Cognitive impairment this is a decrease in one or more cognitive functions of a person, relative to their usual state. Cognitive functions are those that are responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing, storing and using information received from the outside world. Namely, these are perception, attention, gnosis, memory, intelligence, speech and praxis.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Cognitive Impairment Videos
Views
There are several classifications of cognitive impairment:
- By the type of function that is broken:
- Attention disorders - it can be a decrease or complete inability to concentrate on one action, an increased reaction to distracting stimuli.
- Violations of gnosis - in this case, agnosia most often occurs (lack of recognition of various well-known objects, people), for example, visual, auditory, gustatory, olfactory up to total, combining all these views. Much less common are illusions, pseudo-hallucinations, or true hallucinations; they usually occur when combined with psychiatric pathology.
- Memory disorders - hypomnesia - a decrease in memory function (progresses according to Ribot's law), amnesia - complete loss of memory for any events or period of time, paramnesia - replacement of real memories fictional or gleaned from books / films (confabulations) or replacing with their own memories related to another time, for example, childhood, adolescence (pseudo reminiscences).
-
Violations of the intellectual sphere. This dementia is a very large group of disorders, often found in both adults and children. Congenital dementia with an increase in mental retardation includes oligophrenia (mild impairment, patients are difficult to learn, but may well do simple work), imbecility (medium) and idiocy (extreme backwardness with a lack of self-care skills and sense of self). Acquired dementia develops at an older age. There are 3 types - lacunar (with the loss of one or several cognitive functions and the safety of the rest) and total (all functions suffer and the "core of the personality" is gradually lost a person, existence remains at the level of basic instincts), marasmus (the terminal stage of Alzheimer's, Pick's, neurosyphilis diseases, when even the food reflex and self-preservation).

- Speech impairments are very numerous. This can be bradyphasia (delayed speech), aphasia (lack of understanding of someone else's speech and loss of the ability of one's own), paraphasia (replacement of sounds, syllables or words with similar sounds, distortion of words), dysarthria (incorrect pronunciation), mutism (lack of speech while maintaining the vocal apparatus), verbigeration (repetition of words or phrases, shouting out) and many others.
- Praxis pathology - the complexity or impossibility of purposeful voluntary actions, even previously performed constantly. Apraxia is their complete impossibility, parapraxia is the performance instead of some actions by others that are remotely similar to the necessary ones, perseverations are being stuck on any action, its repeated repetition.
- By the age at which the disorder occurred: childhood, adolescence, adult, elderly and senile. At each age, cognitive impairment has its own causes, manifestations, and treatment tactics.
- According to the morphology of the lesion (brain area), vascular cognitive disorders can be cortical (only in the cortical area of the brain, manifestations can be compensated for a long time and be soft enough), subcortical (structures such as the hippocampus or thalamus are involved, have more pronounced and rough manifestations with neurological symptoms), and mixed.
- Vascular cognitive disorders in their pathogenesis can be of 2 variants: arising as a result of damage to large vessels (happens as a result of cardioembolism or atherosclerosis of large arteries brain with subsequent damage to large foci of the cerebral cortex) or small vessels (disorders often arise gradually and the defeat involves the subcortical structures and the anterior parts of the brain).
- In depression, cognitive impairment can be primary or secondary. With primary depression, it develops against the background of impaired cognitive function (for example, with Alzheimer's disease or vascular pathologies). Secondary ones appear after the onset of depression.
Stages and degrees
Cognitive impairments are various in severity - mild, moderate and severe cognitive impairment. With a mild degree, a person feels a decrease in cognitive functions and this may bother him. At the same time, the quality of his life does not suffer and there are no external signs of this condition.
With a moderate degree of impairment, in addition to expressed complaints and anxiety about his condition, the patient can already outwardly stand out with his behavior, speech. In this case, the ability for complex mental work, previously performed without difficulty, is lost or hindered. Household and social skills are retained.
With severe violations, a person becomes maladjusted in society, unable to perform even simple tasks. In the final stages, the loss of self-care and self-control skills is possible.
Dementia is mainly of either vascular or neurodegenerative etiology (cerebral atrophy, cerebral infections, Alzheimer's disease).
There are also 3 stages of the course of dementia:
- The initial stage, characterized by mild memory impairments, is often latent.
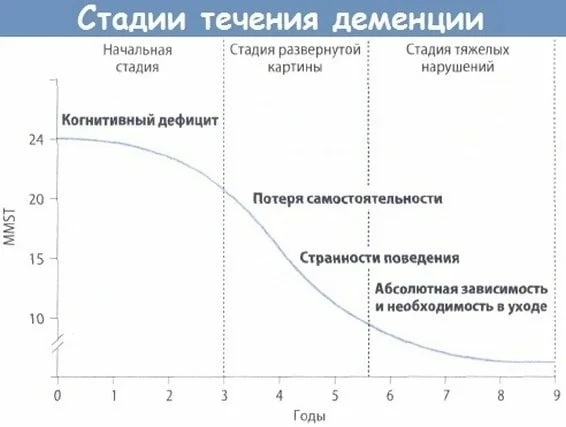
- At this stage, the decrease in memory increases, difficulties in orientation in place and in time are added, and everyday skills and self-care begin to suffer.
- In this final stage, violations become immediately apparent. Patients are disoriented in space, time and self.
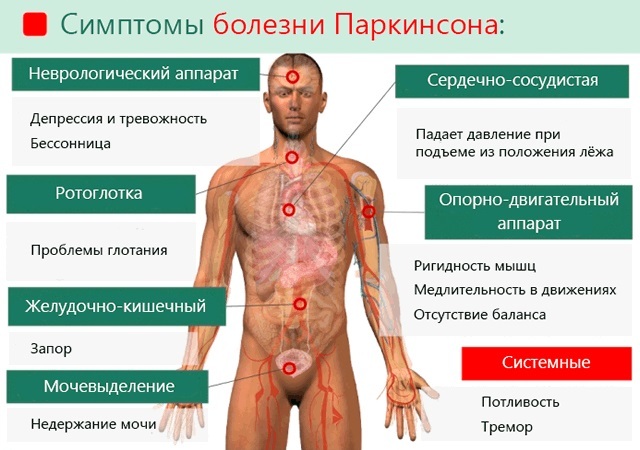
Symptoms
Cognitive impairments are pathological conditions in which the symptoms are very diverse, since there are quite a few cognitive functions. The clinical picture depends on the affected part of the brain, the cause of this lesion, the stage of the disease, the patient's age.
With disorders of cerebral circulation, the symptoms appear and intensify gradually. At the initial stages, complaints may appear about a decrease in the ability to concentrate, slowness of thinking, impulsivity, stuck thoughts on one thing, it becomes difficult to think abstractly.
In neurodegenerative processes, the memory function is most often affected in the beginning. At first, the current events are forgotten, but with the progression of the disease, the events of the past are gradually erased, from later to early ones (this is called Ribot's law).
Sometimes, in the end, the patient only remembers his childhood and considers himself a child. This makes it difficult not only to learn new skills, but also to get the job done. Also, initiative decreases, interest in the world around us, often there is an unreasonable depression, orientation in space and the correctness of speech are disturbed. Emotional lability is possible.
With the further course of the disease, speech, abstract and logical thinking deteriorates, and recognition of familiar people or objects becomes difficult. Complaints of weakness, fatigue, decreased performance and emotional background begin to appear. Neurological symptoms in the form of dizziness, headache, sleep disturbances can also be added.
In the later stages, patients may not recognize those closest to them and may not remember their past. These people can be lethargic and passive, or angry or aggressive. They have no criticism of their own state, sometimes even understanding speech is difficult.
In children, a decrease in cognitive functions is manifested in going beyond the upper boundaries of the age norm in terms of mental and speech development, as well as everyday skills. That is, the child is not able to acquire new skills and abilities with an adequate speed, it takes a lot of time for him.
IQ indices may be reduced, the ability to make comparisons and generalizations, as well as abstract thinking may be absent. Such children cannot correctly explain proverbs, come up with what is depicted in the form of Rorschach inkblots, their thinking is concrete and slowed down.
Reasons for the appearance
Cognitive impairments are functional or organic disorders of cognitive functions:
- Functional disorders are caused by a temporary disruption of the processes of the brain with its completely preserved healthy structure. When the cause that caused these disorders is eliminated, cognitive and other functions are restored in full. The reasons for such conditions can be chronic fatigue, stress, overwork, sleep disturbances, negative events, as well as psychiatric diagnoses - depression, bipolar disorder, psychosis, schizophrenia.
Organic disorders occur as a result of damage to the structures of the brain as a result of a large number of possible causes. Most often they occur in old and old age and are permanent in nature with a tendency to worsen the condition.
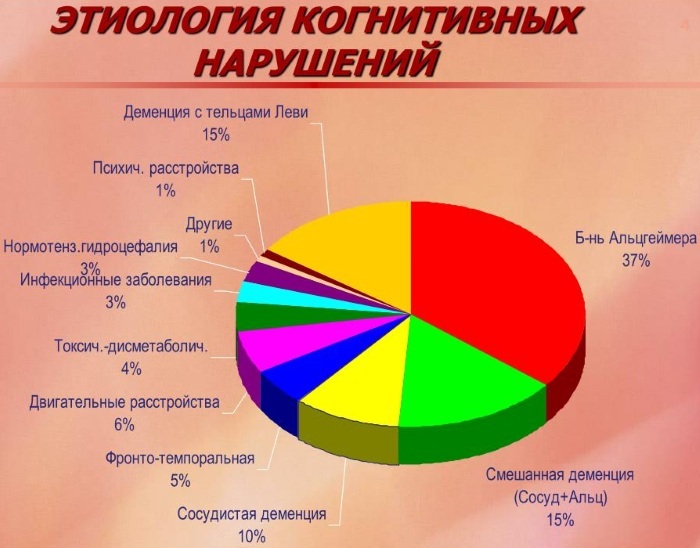
Causes of organic lesions:
- vascular - chronic and acute cerebrovascular accidents ischemic or hemorrhagic (their causes are atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, sugar diabetes),
- neurodegenerative diseases (encephalopathy, Alzheimer's disease, brain atrophy)
- brain infections (encephalitis, meningitis of a nonspecific and specific nature, including syphilis, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, parasitic invasions of the brain)
- neoplastic diseases of the brain,
- brain cysts
- consequences of injuries (bruises, compression, concussions) and operations,
- intoxication brain damage (happens as a result of alcohol, drug abuse, exposure to harmful substances in industries, especially heavy metals),
- perinatal brain damage in children, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, epilepsy.
Diagnostics
Cognitive impairments can be detected and investigated at various stages of diagnosis.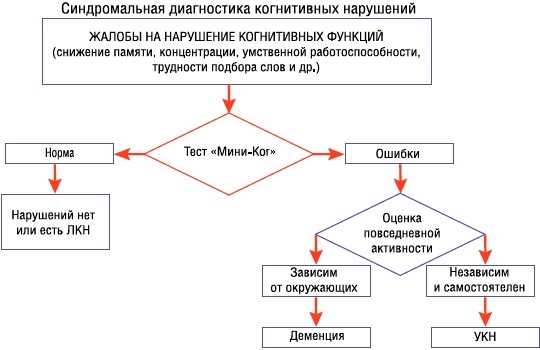
This is:
- Anamnesis collection, which helps to identify the first subjective signs of the disease, complaints, to assess previous examinations and treatment (if any), and may also indicate trauma, surgery, aggravated heredity. The predisposition to hypertension, diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer's disease has been proven.
- Physical and neurological examination can reveal abnormalities in various organs and systems, establish the organic or functional nature of the abnormalities.
- Assessment of the mental status and the degree of cognitive impairments allows us to clarify their degree and stage, as well as check how much of them has suffered. Patients are asked to retell a book or movie they have read, give names to objects, choose synonyms to words, concentrate and remember pictures and put them in their places, interpret proverbs, create a plan action. With various cognitive impairments, difficulties arise with one or another task.

- The study of blood and cerebrospinal fluid (for beta-amyloid and tau protein) can indicate the cause of the disease and help in choosing a treatment tactics.
- The main diagnostic tool is neuroimaging, namely X-ray computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. With their help, it is possible to fix changes in brain tissue and to carry out differential diagnostics between vascular, neurodegenerative or other types of dementia. The degree and localization of blood flow disorders is clarified using rheoencephalography (REG), which displays the blood flow velocity through the main vessels of the brain. With a moderate degree of cognitive impairment, changes in the brain are already present, albeit more delicate. In the initial stages, it is quite rare to see deviations in the structure of the brain tissue.
The cost of such studies is high, from 5-7 thousand rubles, and they are usually carried out in large medical institutions. In addition to the image itself, the qualifications of the doctor who describes it is very important.
- Sometimes, to clarify the causes of the disease, the following tests can be prescribed: blood test for thyroid hormones, glucose, vitamin B12, folate, calcium ions, HIV tests, syphilis, tuberculosis and other infections, and kidney examinations and liver.
When to see a doctor
Cognitive impairment is the case when the first signs of the disease can be seen only by the patient himself. This is just the mildest degree of impairment, which is difficult to detect with the help of non-brain imaging techniques.
If it becomes difficult to concentrate, sharpen your attention, navigate the terrain, formulate your thoughts, plan an event, then it makes sense to visit and conduct some tests.
A visit to a psychologist can help assess the mental status, a neurologist - to notice signs of damage in time central nervous system, therapist and endocrinologist - to identify diseases that also lead to cognitive disorders.
In this case, the earlier deviations are detected, their cause is found, the more favorable the prognosis for the course of the disease. Therefore, it is imperative to consult a doctor, even if there is a suspicion of impaired cognitive functions.
Prophylaxis
Unlike vascular disorders, it is not yet possible to prevent cognitive impairment caused by neurodegenerative diseases. However, it is possible to slow down the progression of these diseases and improve the quality of life.
How:
- Lead a calm lifestyle without stress, with proper sleep (at least 8 hours a day) and nutrition, and also give up alcohol and nicotine.
- Observe sufficient, but not excessive nutrition, include in the diet rich in omega-3,6 and 9 foods, vegetables, fruits and nuts. You should refrain from heavy fatty fried foods, carbonated drinks, sweets.
- Physical activity is adequate to the state of health and maintaining oneself in physical and mental tone.
- Regular mental exercise, reading, writing, solving crossword puzzles, learning something new is required.
- Regular medical examination with control over the main indicators of health - blood pressure, glucose, cholesterol.
Treatment methods
The choice of treatment for cognitive disorders depends on the underlying cause. The most effective is the therapy of functional cognitive disorders, since in this case they are reversible and the brain tissue does not have pathological changes.
In organic diseases of various origins, treatment is most often long-term, sometimes lifelong. It is aimed at preventing the development of dementia and improving the prognosis of the disease.
Medications
- Nootropics optimize blood flow and metabolism in the brain. This is manifested by an improvement in mental functions, memory and attention. Therefore, they are recommended to be prescribed in most cases. Piracetam (1200 mg, 2 tab. 3 times a day, prescribed for at least 30 days), Glycine (1 tab. 3 times a day, it must be taken for at least 2 weeks, preferably 4-6 weeks),
- Rivostigmine (patch), Galantamine, Donezepin, Memantine stimulate the activity of nerve cells, prevent their degeneration and exhaustion, and are similar in action to nootropics.
- Vasodilators Cavinton, Pentoxifylline, Intestinon can enhance the nutrition of the brain due to the expansion of capillaries and small vessels. Usually they are injected in small courses.
- For depression, antidepressants are usually prescribed, such as Heptral (800 mg at night, a course of up to several months), Anafranil (25 mg 2-3 times a day), Paxil (20 mg, in the morning). With recovery from depression, cognitive function is restored.
- If the cause of cognitive impairment is associated with a sleep disorder, prescribe Zolpidem or Zopiclone (1 tablet at bedtime, course of treatment for at least 30 days), Nitrazepam (taking 1 tablet. half an hour before bedtime, the course of treatment is at least a month).
- With arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis, antiplatelet agents (Aspirin and its derivatives), blood cholesterol-lowering drugs (drugs of the statin class), antihypertensive drugs are included in therapy.
- If necessary, therapy for endocrine pathologies, infections and intoxications is carried out.
Traditional methods
With the help of traditional methods of treatment, you can gently correct and improve the condition of patients. They very well complement the main treatment tactics and have a minimum of contraindications and side effects.
| Means | Recipe | Action on the body |
| Mint and ginger | Grate root and mix with mint leaves, then pour 1 liter of boiling water over the mixture and leave. Take cold after cooling, preferably with the addition of honey | Strengthens capillary walls, improves blood flow and helps restore blood pressure |
| Blueberry | Teas, compotes, fruit drinks are made from dried berries, frozen can be eaten after thawing in pure form or squeezing juice | Is a capillary protector, strengthens the walls and reduces vascular permeability |
| Elecampane root | 1 tsp add elecampane to a glass of warm water, cover and wait for cooling | Consume at least 3 times a day before each meal |
| Sage | 1 tbsp. l. leaves are mixed with two glasses of hot water and left. Take cold 3 times a day. | Improves memory and concentration |
| Rowan bark | Mix 50 g of bark with 250 ml of boiling water and let stand for 5-10 minutes over low heat. Reception for 3 tbsp. l. decoction, 4-5 times a day | Strengthens the walls of blood vessels |
| Ginseng and Eleutherococcus | Comes as drops that are added to cold drinks several times a day | Improves thinking and memory functions |
| Melissa | For a decoction for 1 tbsp. l. leaves need two glasses of boiling water and stand until cool. Reception 3 times a day. Lemon balm leaves can also be simply added to tea leaves. |
Simulates the function of brain neurons |
| Ginkgo biloba | Sold ready-to-drink in the form of tea, you need to drink every day | Improves blood coagulation and improves vascular blood flow |
Other methods
Several psychotherapeutic techniques are very effective when dealing with mild to moderate cognitive impairment.
These include various planning and writing (journaling supports writing skills), group therapy (allowing communicate a lot, perform various tasks for intelligence, attention, memory), art and music classes, development own hobbies in hobby groups, learning some new knowledge or skill (learning a new language, applied skills).

Physiotherapy can also improve brain function. For this, effective course treatment by methods of electrophoresis, pulse currents, ultrasound, microwave therapy, as well as massage and therapeutic gymnastics. In addition, baths are recommended - nitrogenous, oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Sociotherapy means maintaining a wide range of communication, visiting public places - theaters, concerts, museums and exhibitions, followed by the exchange of impressions about what was seen and remembered.
Possible complications
Complications of cognitive disorders can be the aggravation of these impairments, or the complete loss of any of the cognitive functions.
For example, partial agnosia can change to complete, bradyphasia can turn into aphasia or mutism. Patients especially experience memory loss that is accompanied by personality disorder. With good care and supportive therapy that corrects the underlying and concomitant pathologies, the progression of the disease can be slowed down.
Disorders of various cognitive functions are common in both children and adults. They accompany many diseases and require the obligatory consultation of specialists. If the correction of violations is started in a timely manner, the prognosis may be favorable.
Author: Natalia Kalegova
Cognitive Impairment Videos
What are cognitive impairments: