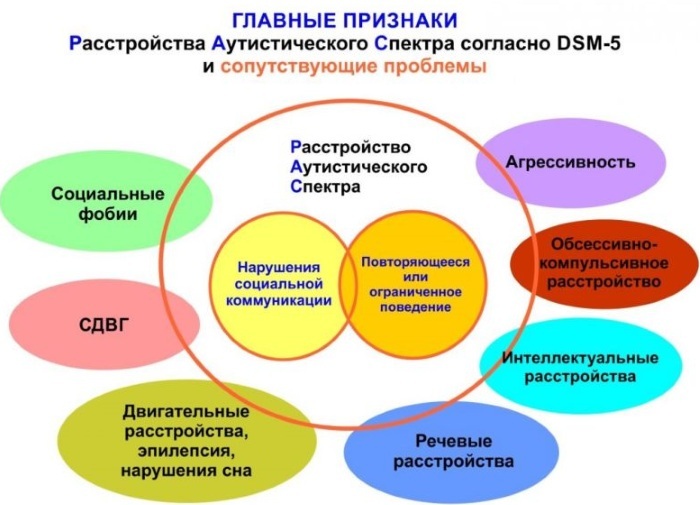
The main signs of the disorder:
- pronounced communication problems that cannot be corrected by conventional educational methods;
- tendency to seemingly meaningless repetition of movements and phrases;
- limited behavior - characterized by a narrow focus of interest, for example, towards one particular toy.
Signs of impaired psychomotor development appear at a very young age and are not always regarded by parents as deviations that should be corrected.
Patients with ASD also have symptoms such as:
- violation of the ability to contact people around (conduct a dialogue, use gestures), which leads to difficulties in social adaptation;
- inability to show adequate interest in the actions of other people, while the patient is inclined to focus on his own interests;
- lack of imagination (which leads to a misunderstanding of the rules of some children's games);
- inability to display emotions in the usual way;
- scanty gestures;
- unusual speech and intonation (speech can be very slow, and the intonation is too monotonous), echolalia is possible - an unconscious repetition of the phrases heard (echo symptom);
- excessive isolation, withdrawal into your inner world, unwillingness to share experiences;
- weak empathy (emotional empathy);
- the need for constancy, ritual behavior (the same daily routine, walking route, diet), the patient can react very painfully to minor changes;
- in some cases, catatonia of varying severity is observed, up to a complete absence of movement and speech;
- there are problems with falling asleep, superficial sleep, restless;
- stereotypy - aimless swaying of the body, head rotation and other actions that do not have a specific purpose and clear semantic load;
- compulsive behavior - following some kind of inner feeling that forces you to perform actions according to strict rules, for example, to lay out things or toys in a certain order (failure to follow the rules causes increased anxiety and anxiety);
- in patients with ASD, autoaggression is manifested, that is, an unconscious tendency to self-harm, which requires special attention.
Difficulties in maintaining normal eye contact are also observed, as this can provoke unpleasant sensations. This behavior is a hallmark in autistic disorders.
Patients with the disorder may also have difficulty understanding non-verbal behavioral cues and using them correctly. Their gestures differ from the usual, but can be corrected by conscious effort (while maintaining intelligence).
In severe cases, the patient practically does not have the ability to look into the eyes of the interlocutor to maintain eye contact, cannot demonstrate normal facial expressions and gestures.
Patients with the disorder have unusual and obsessive interests, such as attachment to a household item, endless rewriting of bus schedules.
At the same time, patients are distinguished by excessive focus on their actions, they experience an irresistible craving for order. For example, a small child with ASD will spend hours trying to arrange toys or objects in a strict and unchanging order.
Such an ability to concentrate and concentrate, a tendency to order - can serve as a plus in social adaptation. With the right type of occupation, the patient with ASD can achieve significant success in them.
Reasons for violations
Autism spectrum disorders are an understudied problem, and in the vast majority of children, the reasons for its occurrence remain unclear. It is believed that autism is more common in boys.
In ASD, pathological changes in the brain of unclear etiology are noted. There is an assumption that the disorder may be due to organic brain damage.
Diseases against which a sufficient number of identified cases of ASD (which allows for a relationship between them):
- congenital rubella - an infectious disease that is transmitted from the mother to the fetus and can lead to anomalies in its development;
- CMV - cytomegalovirus infection (congenital and perinatal) - leads to a delay in the development and growth of the child;
- phenylketonuria - manifested by mental retardation, impaired behavioral reactions caused by a pathologically elevated level of the amino acid phenylalanine;
- TSC - tuberous sclerosis complex - a hereditary disease characterized by the formation of tumors (tuber), including in the brain, which leads to disturbances in its work;
-
genetic pathology in the X chromosome - leads to mental retardation.
Some children with ASD have enlarged cerebral ventricles and abnormalities in the development of brain nuclei. Some increase in brain volume was also noticed.
The theory of vaccinations as a possible cause of the disorder was not confirmed after the discovery of the fact of falsification of the ongoing research. The negative impact on the body of unfavorable environmental conditions has also not been confirmed as a reliable cause of ASD.
It is only known that disorders leading to disorders are formed at the initial stages of brain development.
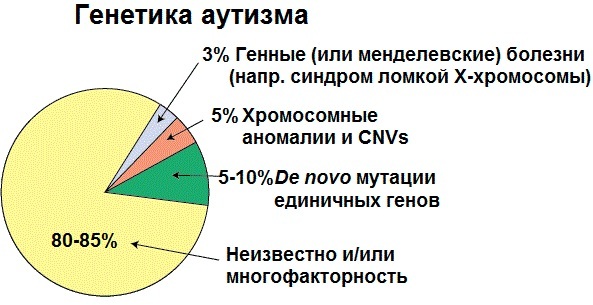
Genetic factors
The genetic theory for ASD as a result of mutations is based on studies that have shown that parents with the disorder the probability of having a child with developmental problems is quite high, 50 or even 100 times higher than that of parents without an identified disorders. There is also a high probability of detecting autism in monozygotic twins.
Genetic studies have identified regions of genes responsible for the formation of the central nervous system that are potentially associated with ASD. Attention is also paid to genes that are related to serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (abbreviated as GABA). An association was found between abnormal GABA functions, elevated levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin, and the onset of the disorder.
Psychological factors
The following psychological factors can be considered as possible causes of ASD:
- severe stress due to the coldness of the mother, a crisis in the family - in this case, the psyche of the child may be so traumatized that pronounced disorders will appear in the further development;
- chronic depression in the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- pronounced perfectionism in parents or family members - as the cause of the child's painful tendency to order.
When identifying psychological problems in the family, family psychotherapy is recommended.
What is on the autism spectrum? ASD classification
According to ICD-10, the autism spectrum includes:
- children's autism, as a result of organic brain damage, as well as with an unexplained cause;
- atypical autism;
- Rett syndrome;
- Geller's syndrome;
- hyperactive disorder;
- Asperger's syndrome;
- disorder, unspecified.

Autism spectrum disorder, as a separate diagnosis, is absent in the ICD-10 and appears in the next version (11), combining the autism spectrum. In RAS, subtypes are distinguished with different codes, depending on whether intelligence and functional language are preserved or not.
Childhood autism
Infantile autism, or in another way - Kanner's syndrome - occurs as a result of disorders in the brain. The disease is characterized by the main autistic features: a lack of communication, repetitive actions, ritual behavior, a desire for strict order, limited interests. The disease manifests itself quite early, often up to 3 years of age.
Atypical autism
Differs from childhood autism in later onset (after 3 years). It is also possible that some of the main signs of the disease are absent. For example, children with atypical autism may not be prone to stereotyping, that is, aimless repetition of phrases or movements. But there are communication difficulties. This type of illness is also characterized by self-limited interests that are common in autism.
Asperger's Syndrome
Intellectual abilities are generally retained, which is the hallmark of this syndrome. There is a pronounced stereotyping of behavior, a craving for repetitions, and ritual behavior.
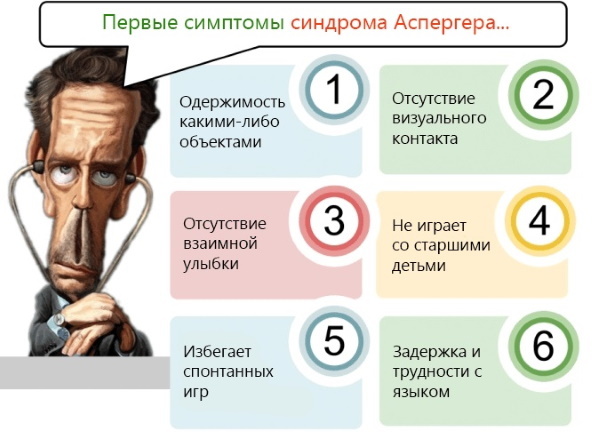
Difficulties arise in communication due to misunderstanding of non-verbal signals, limited empathy (ability to empathize). Asperger's syndrome is characterized by awkwardness, clumsiness. The condition may improve with age, but communication problems do not completely disappear.
Childhood Disintegrative Disorder
Geller's syndrome, "childhood dementia". A fairly rare developmental disorder that usually occurs at 3 years of age. It is manifested by a sharp loss of previously acquired skills, including the loss of the skill to control urination and defecation. Speech deteriorates. The disease is serious and leads to mental retardation. Unfortunately, there is no cure for “childhood dementia”.
Other pervasive developmental disorders
General mental disorders (pervasive). Manifested by severe violations of the ability to communicate (problems with speech and gesticulation). There is a pathological craving for order, repetitive movements (ritual behavior).
Development is uneven: in some ways such children are ahead of their peers, in others they are very far behind. Children have strange games, unusual addictions and taste preferences.
Rett syndrome
Hereditary neuropsychiatric pathology, which occurs mainly in girls.
The disease manifests itself after 18 months, when the child begins to lose previously acquired skills, including speech, up to the complete loss of the ability to speak (mutism). There is a tendency to repetitive, uniform movements, which is characteristic of autistic disorders. Lethargy appears.
The face takes on a "lifeless" and sad expression, which is unusual for children. Convulsive seizures, bouts of impulsive behavior, unmotivated laughter are possible. There are disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory and digestive organs (short-term cessation of breathing, the reverse movement of food from the stomach into the esophagus). Severe scoliosis (lateral curvature of the spine) appears.
The disease requires constant supervision of specialists, assistance in acquiring and maintaining basic life skills. A complete cure is impossible. With a favorable course, patients reach 50 years of age or more.
Severity of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Depending on the patient's developmental ability and ability to maintain communication, different types of the autism spectrum can be mild or severe.
| ASD type | Mild degree | Severe degree |
| Asperger's Syndrome | + | |
| Kanner's syndrome | + | + |
| Atypical autism | + | |
| Rett syndrome | + | |
| Geller's Syndrome | + |
An easy degree is characterized by the possibility of adjustment and acceptable social adaptation. In severe cases, there is progressive childhood dementia (dementia) and a complete inability to socially interact.
Features of symptoms and characteristics of children with ASD
Autism spectrum disorders are manifested by a lack of communication. Children with ASD avoid communication with adults and peers. Usually, deviations begin to actively manifest themselves by the age of 3, when the stage of primary socialization begins.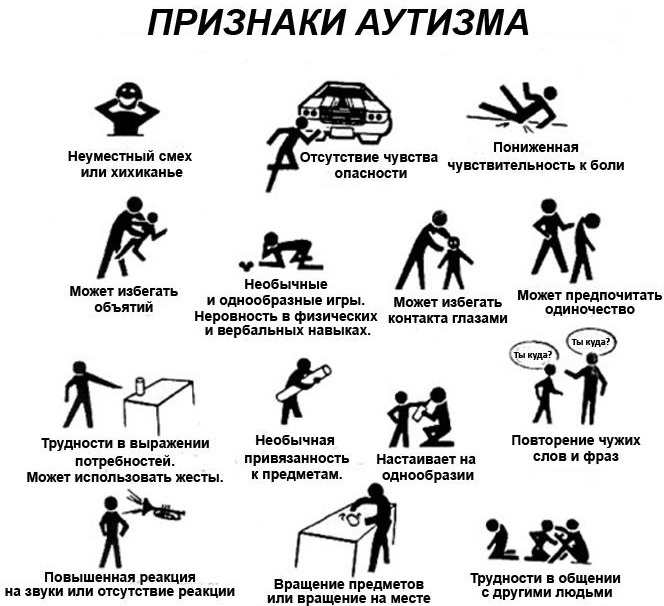
But developmental disorders can be noticed earlier, for example, if the child does not begin to speak syllables in due time (about a year), does not point his hand at an object, as babies usually do.
The earlier the problem is identified and the correction is started, the more likely it is that it will be possible to prepare the child for school. Unsolvable problems arise when parents do not want to notice the obvious in the child developmental delays, do not go to the doctor for a long time, delay the examination and treatment, hoping for a miracle.
Disruption of communication
A child with ASD can sit alone in a corner for hours. If he has a desire to take part in general games, then there may be special difficulties with those games where imagination is required. For a child with a disorder, mastering the rules of this game can be overwhelming, which will further exacerbate communication problems.
Difficulties in communication arise due to insufficient ability to maintain a conversation, to adequately respond to facial expressions and gestures of the interlocutor. Children with the disorder rarely smile and may not respond to their name. However, they are very vulnerable.
This makes it difficult or completely impossible to make friends with peers, communication with adults, which is compensated by an increased interest in some thing or toy. Children with the disorder are also very attached to animals, with which they can connect more easily than people.
Conduct disorder
A child with a disorder can express his desires in a non-standard way, taking the hand of an adult and thus pointing to the thing he needs. Children with ASD may have poor understanding of what is wanted from them, for example, they cannot fulfill a request to raise an arm or a leg, turn around, or repeat a simple movement.
It is difficult for them to understand what can and cannot be done. At the same time, hyperactivity and restlessness are manifested.. In such situations, it is usually said that the child is naughty and completely unruly. But in a disorder, this behavior is due to a feature of the brain.
Children with ASD have some deviations in the formation of behavioral patterns (patterns), which are most actively formed in childhood. For example, they can repeat the same simple action or phrase countless times, since the brain cannot assimilate it and fix it in order to use it only when it really is necessary.
If the pattern is nevertheless formed, then the child with the disorder will become manic to follow the developed habits, the slightest deviation in the fixed ritual leads to severe nervous breakdowns. At the same time, anger is more likely to arise in cases where the child with the disorder has difficulty mastering the language and cannot verbally explain his needs.
Stereotypy in ASD
Aimlessly repetitive movements and actions are one of the main characteristics of ASD.
Manifestations of stereotypy and stereotypical actions:
- swinging the body;
- senseless blinking;
- marching in one place;
- aimless head nod;
- constant tapping with your fingers;
- drawing the same picture.
A distinctive feature of such actions is the lack of meaning and cognitive nature in them, as well as their constant repetition.
Associated features supporting the diagnosis
Autism Spectrum Disorders may present with dangling gait or a desire to constantly tiptoe. It may also be found that the child, unlike his peers, does not know how to jump at all.
There is an unusual indifference to hunger, stimuli, such as insensitivity to cold and pain. In this case, the child can give out a violent reaction to ordinary smells and sounds.
Indifference to pain can provoke bouts of auto-aggression and self-harm (hair pulling, skin cuts). Such auto-aggression in most cases is not regarded by experts as suicidal intentions, but when clearly severe anxiety and depression, repeated episodes of auto-aggression require drug treatment and monitoring specialists.
Differential diagnosis
Autism spectrum disorders are diagnosed based on observation of the patient, as well as on the results of tests and questionnaires that establish the level of social adaptation. Children are tested by pediatricians and psychologists who specialize in behavioral therapy. At an early age, children with suspected ASD undergo a special M-CHAT-R test.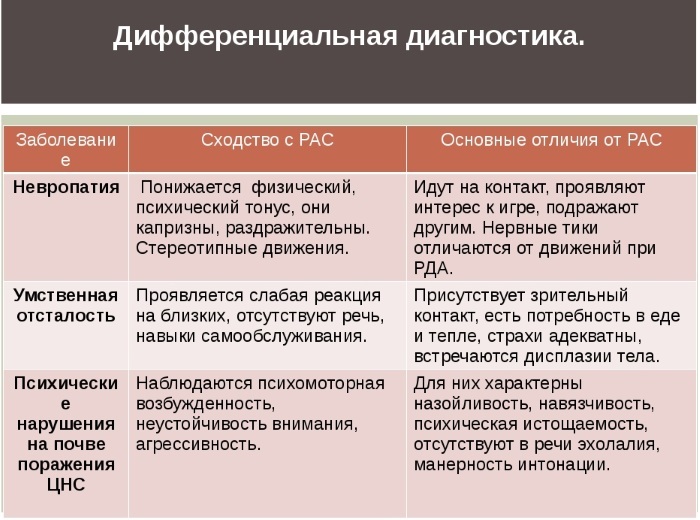
It is necessary to distinguish ASD from developmental disorders such as:
- mental retardation (as a separate neuropsychiatric disease);
- ADV - stands for attention deficit disorder - manifested by excessive impulsivity and inability to concentrate, in combination with hyperactivity it is referred to as ADHD;
-
dyslexia - a disorder of intellectual activity, which is characterized by a violation of the ability to learn (mainly difficulties with reading, pronounced problems with spelling and writing).
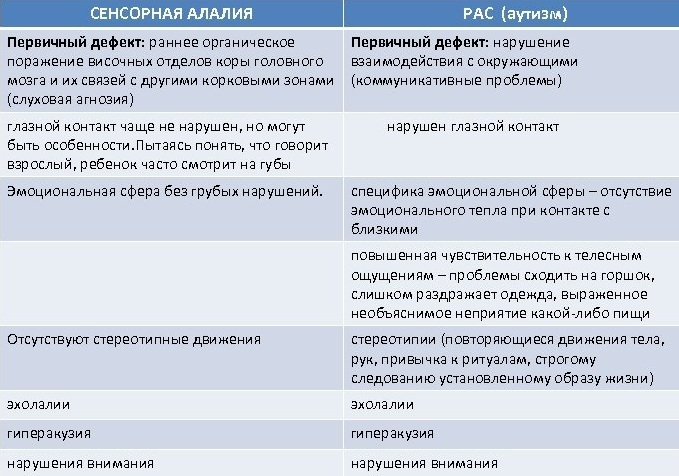
Autism spectrum disorders are distinguished from schizophrenic spectrum disorders, which are manifested by a strong detachment from the outside world and excessive isolation of the patient with himself.
According to the DSM-5 guidelines, confirmation of the diagnosis of ASD requires the presence of at least 2 obvious disorders in communicative behavior, as well as at least 2 manifestations of stereotypy.
Treatment of Autistic Disorders
Disorder therapy is aimed primarily at improving the patient's communication capabilities and increasing his independence. When behavioral therapy is not enough, drug treatment is used to correct anxiety, uncontrolled aggression, and with frequent bouts of auto-aggression. Good results are seen with pet therapy (pet therapy).
Applied Behavior Analysis (PAP)
The initial stage of PAP is to analyze the patient's behavior in order to find out the most significant deviations. Then correction is carried out - work with separate blocks, where each action is learned separately: the correct ones are fixed, the wrong ones are cut off quite rigidly. This changes the behavior itself.
In the process, the patient's environment is taken into account, a strategy for further interaction with loved ones is developed. Improvement occurs with the stable preservation and consolidation of new skills that are more acceptable for social adaptation.
TEACCH
The method involves the analysis and assessment of the condition of children with ASD, treatment and assistance in education. The main goal is to help establish a stable associative connection in the patient's mind between his actions and further results.
The method includes a study of the patient's psychological status, with an emphasis on the shortcomings of socialization. Then an individual model of upbringing and development is created, training and exercises are carried out. Parents are actively involved in the program. The ultimate goal of the program is to acquire the necessary social and domestic skills.
Speech and speech therapy
The task of this type of correction is to establish a speech connection between an adult and a child with ASD. Therapy includes gymnastics for the tongue, training of facial muscles involved in the process of speech production.
When teaching, phrases and sentences are pronounced clearly and slowly. The correct intonation matters. For better comprehension of written language, pictures and illustrations are used. If speech therapy is carried out in a playful way that the child understands, this increases its effectiveness.
Drug treatment
With severe anxiety, seizures, sleep problems, seizures anger and auto-aggression are prescribed tranquilizers (benzodiazepines):
- Diazepam - tablets (2 mg), injections (i / m, i / v), rapid sedative effect, possible drowsiness, lethargy, lethargy;
- Lorazepam - tablets (2.5 mg), anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic (in some cases, excessive agitation is possible in the form of a side effect).
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers can be addictive (benzodiazepine dependence), therefore, the use of these drugs (especially long-term) requires medical supervision.
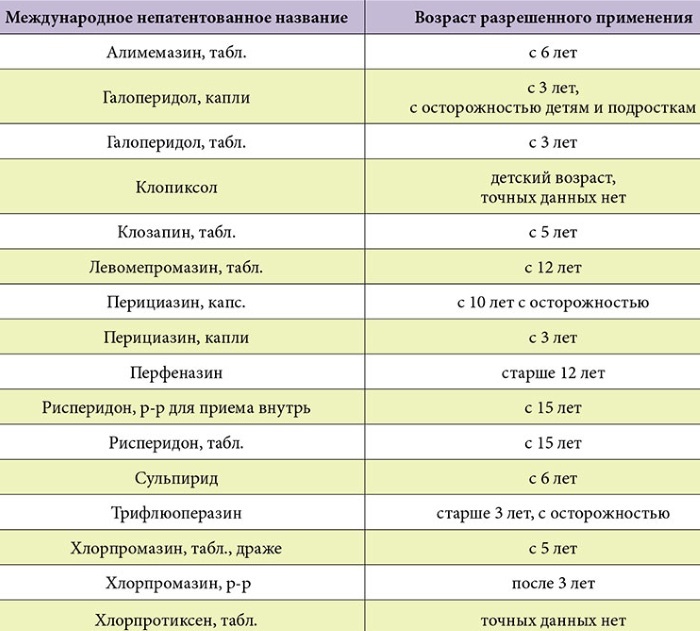
According to indications, antidepressants, antipsychotics, psychostimulants can be prescribed.
Corrective work with children with ASD
The main stages of correctional work:
- Establishing initial contact, taking into account the individual characteristics of the mental and physical condition of a child with ASD.
- Gradual stimulation and encouragement of activity, involvement in the learning process.
- Elimination of emerging fears, removal of tension, isolation, distrust. Relief of anxiety, aggression and autoaggression. Leveling negativism.
- Formation of a new model of social behavior, maintaining and encouraging desirable behavior.
- Consolidation of the acquired skills.
The work requires a lot of attention and patience. It is recommended not to skip or interrupt classes until the child has developed a new, stable pattern of behavior.
Pedagogy and teaching
In case of mild disorder, after the necessary correction, it is possible to receive an inclusive education, that is, on a general basis. At the initial stage of adaptation to the training program, you may need the help of a tutor (tutor) and individual preparation.
According to Law 273 "On Education", adopted in 2012, children with ASD are legally entitled to an accessible education. In 2014, Appendix 8 was adopted on the approval of a new standard in primary education, which takes into account the interests of children with disabilities.
Patients with autism spectrum disorder have the opportunity to socialize. This is equally important for relatives and closest associates. Children with ASD, after the necessary correction and adaptation, have access to inclusive education.
While maintaining intellectual abilities, it is possible to acquire professional skills, find, for example, remote work with a minimum of emotional interaction. With timely commenced correction, patients have the opportunity to communicate and develop at an acceptable social level with acceptance of themselves and their characteristics.
Video about ASD
About Autism Spectrum Disorders:



